Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 42 Global Environmental Change
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 42 Multiple Choice Objective Questions
Question 1.
Percentage of CO2 in the air
1. 0.3%
2. 0.03%
3. 0.003%
4. 3.3%
Question 2.
The main green house gas is
1. Freon
2. Methane
3. CO2
4. O2
Question 3.
When the Ozone day is celebrated
1. 16 September
2. 16 October
3. 26 September
4. 1 January
Question 4.
The meaning of Ozone hole is
1. Hole in the Ozone layer
2. Less Ozone in the troposphere
3. Increased Ozone thickness in the troposphere
4. Reduced Ozone concentration is the stratosphere.
Question 5.
Excess of which causes acid rain
1. O2
2. CO2 and CO
3. SO3 and CO
4. SO2
Answers :
1. (2)
2. (3)
3. (1)
4. (4)
5. (4)
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 42 Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Give the chemical symbol of Ozone.
Answer :
O3
Question 2.
Which is the most affected country because of Ozone hole?
Answer :
Australia
Question 3.
Where the maximum O3 is found in the atmosphere?
Answer :
Stratosphere layer of atmosphere.
Question 4.
Name the green house gases.
Answer :
CO2, CH4, CFC, O3, N2O
Question 5.
What will happen due to excessive green house effect.
Answer :
Global warming
Question 6.
Give one prime measure to prevent green house effect.
Answer :
Less production of green house gases.
Question 7.
What is Global warming?
Answer :
Increase in the atmospheric temperature due to green house effect.
Question 8.
What is El Nino effect?
Answer :
It is a weather phenomenon
Question 9.
What is the role of Ozone layer?
Answer :
Protection from cosmic rays and UV rays.
Question 10.
Write the full form of CFC.
Answer :
Chloro-Floro-Carbon
Question 11.
In which industries, CFC is used?
Answer :
Refrigeration industry.
Question 12.
The height of troposphere from the sea level.
Answer :
0 to 12 km.
Question 13 .
In which part of year, the El-Nino effects occurs.
Answer :
Last part of year
Question 14.
Define acid rain.
Answer :
Rain water with acid like H2SO4, HNO3 etc.
Question 15.
Write harmful effect of Ozone depletion.
Answer :
Skin cancer, Cataract, Reduced production of rice etc.
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 42 Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by green house effect?
Answer :
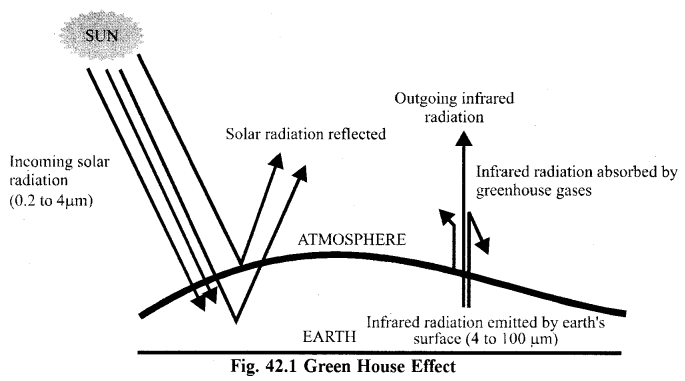
The atmosphere around the earth acts as a glass wall of the green house. The CO2, Methane. N2O. CF. water vaporous etc. absorb the heat radiations and generate a specific atmospheric temperature (global temperature), i.e. the atmosphere is warmed by absorption of infrared thermal radiations (shorter wavelength radiant energy from the Sun and and convective heat fluxes from the surface). These gases in the atmosphere radiant energy. some of which towards the earth surface. This phenomena is termed as green house effect and these gases are called as green house gases.
Question 2.
What are the main causes of green house effect?
Answer :
- Green plants perform photosynthesis in presence of chlorophyll to synthesize the food. The photosynthesis is the only biological process that consumes CO2. According to a report. there is deforestation at a rate of 38 acre per minute. Moreover, there is combustion of the forests. As a result, the CO2 is increasing due to its less consumption. Therefore, deforestation is the primary cause of increase in CO2.
- Burning of coke and wood also generate CO2.
- increased industrialization and motor vehicles are another good sources of increase in CO2.
Question 3.
How green house effect can be controlled?
Answer :
Green house effect can be controlled b reducing the formation of green house gases such as CO2, Methane. Troposphere O3 etc.
Question 4.
what is atmosphere?
Answer :
There is air around the earth upto the height of 800 to 1000 km. it is called as atmosphere. The air of lower layer is heave and dense where as the air of upper layer is lighter.
Question 5.
Define Ozone layer.
Answer :
About 90% of atmospheric O3 is situated in the Stratosphere at a height of 15 to 30 km. It is called as Ozone layer.
Question 6.
What are the adverse effects of green house effect?
Answer :
- Increase in the green house will increase global temperature. It will cause heavy rains and flood in coastal regions and droughts in average rainfall regions. It is reported that if the temperature continues to rise than it will increase by 3.6°C upto 2100. It will lead to drought, cyclones, hurricane, flood, epidemics and may lead to final destruction of the Universe.
- The green house effect will decrease production of agricultural products and fish production in India and other developing countries.
- The sea level will rise due to melting of polar ice because of increased temperature. As a result, the coastal regions will be merged under sea water.
Question 7.
Define stratosphere.
Answer :
It is the second lowest layer of Earth’s atmosphere. It lies above the troposphere and both are separated by tropo-pause. This layer extends roughly from 12 km. to 50 km. It contains the ozone layer which is a part of Earth’s atmosphere.
Question 8.
How Ozone layer protects from the U-V rays of Sun.
Answer :
The ozone absorbs cosmic rays and U-V rays, and protect the Earth’s life (animals, human beings, plants etc.) from the harmful effects of radiation.
Question 9.
Explain in brief the El-Nino effect.
Answer :
El-Nino is a weather phenomenon and this name was given by fisherman of South America in 1960.
El Nino is a Spanish name which means The little boy or Christ Child. The name was chosen based on the time of year (around December and Near the birth of Jesus) during which these warm water events tend to occur.
Question 10.
Write the Main factors causing Ozone depletion.
Answer :
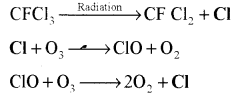
- CFC (Chloro Floro Carbon), CBC (Chloro Bromo Carbon) and BFC (Bromo Floro Carbon). These compounds are collectively called as Freon and they are highly volatile organic compounds. They are used in refrigeration industries, Aerosols, formation of foam, cleaning of many industrial machines etc. The CFC compounds release Chlorine radicals which re-main active for about two years and destroy 1 lakh molecules of Ozone by chain reaction.
CFCl3 → CF CL2 +Cl
Cl + O3 → ClO + O2
ClO + O3 → 2O2 + Cl - Nitrogen Oxides (NO—Nitric Oxide, N2O—Nitrous oxide)—They are released mainly by the chemical fertilizers and they destroy the Ozone.
- Jet Aeroplanes – Most of the jet aeroplanes prefer to fly in/close to the stratosphere. The jet of air and other pollutants released by them harm the Ozone.
- Nuclear blasts also harm the Ozone.
- Deforestation is also a major cause of Ozone depletion.
- Sulphur oxides (SO2, SO3) and Hydrochloric acid (HCl).
Question 11.
Define El-Nino effect.
Answer :
The sea currents that cause fluctuations in water also affect the environment. One of them is El Nino effect. It is caused by the warming of the pacific ocean near the equator, off the coast of South America.
Question 12.
What are the main reasons of atmospheric heating?
Answer :
Increase of CO2 in the atmosphere causing green house effect. As a result the atmospheric average temperature is increasing. It is called as global warming.
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 42 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Define green house effect. Write its adverse effects and how to control it?
Answer :
A green house is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of transparent material, such as glass, in which plants are grown. These structures range in size from small shed to large building. The interior of a green house exposed to sunlight becomes significantly warmer than the external temperature.
Earth is covered by a dense covering of atmosphere upto the height of 30 km though it is found upto 800 to 1000 km heights The atmosphere is mixture of many gases which are as follows—
- Nitrogen 78%
- Oxygen 21%
- Argon 0.93%
- CO2 0.04% (0.03 to 0.07%)
- Others 0.03%
[Methane, Water vapors, N2O, CFC, 03 etc]
The atmosphere around the earth acts as a glass wall of the green house. The CO2, Methane, N2O, CF. water vaporous etc. absorb the heat radiations and generate a specific atmospheric temperature (global temperature), i.e. the atmosphere is warmed by absorption of infrared thermal radiations (shorter wavelength radiant energy from the Sun and and convective heat fluxes from the surface). These gases in the atmosphere radiant energy, some of which towards the earth surface. This phenomena is termed as green house effect and these gases are called as green house gases.
Green House Gases :
The green house gases include CO2, CFC, N2O, CH4, Water vapors O3. Increase in the green house gases will increase the global temperature and the earth will become like boiling mass. For example, the atmosphere of Venus planet contains 90% CO2 (3% N2 and 0.5%. O2). therefore there temperature is 477°C.
Causes of green house effect :
The increase in the green house gases in the atmosphere increasing the atmospheric temperature. The major green house gas is CO2. (contribute 60% in green house effect) is increasing continuously because of the following reasons—
- Green plants perform photosynthesis in presence of chlorophyll to synthesize the food. The photosynthesis is the only biological process that consumes CO2. According to a report, there is deforestation at a rate of 38 acre per minute. Moreover, there is combustion of the forests. As a result, the CO2 is increasing due to its less consumption. Therefore, deforestation is the primary cause of increase in CO2.
- Burning of coke and wood also generate CO2.
- Increased industrialization and motor vehicles are another good sources of increase in CO2.
Side effects of green house effect –
- Increase in the green house will increase global temperature. It will cause heavy rains and flood in coastal regions and droughts in average rainfall regions. It is reported that if the temperature continues to rise than it will increase by 3.6°C up to 2100. It will lead to drought, cyclones, hurricanes, flood, epidemics and may lead to final destruction of the Universe.
- The green house effect will decrease production of agricultural products and fish production in India and other developing countries.
- The sea level will rise due to melting of polar ice because of increased temperature. As a result, the coastal regions will be merged under sea water.
Increase of CO2 in the atmosphere causing green house effect. As a result the atmospheric average temperature is increasing. It is called as global warming. The increase in temperature will cause many problems. Significant melting of old glaciers is already observed. The incoming water will cover fresh water marshlands, low-lying cities and islands with sea water. There will be change in the rainfall and vegetation patterns. The increase in CO2 is to be checked to prevent increase in global temperature. Otherwise it is bound to have very serious and very negative effects.
Question 2.
Write the adverse effects of depletion in Ozone and how it can be controlled?
Answer :
Ozone is a gas and its symbol is O3. It gives a smell of rotten fish. The concentration of the ozone is measured at the surface of earth with the help of dobsonmeter. The unit of measurement is dobson unit (DU) and 1DU is equal to 27 million ozone molecules per cm³.90% of atmospheric ozone is situated in the stratosphere at a height from 15 to 30 km. [12 to 35 km. range] but at the poles the height is only 8 km. The concentration of ozone in the ozone layer is found to be 300 DU.
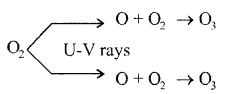
In the nature, ozone is formed as follows (Given by Sydney Chapman (1930).
The ozone absorbs cosmic rays and U-V rays, and protect the Earth’s life (animals, human beings, plants etc.) from the harmful effects of radiation.
Depletion of Ozone :
There is depletion in the ozone at many places due to increase in environmental pollution. For example, depletion in the ozone concentration is observed over Scandinavian countries (Sweden, Denmark, Norway and Northern part of Finland).
Forman, Gardiner and Shanklin reported, in Nature of May, 1985, a 70% depletion in Ozone over the Antartica. It is named as Ozone hole. In this region, the Ozone concentration is reduced to 117 DU from 300 DU. The diameter of the Ozone hole varies from 83 to 100 lakh Square Mile.
The most affected country because of to ozone hole is Australia. The increase in the radiation due to Ozone hole resulted in skin cancer, cataract and a significant decrease in the production of rice, as UVB killed Cyano-bacteria found in the roots of paddy plants as symboiont. During winters PSC (Polar Stratospheric Clouds) are formed over the Antartica and the sunlight fail to reach upto the pole. As a result winters at Antartica is total dark and the temperature is droped upto -80°C. In this conditions, PSC develops Ice particles containing NAT (Nitric Acid Trihydrate). These ice particles provide surface for the chemical reactions and NAT reacts with CFC to release Chlorine radicles. These chlorine radicles destroy ozone and resulted in the formation of ozone hole.
Factors responsible for Ozone depletions :
The main factor that cause Ozone depletion are as follows
- CFC (Chloro Floro Carbon), CBC (Chloro Bromo Carbon) and BFC (Bromo Floro Carbon). These compounds are collectively called as Freon and they are highly voltile organic compounds. They are used in refrigeration industries, Aerosols, formation of foam, cleaning of many industrial machines etc. The CFC compounds release Chlorine radicals which remain active for about two years and destroy 1 lakh molecules of Ozone by chain reaction.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NO—Nitric Oxide. N3O—Nitrous oxide)- They are released mainly by the chemical fertilizers and they destroy the Ozone.
- Jet Aeroplanes – Most of the jet aeroplanes prefer to fly in/close to the stratosphere. The jet of air and other pollutants released by them harm the Ozone.
- Nuclear blasts also harm the Ozone.
- Deforestation is also a major cause of Ozone depletion.
- Sulphur oxides (SO3. SO3) and Hydrochloric acid (HCl).
Adverse Effects of Ozone Depletion :
- Increase in skin cancer and cataract in the eyes.
- Depletion in paddy and other cereals production.
- Disturbance in the marine food chains.
Question 3.
Write about global warming.
Answer :
Increase of CO2 in the atmosphere causing green house effect. As a result the atmospheric average temperature is increasing. It is called as global warming. The increase in temperature will cause many problems. Significant melting of old glaciers is already observed. The incoming water will cover fresh water marshlands, low-lying cities and islands with sea water. There will be change in the rainfall and vegetation patterns. The increase in CO2 is to be checked to prevent increase in global temperature. Otherwise it is bound to have very serious and very negative effects.
Question 4.
Explain El-Nino effect.
Answer :
El-Nino effect :
El-Nino is a weather phenomenon and this name was given by fisherman of South America in 1960.
El Nino is a Spanish name which means The little boy or Christ Child. The name was chosen based on the time of year (around December and Near the birth of Jesus) during which these warm water events tend to occur.
The sea currents that cause fluctuations in water also affect the environment. One of them is El Nino effect. It is caused by the warming of the pacific ocean near the equator, off the coast of South America. This occurs when the normal trade winds weaken, which lets the warm water flow towards the east. This warm water displaces the cooler water (found near the surface of the eastern Pacific) setting off atmospheric changes that effect weather patterns in many parts of the word.
The effects of El Nino are strong and can wreak havoc on weather systems around the word. Along the Pacific coast of the America, El Nino can cause severe storms and flooding. Peru and Ecuador usually receive the brunt of the force of El Nino. During the month of April to October, this area experiences increased rain fall. During El Nino year the colder water is replaced by the wanner water that lack the nutrients (food source of marine life). This nutrient deficient water starves the bottom of the food chain and the effects cause a die-off of large fish. The El Nino causes drought in the western Pacific region and may cause the dangerous bush fire in Australia.