RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression Ex 5.1 is part of RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths. Here we have given Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression Exercise 5.1.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression Ex 5.1
RBSE Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Question 1.
Find the first term and common (RBSESolutions.com) difference for the following A.P –
(i) 6, 9, 12, 15, ….
(ii) – 7, – 9, – 11, – 13
(iii) \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 } ,\frac { 1 }{ 2 } ,\frac { -1 }{ 2 } ,\frac { -3 }{ 2 } ,….\)
(iv) 1, – 2, – 5, – 8 ……
(v) -1, \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\), \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\), ….
(vi) 3, 1, -1, -3, ….
(vii) 3, -2, -7, -12, …..
Solution :
(i) Given A.P. is 6, 9, 12, 15. …
First term (a1) = 6
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1
= 9 – 6 = 3
Thus, a1 = 6 and d = 3
(ii) Given A.P. is -7, -9, -11, -13, ……
First term (a1) = – 7
Common (RBSESolutions.com) difference (d)
= a2 – a1
= -9 – (-7)
= -9 + 7 = -2
Thus, a1 = -7 and d = -2
(iii) Given A.P. is \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 } ,\frac { 1 }{ 2 } ,\frac { -1 }{ 2 } ,\frac { -3 }{ 2 } ,….\)
First term (a1) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\)
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) – \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\)
= \(\frac { 1-3 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { -2 }{ 2 }\)
= -1
Thus, a1 = and d = – 1
(iv) Given A.P. is 1, -2, -5, -8, …….
First term (a1) = 1
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1
= -2 – (1)
= -3
Thus, a1 = 1 and d = -3
(v) Given A.P. -1, \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\), \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\), …..
First term (a1) = – 1
Common (RBSESolutions.com) difference (d) = a2 – a1
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) – (-1)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) + 1
= \(\frac { 1+4 }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac { 5 }{ 4 }\)
Thus, a1 = -1 and d = \(\frac { 5 }{ 4 }\)
(vi) Given A.P. is 3, 1, -1, -3, …..
First term (a1) = 3
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1
= 1 – 3
Thus, a1 = 3 and d = -2
(vii) Given A.P. is 3, -2, -7, -12 , …..
First term (a1) = 3
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1
= -2 – 3
= -5
Thus, a1 = 3 and d = -5
RBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Question 2.
If first term a and common (RBSESolutions.com) differenced of an AP is given as follows, then find next four terms of that series.
(i) a = -1, d = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(ii) a = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) , d = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\)
(iii) a = 0.6 , d = 1.1
(iv) a = 4, d = -3
(v) a = 11, d = -4
(vi) a = – 1.25, d = -0.25
(vii) a = 20, d = \(\frac { -3 }{ 4 }\)
Solution :
(i) Given a = -1, d = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
First term (a) = -1
Second term (a + d) =-1 + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) = –\(\frac { -1 }{ 2 }\)
Third term (a + 2d) = -1 + 2 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) = o
Fourth term (a + 3d) = -1 + 3 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
= -1 + \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\)
= \(\frac { -2+3 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
Thus, First four terms of A.P. are – 1, – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\), 0 and \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\).
(ii) Given a = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\), d = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\)
First term (a) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)

(iii) Given a = 0.6, d = 1.1
First term (a) = 0.6
Second (RBSESolutions.com) term (a + d) = 0.6 + 1.1 = 1.7
Third terms (a + 2d) = 0.6 + 2 × 1.1 = 2.8
Fourth term (a + 3d) = 0.6 + 3 × 1.1 = 3.9
Hence, four terms of A.P are 0.6, 1.7, 2.8 and 3.9.
(iv) Given a = 4, d = -3
First term (a) = 4
Second term (a + d) = 4 + (-3) = 1
Third term (a + 2d) = 4 + 2 (-3) = 4 – 6 = -2
Fourth term (a + 3d) = 4 + 3(-3) = 4 – 9 = -5
Hence, four terms of A.P are 4, 1, -2 and -5.
(v) Given a = 11, d = -4
First term (a) = 11
Second term (a + d) = 11 + (-4) = 11 – 4 = 7
Third terms (a + 2d) = 11 + 2 (-4) = 11 – 8 = 3
Fourth terms (a + 3d) = 11 + 3 (-4) = 11 – 12 = -1
Hence, first four terms of A.P. are 11, 7, 3 and -1.
(vi) Given a = -1.25, d = -0.25
First term (a) = -1.25
Second (a + d) = -1.25 + (-0.25)
= -1.25 – 0.25 = -1.50
Third term (a + 2d)
= -1.25 + 2 (-0.25)
= -1.25 – 0.50 = – 1.75
Fourth term (a + 3d) = -1.25 + 3(-0.25)
= -1.25 – 0.75 = – 2.00
Hence first four (RBSESolutions.com) terms of A.P. are -1.25, -1.50, -1.75 and -2.00.
(vii) Given a = 20, d = \(\frac { -3 }{ 4 }\)
First Term (a) = 20
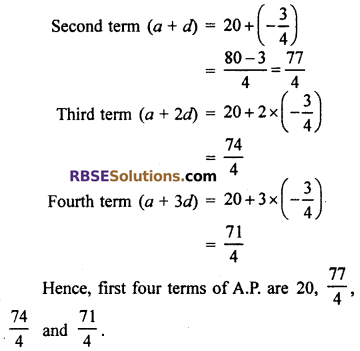
Ex 5.1 Class 10 RBSE Question 3.
Test A.P for given series of (RBSESolutions.com) numbers. For an A.P., find its common difference and next four terms also.
(i) 2, \(\frac { 5 }{ 2 }\), 3, \(\frac { 7 }{ 2 }\) ……
(ii) \(\frac { -1 }{ 2 } ,\frac { -1 }{ 2 } ,\frac { -1 }{ 2 } ,\frac { -1 }{ 2 } ,….\)
(iii) a, a2, a3, a4, ……
(iv) √3, √6, √9, √12, ……
(v) √2, √8, √18, √32, …..
(vi) a, 2a, 3a, 4a
(vii) 0.2, 0.22, 0.222 ……
(viii) 3, 3 + √2, 3 + 2√2 , 3 + 3√2, ….
Solution :
(i) Given series 2, \(\frac { 5 }{ 2 }\), 3, \(\frac { 7 }{ 2 }\)
Here a1 = 2, a2 = \(\frac { 5 }{ 2 }\), a3 = 3, a4 = \(\frac { 7 }{ 2 }\)
Difference between two consecutive terms (d) :
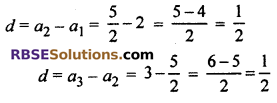
![]()
∵ Difference between two (RBSESolutions.com) consecutive is same, d = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
∴ Given series is A.P.
Next four terms are
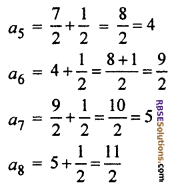
Hence d = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) and next four (RBSESolutions.com) terms of series are 4, \(\frac { 9 }{ 2 }\) , 5 and \(\frac { 11 }{ 2 }\)
(ii) Given series \(\frac { -1 }{ 2 } ,\frac { -1 }{ 2 } ,\frac { -1 }{ 2 } ,\frac { -1 }{ 2 } ,….\)
Here a1 = \(\frac { -1 }{ 2 }\) , a2 = \(\frac { -1 }{ 2 }\), a3 = \(\frac { -1 }{ 2 }\), a4 = \(\frac { -1 }{ 2 }\)
Difference between two consecutive terms (d) :
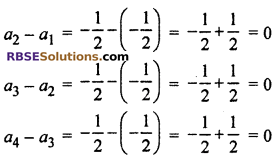
∵ Difference between two consecutive (RBSESolutions.com) terms is same, common difference = 0
Thus, given series is a A.P.
Fifth term a5 = Fourth term a4 + Common difference d
= – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) + 0 = –\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
Sixth term a6 = Fifth term a5 + Common differece d
= – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) + 0 = – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
Seventh term a7 = sixth term a6 + common difference d
= – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) + 0 = –\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
Eight term a8 = Seventh term a7 + Common difference d
Hence common difference d = 0 and next four terms are –\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) , –\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) , –\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) and –\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(iii) Given series a, a2, a3, a4, …
Here a1 = a, a2 = a2, a3 = a3, a4 = a4
Difference between two (RBSESolutions.com) consecutive terms d :
a2 – a1 = a2 – a = a(a – 1)
a3 – a2 = a3 – a2 = a2(a – 1)
∵ Difference is not same
i.e., a2 – a1 ≠ a3 – a2
Hence, given series is not an A.P.
(iv) Given series √3, √6, √9, √12, ……
a1 = √3, a2 = √6, a3 = √9, a4 = √12
Difference between two consecutive terms d :
a2 – a1 = √6 – √3 = √3(√2 – 1) = 0.717
a3 – a2 = √9 – √6 = √3(√3 – √2) = 0.530
∵ Difference is not same
i.e., a2 – a1 ≠ a3 – a2
Thus, Given senes is not A.P
(v) Given series is √2, √8, √18, √32, …..
Here a1 = √2, a2 √8,, a3 = √18, a4 = √32
Difference between two (RBSESolutions.com) consecutive terms d :
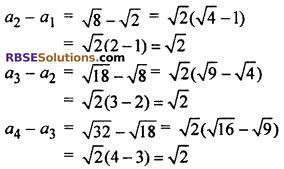
∵ Difference is same
Common difference d = √2 and given series is an A.P.
Then 5th term a5 = a4 + d
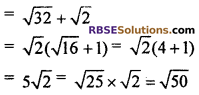
6th term a6 = a5 + d
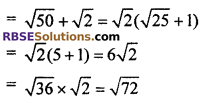
7th term a7 = a6 + d
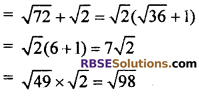
8th term a8 = a7 + d
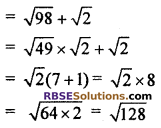
Hence, common difference d = √2 and (RBSESolutions.com) next four terms of series are √50, √72, √98 and √128
(vi) Given series is a, 2a, 3a, 4a,…
Here a1 = a, a2 = 2a, a3 = 3a, a4 = 4a
Difference between two consecutive terms (d) :
a2 – a1 = 2a – a = a
a3 – a2 = 3a – 2a = a
a4 – a3 = 4a – 3a = a
∵ Common difference is same
Thus, common difference d = a and given series is an A.P.
Then 5th term a5 = a4 + d
= 4a + a = 5a
6th term a6 = a5 + d
= 5a + a = 6a
7th term a7 = a6 + d
= 6a + a = 7a
8th term a8 = a7 + d
= 7a + a = 8a
Hence, common (RBSESolutions.com) difference d = a and next four terms arc 5a, 6a, 7a and 8a.
(vii) Given series is
0.2, 0.22, 0.222. 0.2222, …
Hear a1 = 0.2, a2 = 0.22, a3 = 0.222, a4 = 0.2222.
Difference of two consecutive terms (d) :
a2 – a1 = 0.22 – 0.2 = 0.02
a3 – a2 = 0.222 – 0.22 = 0.002
a4 – a3 = 0.2222 – 0.222 = 0.0002
Difference is not same
i.e., a2 – a1 ≠ a3 – a2 ≠ a4 – a3
Hence given series ¡s not AP.
(viii) Given series is 3, 3+√2, 3+2√2, 3+3√2, …….
ie., a1 = 3, a2 = 3+√2, a3 = 3+√2, a4 = 3+√2
Difference between two consecutive terms (d) :
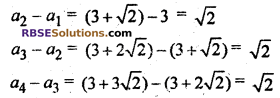
∵ Difference is same.
∴ Common (RBSESolutions.com) difference d = √2, and given series is an A.P.
Then, fifth term a5 = a4 + d
= 3 + 3√2 + √2
= 3 + √2(3 + 1) = 3 + 4√2
Then, sixth term a6 = a5 + d
= 3 + 4√2 + √2
= 3 + √2(4 + 1) = 3 + 5√2
Then, seventh term a7 = a6 + d
= 3 + 5√2 + √2
= 3 + √2(5 + 1) = 3 + 6√2
Then, Eighth term a8 = a7 + d
= 3 + 6√2 + √2
= 3 + √2(6 + 1) = 3 + 7√2
Hence, common difference d = √2 and next four (RBSESolutions.com) terms of series are 3 + 4√2, 3 + 5√2, 3 + 6√2 and 3 + 7√2
We hope the given RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression Ex 5.1 will help you. If you have any query regarding Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression Exercise 5.1, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.