Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 40 Ecosystem: Structure and Function
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 40 Multiple Choice Objective Questions
Question 1.
Term “Ecosystem” was first used by
(1) R. Mishra
(2) Odum
(3) Climentus
(4) Tansley
Question 2.
Assimilation of organic compounds at consumer level is called
(1) Primary producton
(2) Gross production
(3) Secondary production
(4) Real production
Question 3.
Trophic level concerns with
(1) only plants
(2) only animals
(3) only carnivores
(4) organisms associated with food chain
Question 4.
The energy pyramid of grassland or pond ecosystem is always
(1) Inverted
(2) Inverted or straight
(3) Straight
(4) None of these
Question 5.
Alternative path of energy flow are found in
(1) Food web
(2) Food Chain
(3) Ecological Pyramid
(4) Bio geo chemical cycle
Answers :
1.(4)
2.(3)
3.(4)
4.(3)
5.(1)
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 40 Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
The equivalent name of ecosystem given by Prof. Mishra.
Answer :
Ecocosm
Question 2.
Crop field and Garden are which type of ecosystem?
Answer :
Artificial ecosystem
Question 3.
Fresh water ecosystem is divided into how many parts? Write their names.
Answer :
Two parts viz. Lotic and Lentic
Question 4.
Write the names of main components of ecosystem.
Answer :
Biotic and Abiotic components
Question 5.
Who proposed the term convert for the producers?
Answer :
E.J. Kormondy .
Question 6.
Who first gave the concept of ecological pyramids?
Answer :
Charts Elton (1972)
Question 7.
What is photosynthetic Active radiation (PAR) for plants?
Answer :
Solar radiation from 400 to 700 nano meters (spectral band)
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 40 Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Give the definition of ecosystem given by Tansley.
Answer :
There is an interaction between all organism and their physical environment that maintain a balance between the organisms & physical environment. exchange of the substance and flow of energy. It is called as Ecosystem or Ecological system.
Ecosystem is a functional unit of ecology.Term ecosystem was first used by British ecologist Arthur Tansley. Tensley defined ecosystem as the interaction between the biotic factors (plants, animals & other organisms) and abiotic factor (weather, soil.air & temperature).
Before Tansley, Karl Mobius (1877) called it as Biocoenosis, Forbes(1987) as Microcosm and Mishra as Ecocosm. But the ecosystem, is universally accepted.
Question 2.
What do you mean by functions of Ecosystem.
Answer :
Ecosystem function is the technical term used to define the biological, geochemical and physical processes and components that takes place within an ecosystem. In other words. it relates to the structural components of an eco system and how they interact with each other within ecosystem. The ecosystem functions can be explained with the help of –
(A) Ecological Pyramids
(B) Food Chains and Food Webs
(C) Energy Flow
(D) Cycling of Minerals.
Question 3.
Define Ecological efficiency?
Answer :
The efficiency with which energy is transferred from one tropic level to the next. On average, it is estimated that it is only 10%.
Question 4.
Differentiate Primary producers and Secondary producers.
Answer :
Producers (Plants) are called as primary producers and the Quaternary producers are called as secondary producers.
Question 5.
Give two-two examples of blue green algae and symbiotic bacteria associated with Nitrogen fixation.
Answer :
Symbiotic bacteria — Azobactor & Rhizobium.
Blue green algae — Nostoc & Anabaena
Question 6.
Differentiate standing state and standing crop.
Answer :
The amount of abiotic substance (inorganic nutrients) in an ecosystem at a specific time is called as standing state. It tends to very form season to season and ecosystem to ecosystem.
The total amount or number of living thing (biotic) in a particular area at any given time is called as standing crop.
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 40 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by ecological pyramids? Describe ecological pyramids of number and biomass in forest ecosystem.
Answer :
Ecological Pyramids :
The ecological food chain consists of many food levels or tropic levels i.e. each tropic level is a step of food chain and many tropic levels are associated to each other.
The ecological pyramid is a graphical representation designed to show the biomass or bio productivity at each tropic level in a given ecosystem. The concept of pyramid was first given by Charls Elton (1927). Hence, they are also called as Elotonain Pyramids. The pyramids are triangular in shape (Pyramidal shape). The ecological pyramids are of three types viz.
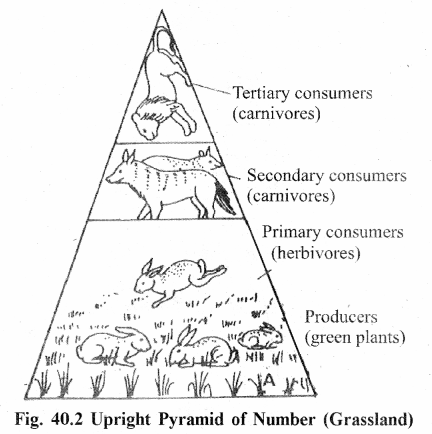
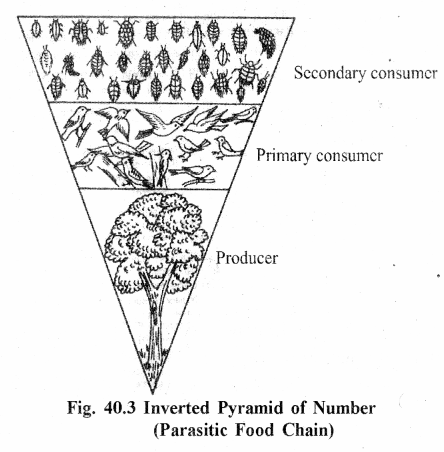
(A) Pyramids of Number :
They represent number of organisms at each tropic level. They show that the number of large organisms is always less than the small organisms. These pyramids may be upright (eg. Grass land ecosystem) or inverted (eg. Parasitic ecosystem).
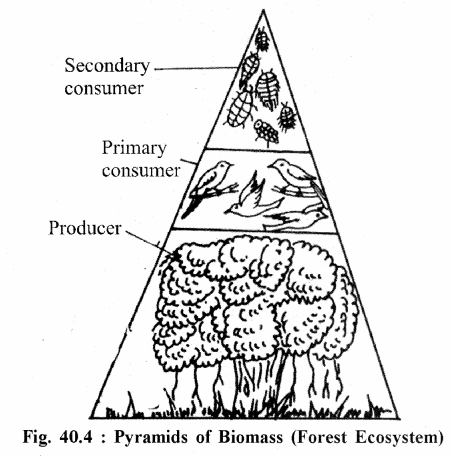
(B) Pyramids of Biomass :
Biomass is the amount of organic matter present in an organism. It shows how much biomass is present in the organisms of each tropic level. They may be upright (eg. Grassland ecosystem, Forest ecosystem, Crop field ecosystem) or inverted (eg. Aquatic ecosystem).
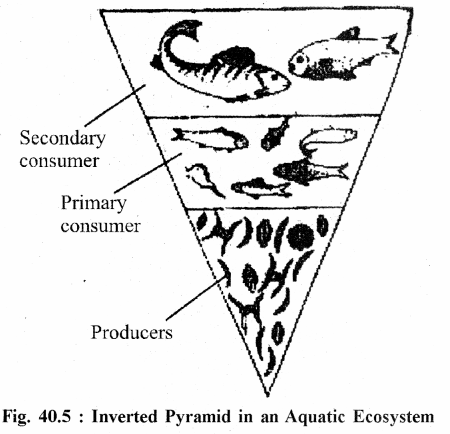
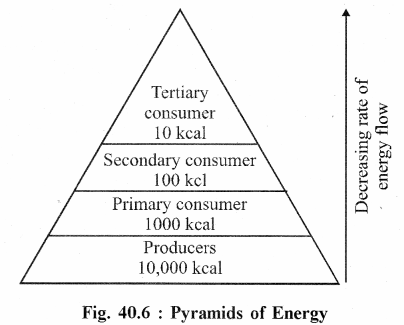
(C) Pyramids of Energy :
They shows the flow of energy through the food chain. The energy pyramids begins with the producers and ends in the top level of the food chain. They are always upright, as flow of energy is gradually reduced at every tropic level.
Question 2.
Explain food chain and food web by giving examples.
Answer :
Food Chain :
The organic substances which are used by plants/animal to get biological energy are called as food. The auto tropic plants (Producers) synthesize their own food by the process of photosynthesis that involves chlorophyll, CO2, H2O and Sun light. The producers are consumed as food by primary consumer (Herbivores), the primary consumers are fed by secondary consumers (Carnivore) which in turn are fed upon by tertiary consumers and they are eaten by a still larger top predators. Hence, there is a series of to eat and to be eaten in the ecosystem which is termed as food chain. Every level in the food chain is called as tropic level which are expressed as T1, T2, T3 and so on.
A food chain shows how the organisms are related with each other by the food they eat. Lengthwise, the food chains maximum include six tropic levels because at every tropic level most of the energy (90%) is used in respiration and other activities and only the remaining (10%) is transferred to next tropic level. Hence very little energy reaches to the top tropic level.
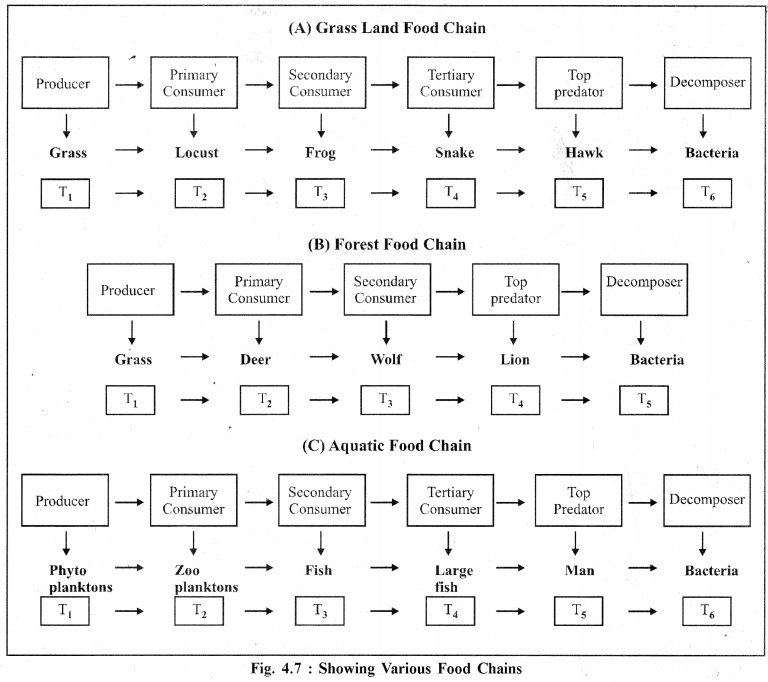
Types of Food Chains :
The food chains are of three types
(a) Grazing food chain : It starts from the living green plants goes to grazing herbivores, and on to carnivores. This type of chain depends on auto tropic energy captured and movement of captured energy into the higher tropic levels. It is dependent on solar energy. Example : Grass ⇒ Rabbit ⇒ Fox ⇒ Lion ⇒ Bacteria
(b) Parasitic Food Chain : It starts with big organisms and ends in small organisms (Parasites). The large organisms are called as hots or heterotrophs and the small organisms as parasite.
Example :
Man(Host) ⇒ Nematod(Parasite) ⇒ Bacteria(Parasite)
(c) Detritus Food Chain : It starts with dead organic material, than to deteriorates and their predators. It is less dependent on the solar energy.
Example :
Dead organic matter ⇒ Earthworm ⇒ Bird ⇒ Bacteria
Question 3.
What do you mean by ecosystem? Describe it structural aspects.
Answer :
There is an interaction between all organism and their physical environment that maintain a balance between the organisms & physical environment. exchange of the substance and flow of energy. It is called as Ecosystem or Ecological system.
Ecosystem is a functional unit of ecology.Term ecosystem was first used by British ecologist Arthur Tansley. Tensley defined ecosystem as the interaction between the biotic factors (plants, animals & other organisms) and abiotic factor (weather, soil.air & temperature).
Before Tansley, Karl Mobius (1877) called it as Biocoenosis, Forbes(1987) as Microcosm and Mishra as Ecocosm. But the ecosystem, is universally accepted.
Structure and Function of Ecosystem :
Structure of ecosystem includes biotic & abiotic components of the ecosystem.The main structure feature of the ecosystem is species composition and stratification can also be expressed by the food relations among organisms. It also includes study of numbers of species, biomass of the organism, life cycle & distribution of the organism and quantity & distribution of the abiotic substance.
The function of flow of energy & flow of nutrients in the ecosystem. In fact flow of energy and nutrients keep the various components of the ecosystem in the form of a unit.
Question 4.
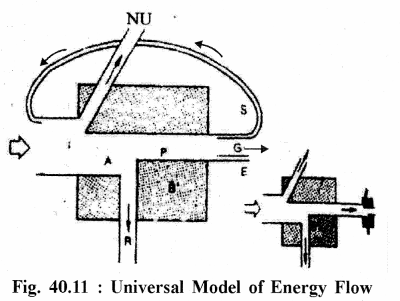
Explain Universal energy flow model in an ecosystem. Give suitable diagram.
Answer :
Universal Energy Flow Model :
E.P. Odum (1983) gave a generalized model by combining both single channel model and Y-shaped model.