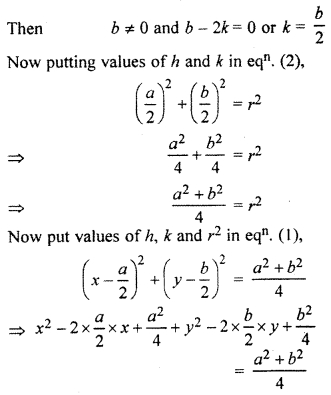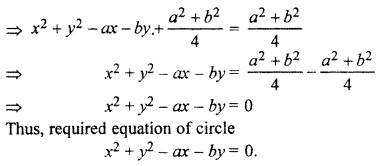Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Maths Chapter 12 Conic Section Ex 12.1
Question 1.
Find the equation of the circle whose:
(i) Centre (- 2, 3) and radius is 4
(ii) Centre (a, b) and radius is a – b
Solution:
(i) According to question,
Centre of circle (h, k) = (- 2, 3)
and Radius of circle r = 4 unit
Then, equation of circle
From formula (x – h)2 + (y- k)2 = r2
[x – (- 2)]2 + (y – 3)2 = 42
⇒ (x + 2)2 + (y – 3)2 = 16
⇒ x2 + 4x + 4 + y2 – 6y + 9 = 16
⇒ x2 + y2 + 4x – 6y = 16 – 9 – 4
⇒ x2 + y2 + 4x – 6y = 3
⇒ x2 + y2 + 4x – 6y – 3 = 0
Thus, required equation of circle
x2 + y2 + 4x – 6y – 3 = 0.
(ii) According to question,
Centre of circle (h, k) = (a, b)
and Radius of circle r = (a – b) unit
Then, equation of circle
From formula (x – h)2 + (y – k)2 = r2
⇒ (x – a)2 + (y – b)2 = (a – b)2
⇒ x2 + a2 – 2ax + y2 + b2 – 2 by = a2 + b2 – 2ab
⇒ x2 + y2 – 2ax – 2by + a2 + b2 – a2 – b2 + 2ab = 0
⇒ x2 + y2 – lax – 2by + 2ab = 0.
Question 2.
Find the coordinates of centre and radius of the following circles :
(i) x(x + y – 6) = y (x – y + 8)
(ii) \(\sqrt { 1+{ k }^{ 2 } } \)(x2 + y2) = 2ax + 2aky
(iii) 4(x2 + y2) = 1
Solution :
(i) x(x + y – 6) = y(x – y + 8)
⇒ x2 + xy – 6x = xy – y2 + 8y
⇒ x2 + y2 + xy – 6x – xy – 8y
⇒ x2 + y2 – 6x – 8y = 0 …(i)
General equation of circle,
ax2 + by2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 …(ii)
Comparing equation (i) and (ii),
2g = -6 ⇒ g = -3
2f = -8 ⇒ f = – 4
c = 0
Thus centre of circle

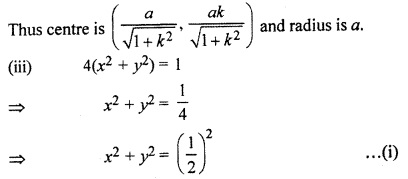
Standard equation of circle,
(x – h)2 + (y – k)2 = a2 …(ii)
Comparing equation (i) and (ii),
h = 0, k = 0, a = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)
Thus centre of circle is (0, 0) and radius is 1/2.
Question 3.
Find the equation of a circle which touches y-axis and cuts an intercept of length 2/on x-axis.
Solution:
In the standard of equation of circle put
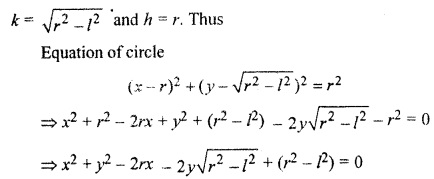
Question 4.
Find the equation of the circle which cuts x- axis at a distance +3 from origin and cuts on intercept at y-axis of length 6 units.
Solution:
Let circle touches x-axis at point E and cuts AB intercepts at y-axis.
According to questions,
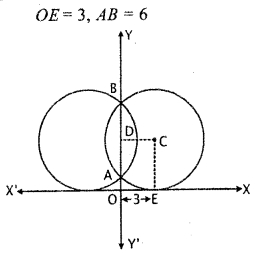
Let C is centre of the circle. Draw CD ⊥AB. Then CD = OE = 3 and
AD = \(\frac { AB }{ 2 } \) = \(\frac { 6 }{ 2 } \) = 3
In right angled triangle ACD,
CA2 = AD2 + CD2
= 32 + 32 = 9 + 9 = 18
= 2 × 9 = 3\(\sqrt { 2 }\)
∴ Radius of circle a = CA = 3\(\sqrt { 2 }\)
whereas CE = CA = 3\(\sqrt { 2 }\)
Thus, centre of circle will be (3, 3\(\sqrt { 2 }\))
Equation of circle,
(x – 3)2 – (y – 3\(\sqrt { 2 }\))2 = (3\(\sqrt { 2 }\))2
⇒ x2 + 9 – 6x + y2 + 18 – 6\(\sqrt { 2 }\) y = 18
⇒ x2 + y2 – 6x – 6\(\sqrt { 2 }\) y + 9 = 0
Similarly circle will be in IInd, IIIrd and IVth quadrant whose centres will be
(- 3, 3\(\sqrt { 2 }\)), (- 3, – 3\(\sqrt { 2 }\)), (3, – 3\(\sqrt { 2 }\))
x2 + y2 + 6x – 6\(\sqrt { 2 }\)y + 9 = 0
x2 + y2 + 6x + 6\(\sqrt { 2 }\)y + 9 = 0
and x2 + y2 – 6x + 6\(\sqrt { 2 }\) + 9 = 0
Thus, total four circles are possible whose equations is
x2 + y2 ± 6x ± 6\(\sqrt { 2 }\)y + 9 = 0
Question 5.
Find the centre and radius of circle
x2 + y2 – 8x + 10y – 12 = 0.
Solution:
According to question, equation of circle
x2 + y2 – 8x + 10y – 12 = 0
⇒ x2 – 8x + y2 + 10y – 12 = 0
⇒ x2 – 8x + 16 – 16 + y2
+ 10y + 25 – 25 – 12 = 0
(On completing square)
⇒ (x – 4)2 + (y + 5)2 – 53 = 0
⇒ (x – 4)2 + [y – (- 5)]2 = 53
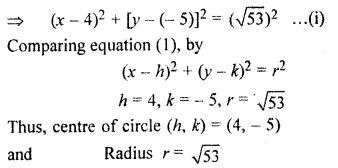
Question 6.
Find the centre and radius of the circle
2x2 + 2y2 – x = 0.
Solution:
According to question, equation of circle
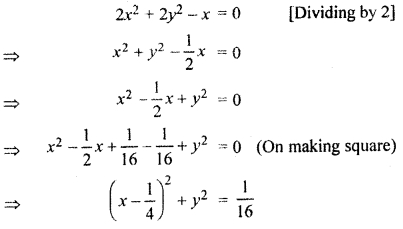
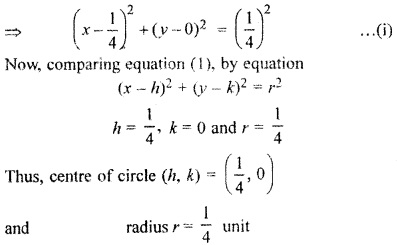
Question 7.
Find the equation of the circle passing through the points (2, 3) and (- 1, 1) and whose centre lie on line x – 3y – 11 = 0.
Solution:
The equation of circle
(x – h)2 + (y – k)2 = r2 …(i)
According to question, circle passes through the point (2, 3) and (-1,1)
Thus (2 – h)2 + (3 – k)2 = r2
⇒ 4 + h2 – 4h + 9 + k2 – 6k = r2
and (- 1 -h)2 + (1 – k)2 = r2
⇒ 1 + h2 + 2h + 1 + k2 – 2k = r2
Again h2 + k2 – 4h – 6k + 13 = r2 …(ii)
and h2 + k2 + 2h – 2k + 2 – r2 …(iii)
Since centre of circle (h, k) lie on line
x – 3y – 11 = 0
Thus h – 3k – 11 – 0
⇒ h – 3k – 11 …(iv)
Subtracting eq. (iii) from (ii),

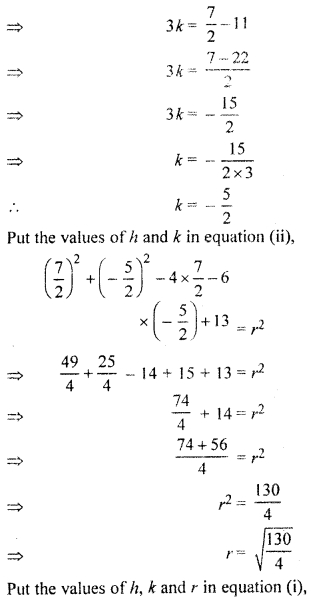
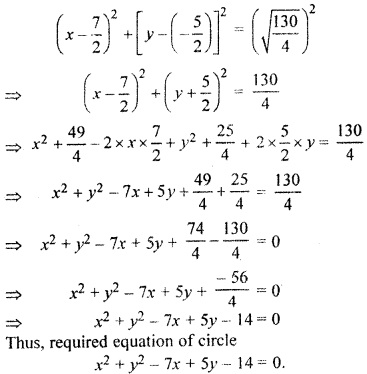
Question 8.
Find the equation of circle of radius 5, whose centre lies on x-axis and which passes through point (2, 3).
Solution:
According to question, centre of circle lies on x-axis. Let centre of circle (h, 0) and radius = 5 unit.
Then equation of circle
(x – h)2 + (y – 0)2 = 52
⇒ (x – h)2 + y2 = 25
But circle passes through point (2, 3).
Then (2 – h)2 + 32 = 25
⇒ 4 + h2 – 4h + 9 = 25
⇒ h2 -4h + 13 – 25 = 0
⇒ h2 – 4h – 12 = 0
⇒ h2 – (6 – 2)h – 12 = 0
⇒ h2 – 6h + 2h – 12 = 0
⇒ h(h – 6) + 2(h – 6) = 0
⇒ (h – 6) (h + 2) = 0
⇒ h = 6 or h = -2
Then centre of each (6, 0) or (- 2, 0)
Put h = 6 in equation (1), the equation of circle
(x – 6)2 + y2 = 25
or x2 + 36 – 12x + y2 = 25
or x2 + y2 – 12x + 36 – 25 = 0
or x2 + y2 – 12x + 11 = 0
Again, putting h = – 2 in eqn. (i), equation of circle
[x – (- 2)2]2 + y2 = 25
⇒ (x + 2)2 + y2 = 25
⇒ x2 + 4x + 4 + y2 = 25
⇒ x2 + y2 + 4x + 4 – 25 = 0
⇒ x2 + y2 + 4x – 21 = 0
Thus, required equation of circle
X2 + y2 – 12x + 11 = 0
⇒ x2 + y2 + 4x – 21 = 0
Question 9.
Find the equation of circle that passes through point (0, 0) and cuts intercepts a and b at axis.
Solution:
According to question, circle passes through (0, 0) and cut intercepts a and b at x and y-axis.
Intersection points of circle with x-axis will be (a, 0) and with y-axis will be (0, b).
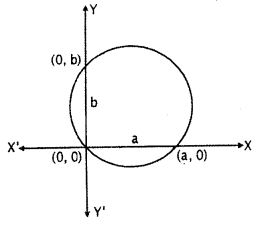
Thus, circle will passed through three points (0, 0), (a, 0) and (0, b).
Let equation of circle,
(x – h)2 + (y – k)2 = r2 …(1)
Circle passes through (0, 0), (a, 0) and (0, b).
Thus, (0 – h)2 + (0 – k)2 = r2 …(i)
(a – h)2 + (0 – k)2 = r2 …(ii)
(0 – h)2 + (b – k)2 = r2 …(iii)
h2 + k2 = r2 …(2)
From eqn. (i),
From eqn. (ii),
a2 + h2 – 2 ah + k2 = r2
⇒ h2 + k2 – 2 ah + a2 = r2 …(3)
From eqn. (iii)
h2 + b2 + k2 – 2bk = r2
⇒ h2 + k2 – 2bk + b2 = r2 …(4)
From eq11. (2) and (3)
r2 – 2ah + a2 = r2
⇒ -2 ah + a2 – r2 – r2
⇒ a2 – 2h = 0
⇒ a(a -2h) = 0
Then a ≠ 0 and a – 2h = 0
⇒ h = \(\frac { a }{ 2 } \)
Similarly, from eqn. (2) and (4)
r2 – 2bk + b2 = r2
⇒ – 2bk + b2 = r2 – r2
⇒ b2 – 2bk = 0
⇒ b(b – 2k) = 0