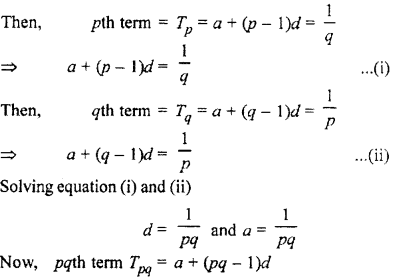Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Maths Chapter 8 Sequence, Progression, and Series Ex 8.1
Question 1.
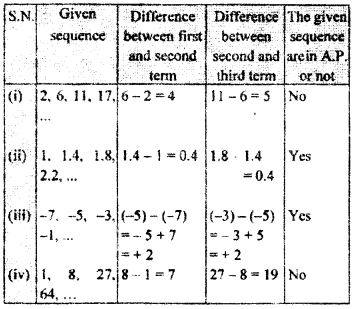
From the following sequence which are in A.P. ?
(i) 2, 6, 11, 17,…
(ii) 1, 1.4, 1.8, 2.2,…
(iii) -7, -5, -3, -1,..
(iv) 1, 8, 27, 64,…
Solution :
Given sequence will be in A.P. only if common difference of two consecutive terms is same.
Question 2.
Find first term, common difference and 5th term of those sequence which have following nth term :
(i) 3n+ 7
(ii) a + (n – 1)d
(iii) 5 – 3n.
Solution :
(i) 3n + 7
nth term, Tn = 3n + 7
First term T1 = 3 × 1 + 7 = 3 + 7=10
Second term T2 = 3 × 2 + 7 = 6 + 7=13
Common difference
d = T2 – T1
= 13-10 = 3
Fifth term T5 = 3 × 5 + 7 = 15 + 7 = 22
Hence, a = 10, d = 3 and T5 = 22
(ii) a+ (n – 1)d
nth term Tn – a + (n – 1)d
First term T1 = a + (1 – 1)d
= a + 0 × d = a + 0 = a
Second term T2 – a + (2 – 1)d = a + d
T2 = 5 – 3 × 2 = 5 – 6 = -1
Common difference
d = T2 – T1= a + d – a = d
Fifth term T5 = a + (5 – 1)d = a + 4d
Hence, ‘a’ = a,’d’ = d and T5 = a + 4d
(iii) 5 – 3n
nth term Tn =5 – 3n
First term, T1 = 5 – 3 × 1 =5 – 3 = 2
Second term T2 = 5-3 × 2 = 5- 6 = -1
Common difference
d = T2 – T1 = (- 1) -2 = -3
Fifth term T5= 5 – 3 × 5 = 5 – 15 = – 10
Hence, a = 2, d = -3 and T5 = – 10
Question 3.
Show that sequence of following nth terms, are not in A.P. :
![]()
Solution :
If the value of Tn +1 – Tn is not independent of n then sequence of nth terms are not in A.P.
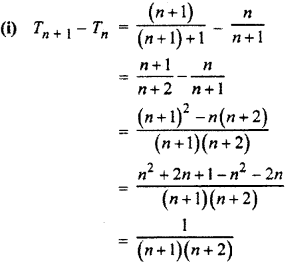
Hence, given sequence of nth term is not in
(ii) Tn+1-Tn = {(n+ 1)2 + 1} – {n2 + 1}
= (n2 + 1 + 2n + 1) – (n2 + 1)
= (n2 + 2n + 2 – n2 – 1)
= 2n+ 1
Question 4.
In an A.P. 2 + 5 + 8 + 11 +… which term is 65 ?
Solution :
Given series = 2 + 5 + 8 + 11 + ….
Let its nth term is 65
Then Tn = 65 and d = 5 – 2 = 3
⇒ a + (n – 1)d – 65
⇒ 2 + (n – 1) × 3 = 65
⇒ 2 + 3n – 3 = 65
⇒ 3n – 1 = 65
![]()
Hence, 22nd term is 65
Question 5.
In an A.P. 4 + 9 + 14 + 19 +… + 124, find 13th term from last.
Solution :
Given series = 4 + 9 + 14 + 19 +…+ 124 a = 4, d = 9 – 4 = 5, l= 124
13th term from last
= l – (n – 1)d
= 124 – (13 – 1) × 5
= 124 – 12 × 5
= 124 – 60 = 64
Hence, 13th term from last is 64.
Question 6.
In an A.P. 2 + 5 + 8 + 11 + … if last term is 95, then find the number of terms of the series.
Solution:
Given series = 2 + 5 + 8 + 11 + … + 95
a = 2, d = 5 – 2 = 3, l = 95
Then, from l = a + (n – 1 )d
⇒ 2 + (n – 1) × 3 = 95
⇒ 3(n – 1)= 95 – 2
⇒ (n – 1) = \(\frac { 39 }{ 3 }\)
= 31
⇒ n = 31 + 1 = 32
Hence, number of terms of the series is 32.
Question 7.
If 9th term of A.P. is zero, then prove that 29th term is twice the 19th term.
Solution :
Let a be the first term and d be the common difference then 9th
term = T9 = 0 Then a + (9 – 1)d= 0
⇒ a + 8d = 0 ….. (i)
29th term = T29 = a + 28d …(ii)
19th term = T19 = a + 18d …(iii)
Putting the value of equation (i) into equation (ii) and (iii)
we get
T29 = (a + 8 d) + 20 d
⇒ T29 = 0 + 20 d
⇒ T29 = 20d … (iv)
⇒ T29 = (a + 8 d) + 10 d
⇒ T29 = 0 + 10d
⇒ T29 = 10d … (v)
From equation (iv) and (v), we have
T29 = 20d = 2 × 10d =2 × T29
T29 = 2T29
Hence Proved.
Question 8.
How many two digit natural number which are divisible by 3 ?
Solution :
First two digit number which is divisible by 3 is 12 and last two digit number is 99
∵ We have to find only the numbers which are divisible by 3, so common difference is 3.
a= 12, d=3, l = 99
Hence, l = a + (n – 1 )d
⇒ 12 + (n- 1) × 3 = 99
⇒ 3(n – 1) = 99 – 12
![]()
⇒ n= 29 + 1 = 30
Hence, two digit natural number which are divisible by 3 are 30.
Question 9.
If in A.P., pth term is q and qth term is p, then find (p + q)th term.
Solution :
Let first term of A.P. = a
and common difference = d
Then pth term = Tp = a + (p – 1)d = q
⇒ a + (p – 1)d = q … (i)
and qth term = Tp = a + (q – 1)d = p
⇒ a + (q – 1)d = p …. (ii)
(p + qth term =) Tp+q
= a+ {(p + q) -1} …. (iii)
Subtracting equation (ii) from (i),
{a + (p – 1)d} – {a + (q – 1)d} = q – p
⇒ a + (p – 1) d – a – (q – 1)d = q – p
⇒ (p – 1 – q + 1 )d = q – p
⇒ (p – q)d – (p – q)
⇒ d = -1
Putting value of d in equation (i)
a + (p- 1) (- 1) = q
⇒ a – (p – 1) = q
⇒ a = q + p – 1
⇒ a = p + q – 1
Putting the value of a and d in equation (iii),
Tp+q = a + [(P + q) -]d
= (p + q – 1) + [(p + q -1)(- 1)]
= (p + q -1) – (p + q – 1)
= 0
Hence, (p + q)th term is zero.
Question 10.
In an A.P. pth term is 1/q and 17th term 1/p, then prove that pqth term is unity.
Solution :
Let first term be a and common difference be d