Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Indian Geography Chapter 7 Monsoon System of India
RBSE Class 11 Indian Geography Chapter 7 Text Book Questions
RBSE Class 11 Indian Geography Chapter 7 Multiple Choice Type Questions
Question 1.
Jet Stream is a part of:
(a) Several air masses
(b) fronts
(c) Cyclones
(d) High level air circulation
Answer:
(d) High level air circulation
Question 2.
The conventional concept about the origin of monsoon is:
(a) Jet stream hypothesis
(b) Inter – tropical convergence hypothesis
(c) Classical hypothesis
(d) El – Nino and La – Nina effect
Answer:
(c) Classical hypothesis
Question 3.
The geologist who believes that the origin of Monsoon is due to the fronts formed with the meeting of different air masses is:
(a) Spate
(b) H. Flohn
(c) Hemiltan
(d) Koteshwaram
Answer:
(a) Spate
RBSE Class 11 Indian Geography Chapter 7 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
By the meeting of which air masses does Inter tropical convergence zone form?
Answer:
When the north – eastern and south – western trade winds meet with the equatorial western wind mass, then the inter tropical convergence zone forms.
Question 2.
Jet stream is considered to be the part of which circulation?
Answer:
Jet stream is an important part of the high level air circulation found in the Himalayas and Tibet region.
Question 3.
What is called Christ Child?
Answer:
The irregular conditions of El – Nino and La – Nina take place near Christmas, so meteorologists have named it as Christ Child.
RBSE Class 11 Indian Geography Chapter 7 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is formed by the meeting of different air masses?
Answer:
Fronts are formed by meeting of different air masses. These are wavy and have surface with special slope which are formed by the confrontation of two air masses having opposite physical nature.
Question 2.
Why does the Jet stream get divided into two branches in winter?
Answer:
Jet – stream winds change according to the season. As the sun moves towards the southern direction, all the winds along with atmospheric belts move towards the south. According to this process, the flow of jet stream also moves to south. On moving towards the south, due to the location of Tibetan Plateau, jet stream winds are divided into two branches. Its northern branch moves to the north of Tibetan Plateau and the southern branch moves to the south of Tibetan Plateau.
Question 3.
What is La – Nina effect?
Answer:
La – Nina is the new concept of Monsoon. It originates due to the change in nature of oceanic temperature in the South Pacific Ocean near the coast of Peru. Near to Christmas, the temperature of oceanic water reduces by 2° or 4°C in the South Pacific Ocean near the coast of Peru. This condition of reduction in temperature is called La-Nina effect.
RBSE Class 11 Indian Geography Chapter 7 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the Jet Stream hypothesis regarding the origin of Monsoon.
Answer:
Jet – stream hypothesis is the latest theory regarding the origin of monsoon and has earned worldwide acceptance from the meteorologists. Under this hypothesis, the responsible factors for the origin of monsoon are not only the climatic conditions, but the wind circulation in the troposphere is also equally responsible. The winds blowing in the troposphere are called the high level air circulation. In this circulation, wind with rapid speed blows, that is known as the Jet Stream. With the seasonal changes, these winds get displaced and thus the summer and winter monsoons originate.
Jet – stream and winter monsoon:
In the winter, as the sun moves towards the southern direction, all the winds along with the atmospheric belts start moving towards south. At the same time, Jet – stream also moves towards the south. The location of Tibetan plateau divides the jet stream into two branches. One of its branches starts moving to the south of Tibetan Plateau. Due to the movement of the zone of winds towards south, the southern flow of jet Stream falls between 20° to 25° northern latitudes. This is why “the origin of winter monsoon takes place in India. The entrance of cyclonic disturbance in India is also a gift of this current.
Jet – Stream and summer monsoon:
As the sun starts moving towards the north, the zones of atmospheric pressure along with the zones of all the winds also start moving to the north. In this period, the flow of jet streams also moves to the north of Tibetan Plateau. Due to such condition, winds blow from the Indian Ocean region towards the north. Rainfall occurs due to abundance of humidity in these oceanic winds which is responsible for the summer monsoon in India.
Question 2.
Explain the contribution of El – Nino and La – Nina effect in the origin of Monsoon.
Answer:
The important effect of El – Nino and La – Nino is visible in the origin of Monsoon. Both originate in the South Pacific ocean near the coast of Peru due to the change in condition of oceanic temperature.
El – Nino is a narrow warm, current which occurs on the coast of Peru in December. It is given the name ‘Christ Child’ due to its development near Christmas. The El – Nino phenomena which influences the Indian monsoon reveals that when the surface temperature goes up in the Southern Pacific Ocean, India receives deficient rainfall, and conversely, India receives sufficient rainfall during La-Nina.
The temperature in the South Pacific Ocean increases or decreases by 2°C or 4°C, this is known as El-Nino and La – Nina respectively.
1. El – Nino Effect and Monsoon:
The condition of atmospheric pressure is affected by the rise in temperature in the South Pacific Ocean near the coast of Peru. Due to the rise in temperature, the atmospheric pressure in this region reduces. It is assumed that this affects the global atmospheric pressure system and air flow system. With lower atmospheric pressure condition near the coast of Peru, the force that pushes out the Soxith – eastern trade winds becomes weaker and hence the force attracting the trade winds gets activated. Due to this reason, the flow of these winds towards Asia becomes weak. This gives rise to the possibility of delayed and weak Summer Monsoon. This nature of El-Nino is being presented in the following map:
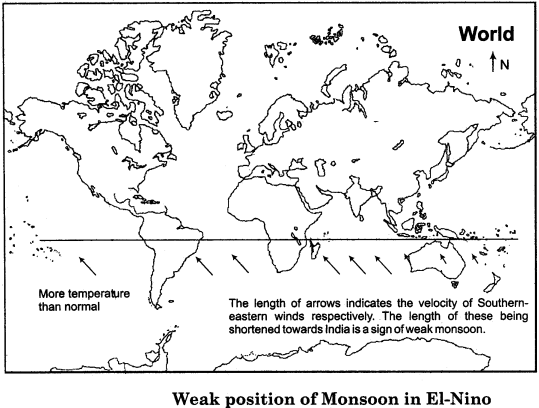
2. La – Nina Effect and Monsoon:
When the temperature reduces in the South Pacific Ocean near the coast of Peru, then higher atmospheric pressure is developed. Due to this reason, the Iprce that pushes out the south-eastern trade winds becomes stronger and hence the force attracting the trade winds gets deactivated. Due to this trend possibility is expressed of an early arrival of active monsoon in India. This nature of La – Nina is being presented in the following map:
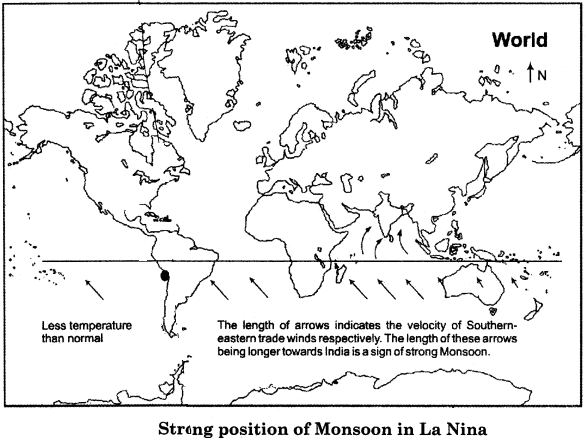
Map Based Questions
Question 1.
Draw a map showing the Jet stream conditions during different seasons.
Answer:
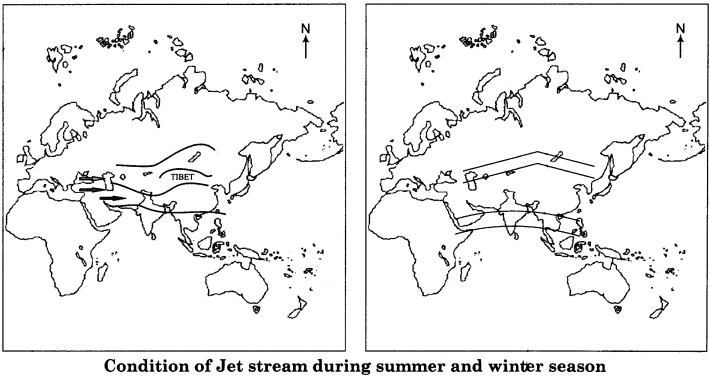
RBSE Class 11 Indian Geography Chapter 7 Other Important Questions
RBSE Class 11 Indian Geography Chapter 7 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Indian climate is known as:
(a) Monsoon
(b) Tropical
(c) Temperate
(d) Taiga
Answer:
(a) Monsoon
Question 2.
Mausim is the word of which language:
(a) Egyptian language
(b) Latin language
(c) Arabian language
(d) Hebrew language
Answer:
(c) Arabian language
Question 3.
The winds blow in the summer:
(a) From sea to land
(b) From land to sea
(c) From sea to sea
(d) From land to land
Answer:
(a) From sea to land
Question 4.
Inter tropical convergence hypothesis is also known as:
(a) Flohn theory
(b) Haily theory
(c) Koteshwaram theory
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Flohn theory
Question 5.
Jet stream winds blow in:
(a) Troposphere
(b) Stratosphere
(c) Mesophere
(d) Ionosphere
Answer:
(a) Troposphere
Question 6.
In the winter season, the Jet stream winds move to:
(a) North
(b) South
(c) East
(d) West
Answer:
(b) South
Question 7.
Where does the El – Nino effect originate?
(a) in the northern part of Pacific Ocean
(b) in the southern part of Atlantic Ocean
(c) in the southern part of Pacific Ocean
(d) in the northern part of Indian Ocean
Answer:
(c) in the southern part of Pacific Ocean
Question 8.
The change in temperature in the condition of La – Nina is:
(a) Normal increase in temperature
(b) Normal decrease in temperature
(c) Rapid increase in temperature
(d) Rapid decrease in temperature
Answer:
(b) Normal decrease in temperature
Question 9.
The trade winds in northern hemisphere blow from:
(a) north to south
(b) south to north
(c) north – east to south – west
(d) south – east to north – west
Answer:
(c) north – east to south – west
Matching type Questions
Question A.
Match Column A with Column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) South – western monsoon | (a) High level air circulation |
| (ii) North – eastern monsoon | (b) Spate |
| (iii) Inter – tropical convergence hypothesis | (c) Summer monsoon |
| (iv) Cyclonic hypothesis | (d) Winter monsoon |
| (v) Jet – stream hypothesis | (e) Flohn |
Answers:
- (c)
- (d)
- (e)
- (b)
- (a)
Question B.
Match Column A with Column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) The Gamble of Monsoon | (a) Strong monsoon in India |
| (ii) A mixture of different air masses | (b) Jet stream towards the north |
| (iii) Winter season | (c) Indian economy |
| (iv) Summer season | (d) Jet stream towards the south |
| (v) Condition of La – Nina | (e) Formation of Front |
Answers:
- (c)
- (e)
- (d)
- (b)
- (a)
RBSE Class 11 Indian Geography Chapter 7 Very Short Answer Types Questions
Question 1.
Why is Indian Climate called as Monsoon climate?
Answer:
There is an important contribution of monsoon winds in the Indian climate. So the Indian climate is called as monsoon climate.
Question 2.
Why does Indian economy depend on monsoon?
Answer:
Indian economy depends on agriculture at large and the process of Indian agriculture mainly depends on monsoon, that’s why, the Indian economy depends on monsoon.
Question 3.
What is meant by the monsoon?
Answer:
The word monsoon is originated from the Arabian word ‘Mausim’, which means weather or season. In this way, the seasonal condition is called the monsoon.
Question 4.
Why is Indian economy called the Gamble of Monsoon?
Answer:
The monsoon in India is irregular and uncertain. Agriculture, the basic of Indian economy, greatly depends on the amount of monsoon. Monsoon largely affects the Indian economy. Thus, the Indian Economy is called the Gamble of Monsoon.
Question 5.
With what is classical hypothesis related?
Answer;
The classical hypothesis is related with various properties in terms of distribution of land and water and their heat and heat release.
Question 6.
What is the relation between temperature and pressure?
Answer:
There is an inverse relation between the temperature and atmospheric pressure of a region. If temperature rises, atmospheric pressure decreases. If. temperature decreases, atmospheric pressure increases.
Question 7.
In which direction do the winds blow in summer and why?
Answer:
The winds blow from sea to land in the summer. The inverse conditions of temperature and atmospheric pressure are responsible for it. In the seas, the air pressure is found to be higher, while it is low on the land. That’s why, winds blow towards the land.
Question 8.
Why do the monsoon winds cause rainfall in summer?
Answer:
In summer, the origin of monsoon winds occurs in oceanic regions. Due to this reason, they are full of humidity and cause rainfall in the related areas.
Question 9.
What does Flohn consider to be the Creator of Monsoon ?
Answer:
German meteorologist Flohn told that fronts originate by the conjunction of the two trade winds moving towards the equatorial low pressure. These fronts are considered to be the Creator of Monsoon.
Question 10.
How do the north – east monsoon gain momentum in India ?
Answer:
The front formed by trade winds moves to the south in winter. Along with it, the movement of atmospheric pressure belts towards the south causes to increase the impact of sub – tropical high pressure in India. So, the anti – cyclonic conditions originate and monsoon starts gaining momentum.
Question 11.
Name the theory of Flohn.
Answer:
Flohn propounded the Inter Tropical Convergence hypothesis, which is related to the convergence of winds. According to it, the monsoon originates by the fronts and by the movement of wind belts.
Question 12.
According to Spate, what is the impact of seasonal change on the fronts?
Answer:
According to Spate, the process of formation of fronts in summer is stronger, while during winter, this process becomes weaker and slow.
Question 13.
What is meant by Jet – stream?
Answer:
Jet stream is a narrow variable band of high level air circulation currents encircling the globe several miles above the earth.
Question 14.
Name the meteorologists who relate jet stream with the monsoon.
Answer:
The meteorologists who consider a close relation between jet stream and origin of monsoon are Koteshwaram, Pant, Ramamurthy, Ramaswami, Flohn, Hamilton etc.
Question 15.
What is the location of Jet stream in winter?
Answer:
The position of the sun in winter is toward the south, it means, that the sun shines straightly on the Tropic of Capricorn. As a result, the flow of jet stream along with the zones of atmospheric pressure and zones of all winds starts moving towards the south.
Question 16.
What is the cause of cyclonic turbulence?
Answer:
The branch of jet stream that blows to the south of Tibetan Plateau reaches to 20° – 25° northern latitude in the winter and causes cyclonic turbulence.
Question 17.
What effects do El – Nino and La – Nina have on Indian monsoon?
Answer:
In the condition of El – Nino, Indian monsoon is delayed and weak, while in the condition of La – Nina, an early and active monsoon is expected.
Question 18.
What is meant by the Trade Winds?
Answer:
The winds that blow from the sub – tropical high air pressure belt to the equatorial low air pressure belt are called trade winds. In ancient time, these winds helped in trade and business so they are named as trade winds.
Question 19.
Why does the flow of trade winds become weak towards Asia?
Answer:
When the air pressure near the coast of Peru lowers down, then the force that pushes the south – eastern trade winds becomes weaker, while the force that attracts the trade-winds becomes active and thus the flow of trade winds towards Asia also becomes weaker.
Question 20.
Why is monsoon more important for India?
Answer:
India is an agriculture dominated country. The nature of agriculture and allied industries is deeply connected to monsoon. That is why, monsoon is more important for India.
RBSE Class 11 Indian Geography Chapter 7 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-I)
Question 1.
Describe the concept of monsoon.
Answer:
The word monsoon has originated from the Arabian word ‘Mausim’, which means weather or season. Monsoon is a seasonal change in the prevailing wind direction that usually arrives with different kind of weather. It almost refers to the Asian Monsoon, a large region extending from India to south – east Asia where monsoon conditions prevail. Agriculture, agriculture – based industries and all other aspects related to Indian economy largely depend upon the monsoon.
Question 2.
How does the Summer Monsoon originate according to Classical hypothesis?
Answer:
According to Classical hypothesis, the opposite nature of water and land is responsible for the origin of Summer Monsoon. According to this hypothesis, land area takes less time to get warm and’ cold, while water takes more time to get warm and cold. In summer season, due to land getting warmed up quickly, low air pressure is developed. On the other hand, water not getting warmed up quickly remains cold, and hence high air pressure is developed there. Thus, in this season, winds start blowing from sea to land. Due to being originated from sea, these winds contain humidity and thus heavy rainfall is caused by these winds.
Question 3.
Explain the Cyclonic Hypothesis of Spate.
Answer;
The meteorologist of Australia, Spate, considers that monsoon winds are the result of cyclones. These cyclones originate due to the formation of fronts by the conjunction of different air – masses. He considers that the process of formation of fronts during summer is very strong. Thus, these fronts attract the winds full of humidity from oceans. On the other hand, in winter, these fronts become weak and shallow, due to which they are unable to attract rainfall.
Question 4.
Explain the condition of summer jet stream.
Answer:
In summer, the sun moves towards the north, it means, it shines straight over the Tropic of Cancer. As a result, all the air pressure belts as well as the winds belts also start moving towards the north. Thus, the complete flow of jet stream begins moving towards the north of Tibetan plateau in the form of a major current. As a result of the movement of this flow towards the north, winds start blowing from the Indian ocean region to the north. This is the process of the formation of Summer Monsoon.
Question 5.
Explain the importance of La – Nina.
Answer:
The condition of La – Nina is very important for Indian Monsoon. It can be described as follows:
- La – Nina effect – makes the monsoon active.
- With the help of La – Nina, a strong force rises in the coast of Peru which pushes the winds out due to higher atmospheric pressure.
- This process is helpful for an early and active Indian monsoon.
RBSE Class 11 Indian Geography Chapter 7 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-II)
Question 1.
Distinguish between winter monsoon and summer monsoon branches under the classical Hypothesis.
Answer:
The difference between the winter monsoon and summer monsoon branches can be described with the help of following points:
| Comparison | Winter Monsoon | Summer Monsoon |
| Temperature | High temperature is found above the sea in winter. | High temperature is found on the land in summer. |
| High temperature region | The condition of high temperature is found in the Indian Ocean. | The condition of high temperature is found in the of Thar Desert. |
| Atmospheric pressure | Due to low temperature, there is high air pressure in Northern India. | Due to low temperature, high air pressure is found in South India. |
| Circulation of winds | In this season, winds blow from land to sea. | In this season, winds blow from sea to land. |
| Humidity | There is less humidity in winter winds as they blow from land to sea. | There is surplus humidity in summer winds as they blow from sea to land. |
Question 2.
Describe the concept of Intra – tropical convergence.
Answer:
The concept of Intra – tropical convergence has been propounded by German meteorologist Flohn. In this concept, the process of front formation has been related to the conjunction of trade winds flowing towards equatorial low air pressure belt. Monsoon originates with help of these fronts. This front shifts towards the north in summer season, so rainfall is received in the form of summer monsoon.
While it shifts towards the south in winter season, and due to this condition, anti cyclonic condition generates and north – east monsoon gets spread in India. Thus, Flohn describes the concept of Intra – tropical convergence that the seasonal change in the direction of Monsoon winds is not due to thermal reasons, rather it is a symbol of re – establishment of trade winds in the planetary wind system.
Question 3.
Distinguish between the conditions of winter and summer Jet stream.
Answer:
The difference found in the conditions of winter and summer jet stream can be described as follows:
| Basis of Comparison | Winter Monsoon | Summer Monsoon |
| Position of sun | During winter, the sun moves in the southern direction. | During summer, the sun moves in the northern direction. |
| Position of Jet stream | The position of jet stream in winter is towards the south. | In summer, jet stream moves towards the north. |
| Flow of jet stream | In this season, the jet stream flows while getting divided into two branches. | In this season, the jet stream flows in the form of one main current. |
| Rainfall | Rainfall occurs in India due to anticyclonic conditions by the southern branch of jet stream. | Rainfall is caused due to the Indian Oceanic winds. |
| Condition of winds | The winds blow from north – east to south. | The winds blow from south -west to north. |
Question 4.
Describe the role of Tibetan plateau regarding Indian monsoon.
Answer:
Tibetan Plateau affects the mechanism of Indian monsoon in the following manner:
- It provides a high level energy source that has a notable impact on the monsoon.
- There is a high atmospheric pressure area over this plateau, which is the part of sub tropical high atmospheric pressure belt.
- This plateau region works as a blocking object.
- Due to its height, it receives higher temperature in comparison to its neighboring areas and it affects the wind circulation in two ways, as a blocking object and as a high level energy source.
- A great role of Tibetan plateau seen in jet – stream deviation.
- In winter season, Tibetan plateau gets very cold, so jet stream gets shifted towards the south in mid – October.
- In summer season, this region forms anticyclones in the form of a hot core.
RBSE Class 11 Indian Geography Chapter 7 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the characteristics of Indian monsoon.
Answer:
The characteristics of Indian Monsoon are as follows:
- Indian monsoon blows from land to sea for six months, and for another six months, it blows from sea to land.
- Indian monsoon is always irregular. It is sometimes delayed or at other times it arrives early.
- The rainfall caused by Monsoon is uneven in the country.
- Indian monsoon is the deciding factor of Indian climate.
- Indian monsoon controls the Indian economy.
- Due to monsoon, different types of agriculture can be done in India and different types of crops can be cultivated.
- About 90 per cent of rainfall in India is received during rainy season.
- Rainfall in India, at some places is in the form of little shower, and at some other places, it is highly excessive.
- The time period of rainy season in India is also not certain. At some places, it extends to 118 days, while in some other regions, it lasts only for 45 days or less.
- The Indian monsoon is famous for floods and droughts.