RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Polynomials Ex 3.1 is part of RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths. Here we have given Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Polynomials Exercise 3.1.
| Board | RBSE |
| Te×tbook | SIERT, Rajasthan |
| Class | Class 10 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 3 |
| Chapter Name | Polynomials |
| E×ercise | Exercise 3.1 |
| Number of Questions Solved | 3 |
| Category | RBSE Solutions |
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Polynomials Ex 3.1
RBSE Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Question 1.
Find the zeros of the following (RBSESolutions.com) quadratic polynomial and test the relation between zeros and coefficients.
(i) 4x2 + 8x
(ii) 4x2 – 4x + 1
(iii) 6x2 – x – 2
(iv) x2 – 15
(v) x2 – (√3 + 1) x + √3
(vi) 3x2 – x – 4
Solution
(i) Given polynomial
f(x) = 4x2 + 8x ⇒ f(x) = 4x(x + 2)
To find zeros of (RBSESolutions.com) polynomial f(x), f(x) will be zero.
f(x) = 0
⇒ 4x(x + 2) = 0
⇒ x = 0 or x + 2 = 0
⇒ x = 0 or x = -2
Thus zeros of f(x) are 0 and -2
Relations between zeros of polynomial and coefficient.
Sum of zeros = 0 + (-2) = -2
and product of zeros = 0 × -2 = 0

Thus, relation between zeros and polynomial is correct.
(ii) Given polynomial
f(x) = 4x2 – 4x + 1 = (2x)2 – 2 (2x). 1 + (1)2 = (2x – 1)2
To find zeros polynomial f(x), f(x) will be zero.
⇒ (2x – 1)2 = 0
It (2x – 1)2 = 0
⇒ 2x – 1 = 0
⇒ x = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
Here zeros of (RBSESolutions.com) polynomial are same.
Therefore, zeros of polynomial are \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) and \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
Relation between coefficient and zeros of polynomial
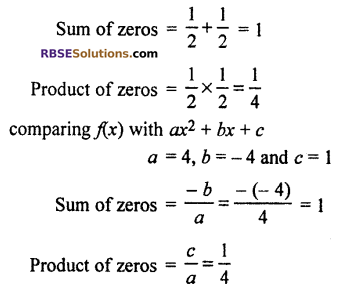
Thus, relation between zeros and polynomial is correct.
(iii) Given polynomial
f(x) = 6x2 – x – 2 = 6x2 – 4x + 3x – 2 = 2x(3x – 2) + 1(3x – 2) = (3x – 2)(2x + 1)
To find zeros of 6x2 – x – 2, f(x) = 0
If 3x – 2 = 0 then 3x = 2 ⇒ x = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
or 2x + 1 = 0 then 2x = -1 ⇒ x = \(\frac { -1 }{ 2 }\)
Therefore zeros of (RBSESolutions.com) polynomial \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) , \(\frac { -1 }{ 2 }\)
Relation between zeros and coefficient of polynomial
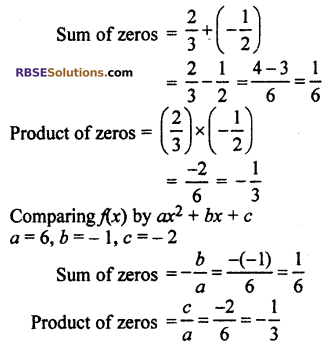
Thus, relation between zeros and polynomial is correct.
(iv) Given (RBSESolutions.com) polynomial f(x) = x2 – 15
To find zeros of f(x), f(x) will be zero
⇒ f(x) = 0
x2 = 15
or x = ±√15
Therefore zeros of polynomial x2 – 15 are = +√15, -√15
Relation between zeros and coefficient of polynomial
Sum of zeros = √15 – √15 = 0
Product of zeros comparing given polynomial = √15 × (-√15) = -15
Comparing given polynomial x2 – 15 = 0 with ax2 + bx + c
a = 1, b = 0 and c = -15

Thus, relation between zeros and polynomial is correct.
(v) Given (RBSESolutions.com) polynomial
f(x) = x2 – (√3 + 1) x + √3
= x2 – √3x – x + √3
= x (x – √3) – 1(x – √3)
= (x – √3)(x – 1)
Therefore, f(x) = (x – √3)(x – 1)
To find polynomial f(x), f(x) will be zero.
⇒ f(x) = o
If (x – √3) = 0 then x = √3
or (x – 1) = 0 then x = 1
Therefore, zeros of polynomial are √3, +1
Relation between zeros and coefficient of polynomial
Sum of zeros = (√3 + 1)
product of zeros = √3 × (+1) = √3
comparing given polynomial by ax2 + bx + c
a = 1, b = -(√3 + 1), c = √3
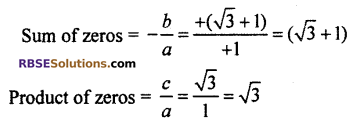
Thus, relation between zeros and polynomial is correct.
(vi) Given (RBSESolutions.com) polynomial f(x) = 3x2 – x – 4
= 3x2 – (4 – 3) x – 4
= 3x2 – 4x + 3x – 4
= x(3x – 4) + 1(3x – 4)
= (3x – 4) (x + 1)
3x2 – x – 4 = (3x – 4) (x + 1)
To find zeros of f(x),
⇒ f(x) = 0
⇒ (3x – 4)(x + 1) = 0
If 3x – 4 = 0 then 3x = 4 ⇒ x = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\)
or x + 1 = 0 then x = -1
Thus, zeros of polynomial are \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\) and – 1.
The relation between zeros and coefficient of the polynomial

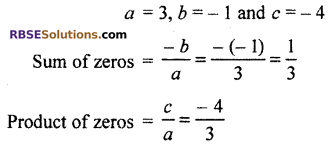
Thus, relation between zeros and polynomial is correct.
RBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Solutions Question 2.
Find quadratic polynomial. Sum and product (RBSESolutions.com) of whose zeros are given numbers respectively.
(i) -3, 2
(ii) √2, \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
(iii) \(\frac { -1 }{ 4 }\) , \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(iv) 0, √5
(v) 4, 1
(vi) 1, 1
Solution
If zeros of quadratic polynomial f(x) are known, then find required polynomial by following formula
Let f(x) = k{x2 – (sum of zeros) x + product of zeros}, where k = a real number
(i) Lef f(x) be a polynomial.
Sum and product of whose zeros are -3 and 2 respectively.
f(x) = k[x2 – (-3)x + 2] = k[x2 + 3x + 2] (∴ k = real number)
Thus required polynomial f(x) = x2 + 3x + 2
(ii) Let f(x) is quadratic polynomial.
Sum and product of whose zeros are √2 and \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) respectively.
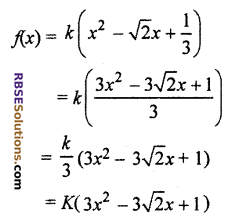
where \(\frac { k }{ 3 }\) is a constant term, real number.
Hence, required polynomial is 3x2 – 3√2x + 1
(iii) Let f(x) is a quadratic (RBSESolutions.com) polynomial sum and product of whose zeros are \(\frac { -1 }{ 4 }\) and \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
respectively.
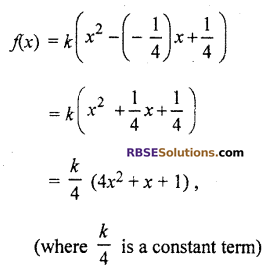
Hence, required (RBSESolutions.com) polynomial is 4x2 + x + 1.
(iv) Let f(x) is a quadratic polynomial.
Sum and product of whose zeros are 0 and √5 respectively.
f(x) = k[ x2 – 0. x + √5 ] = k[x2 + √5 ] (where k is a constant term)
Hence, required polynomial is x2 + √5
(v) Let f(x) is a quadratic polynomial.
Sum and product of whose zeros are 4 and 1 respectively
f(x) = k[x2 – 4x + 1], (where k is constant term)
Hence, required polynomial is x2 – 4x + 1
(vi) Let f(x) is a quadratic polynomial.
Sum and product of whose zeros are 1 and 1 respectively.
f(x) = k{x2 – 1.x + 1) = k(x2 – x + 1), where k is constant term
Hence, required polynomial is x2 – x + 1
Ex 3.1 Class 10 RBSE Question 3.
If sum of square of zeros of (RBSESolutions.com) quadratic equation f(x) = x2 – 8x + k is 40 then find the value of k.
Solution
Given polynomial f(x) = x2 – 8x + k
Let α and β are zeros of polynomial f(x) then
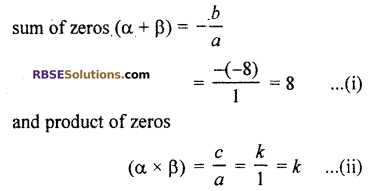
Now, from equation (i)
(α + β) = 8
Squaring both sides,
(α + β)2 = 82
⇒ a2 + β2 + 2αβ = 64 …(iii)
It is given that sum of square of zeros is 40.
i.e., α2 + β2 = 40
Putting values from equation (i) and (ii) in (iii)
40 + 2k = 64
⇒ 2k = 64 – 40
⇒ 2k = 24
⇒ k = 12
Thus k = 12
We hope the given RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Polynomials Ex 3.1 will help you. If you have any query regarding Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Polynomials Exercise 3.1, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.