Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 15 Condensation and Rainfall
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 15 Text Book Questions
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 15 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which is the instrument to measure the humidity of atmosphere.
(a) Hydrometer
(b) Hygrometer
(c) Isobar
(d) Barometer
Answer:
(b) Hygrometer
Question 2.
The cloud at the highest elevation in the atmosphere is:
(a) Cirrus
(b) Stratus
(c) Cumulus
(d) Nimbus
Answer:
(a) Cirrus
Question 3.
Fog visibility is measured by:
(a) Hydrometer
(b) Transmissometer
(c) Cube meter
(d) Millimeter
Answer:
(b) Transmissometer
Question 4.
The afternoon rainfall which takes place in the equatorial linear region is called:
(a) Orographic Rainfall
(b) Cyclonic Rainfall
(c) Convectional Rainfall
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Convectional Rainfall
Question 5.
The actual amount of water vapor present in the atmosphere is called:
(a) Evaporation
(b) Relative humidity
(c) Absolute humidity
(d) Condensation
Answer:
(c) Absolute humidity
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 15 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is humidity?
Answer:
Water vapor present in the atmosphere is called humidity.
Question 2.
What is absolute humidity?
Answer:
The actual amount of water vapor present in the atmosphere is called absolute humidity.
Question 3.
What is cyclonic rain?
Answer:
In cyclones, the wind rapidly proceeds towards the center and starts rising up. As it proceeds from the sea, it is saturated with water vapor. Therefore, when cold air comes in its contact, a type of frontal zone is formed in between and hot air containing water vapor cools down and causes rainfall which is called cyclonic rain.
Question 4.
What is precipitation?
Answer:
When the water vapor in the atmosphere is converted into liquid or solid state by the process of condensation in the atmosphere, it falls on the surface, and is called precipitation. It contains snow, hail and water droplets from the clouds.
Question 5.
What is fog?
Answer:
When the condensation of the water vapor takes place near the surface, the visibility of the surface or atmosphere becomes less than 1 km, then this form of condensed water vapor is called fog.
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 15 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is humidity? State its types.
Answer:
The water vapor present in the atmosphere is called humidity. This humidity is the basis of daily seasonal change.
Types of humidity:
The main types of humidity are as follows:
1. Absolute humidity:
It is also called the real humidity, the amount of water vapor that is found at a certain temperature in a fixed volume of air is called the real or absolute humidity.
2. Relative humidity:
Relative humidity is the ability of air to absorb moisture at a certain temperature and a fixed volume.
3. Specific humidity:
When the air rises up and comes down, there is change in its actual humidity. Therefore, in the study of air masses, specific humidity is used in place of actual humidity.
Question 2.
Differentiate between relative humidity and absolute humidity.
Answer:
Relative humidity:
Relative humidity is the proportion of the humidity potential of the fixed volume of air at a certain temperature and the actual humidity in it. It is expressed in percentage.
Absolute humidity:
The actual amount of water vapor present in the atmosphere is called absolute humidity, or the actual amount of water vapor present in a fixed volume of air is called absolute humidity, and it is expressed in grams per cubic meter.
Question 3.
What is evaporation?
Answer:
The process by which the water changes from liquid state into gaseous state or water vapor, is called evaporation. The atmosphere receives humidity by the process of evaporation. The evaporation is higher in the oceans than on land. The amount and rate of evaporation depends on the speed, temperature and dryness of the air. Greater the temperature at which the air dries up and greater the rate, greater is the amount? and speed of evaporation, water changes into vapor by the process of evaporation.
Question 4.
State the types of clouds.
Answer:
Clouds are divided into the following types, depending on their height, density, expansion and transparency:
1. Cirrus clouds:
These types of clouds are present from an altitude of 8000 meters to 12000 meters.
2. Cumulus clouds:
These types of clouds are found at a height of 4000 meters to 7000 meters.
3. Stratus clouds:
These clouds are like fog and are found closer the earth’s surface.
4. Nimbus clouds:
These are black and dense clouds which are found closest to the surface of earth.
Question 5.
What is the Isohyet line ?
Answer:
The lines which are drawn to join the places of equal rainfall on the map of the world, are called the isohyet lines. By the study of these lines, the distribution of rainfall in the world can be systematically understood. Isohyets prove to be the most useful in showing less and more rainfall across the earth’s surface.
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 15 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Mention the factors influencing rainfall.
Answer:
The main factors that influence rainfall are as follows:
1. Latitude:
The latitudes of any area are responsible for the rainfall in that area. As we proceed towards the poles from the equator, the distribution of rainfall decreases. The equatorial region receives more rainfall due to higher heat reception, and on the contrary, the rainfall is very less due to lesser receipt of heat in polar regions.
2. Prevailing winds:
The condition of transmission of the winds found in any area is the controlling factor of rain. The more warm and dry the air is, its capacity to hold moisture increases and if the air is less dry then this is an obstruction in its tendency to hold moisture.
3. Water Currents:
Precipitation is controlled by the presence of cold and hot water currents found in the world. If the wind passes above the hot water streams, they become more dry but they hold more moisture also. On the contrary, cold streams reduce the capacity of the winds to retain moisture.
4. Distance from sea:
This factor plays an important role in causing rainfall. Wind often absorbs moisture from the oceans and causes rainfall in the terrestrial part. As the distance increases from the sea, the amount of moisture in the air continues to decrease.
5. Water and land conditions:
According to the position of water and land, the nature of the wind is determined. According to the condition of these two, the sea and terrestrial winds blow. In areas where the sea winds move, the amount of rainfall is high, whereas the terrestrial winds are often dry of produce less rainfall.
6. Location and orientation of mountains:
The mountains are an important factor in controlling rain. If the location of the mountains causes obstruction of moisturized winds then the amount of rain is high, whereas, when the direction of the mountains is parallel to the winds, there is less rainfall due to the absence of obstruction.
7. Height:
Along with increase in height from the sea level, there is decrease in temperature. Rain pattern is also controlled by this variation of temperature.
Question 2.
What is condensation? Describe the forms of condensation.
Answer:
The process of change of water form gaseous state into liquid or solid state is called condensation. Condensation takes place if the air temperature goes below the dew point or if the amount of water vapor is increased.
Forms of condensation:
Many forms of condensation are found in which dew, frost, cloud and fog are predominant. All these forms are described as follows:
1. Dew:
In day time, the earth becomes warm and it becomes cold in the night, so some times the earth’s surface becomes so cold that the temperature of the air touching it falls below dew point. This leads to condensation of water vapor present in the air, and it deposits on leaves and other types of surfaces in the form of small droplets, which is called dew. For the formation of dew, it is necessary that:
- Water vapor should be formed, and at the same time.
- The temperature should be so low on the surface that it can cool off the air and make the vapor condense.
2. Frost:
When the water vapor present in the air is condensing and the temperature of the air is 0° or less, then the water vapor takes the form of a solid or snowflake that is the frost. For form to frost, it is necessary that the temperature of the air continues to drop rapidly for long and the sky is cloudless and the air contains water vapor and the temperature of the air is below the freezing point.
3. Fog:
It originates from water vapor condensation near the surface. Fog reduces atmospheric transparency. When the visibility of the ground or the atmosphere decreases below 1 kilometer, then this form of condensed water vapor is called fog. It is necessary for the formation of fog that the temperature of the air falls below dew point and wind speed be slow. Depending on the visibility, the fog is of the following types: Light, simple, intensive and highly dense. The fog visibility is measured by the instrument named transmissometer. The condition of the visibility being slightly low is called mist.
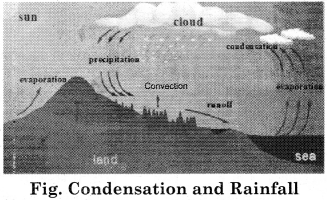
4. Clouds:
The gigantic mass of water particles or snowflakes formed by the condensation of water vapor in the open air, at high altitude, is called cloud. Clouds are found up to a height of 12,000 meters. Cloud is formed at various altitudes from the surface of the Earth.So these are of different types. Therefore, on the basis of their height, density, expansion and transparency, the clouds have been divided into the following types:
- cirrus clouds
- cumulus clouds
- stratus clouds
- nimbus clouds.
Question 3.
Explain the types of rain and also define precipitation.
Answer:
When water vapor in the atmosphere changes through condensation to liquid or solid state and falls on the earth’s surface, it is called precipitation. It can be in a liquid or solid state. It involves water drops falling as snow, hail due to formation of clouds. When the precipitation occurs in the form of water, it is called rain and when the temperature is below 0°, the precipitation occurs in the form of snowflakes, it is called snow fall. Hail, snow and water are included in precipitation.
Types of Rainfall:
Rainfall on the earth is divided into three types on the basis of origin:
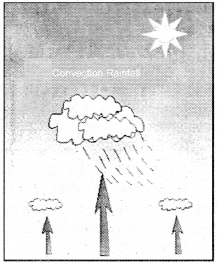
1. Convectional Rainfall:
This rain occurs primarily in the equatorial linear regions after noon, because due to excessive heat, the air rises above and simultaneously the water of the ocean becomes rapidly transformed into vapor and rises up, and the process is called convection. This process of convection results in convectional rainfall.
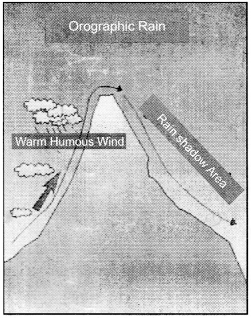
2. Orographic Rainfall:
It can also be called surfacial rainfall. Mountain rains take place in the highest amount in the world, in which the air denser than vapor has to get cooled up while rising along the mountain. By cooling, the air becomes condensed and it causes rainfall. This wind rises due to the obstruction of the mountains and causes rainfall. In the mountainous rain, there is more rainfall towards the windward side on the mountains, but on the other hand, the rainfall is very low on the other side (leeward side) and this side is called Rain Shadow region.
3. Cyclonic Rainfall:
This rain occurs in the mid-latitudinal and sub – tropical countries. It is caused due to the cyclones. In the cyclones, the wind blows rapidly towards the center and begins to rise. Due to coming through the sea, this air is denser than water vapor. So when the cold polar air comes in contact with it, a kind of front region develops in the middle and the warm air containing water vapor cools down, which is called cyclonic rain. This rainfall is not rapid, instead, it is in the form of drizzling. This type of rainfall occurs in regions of temperate cyclones. In the north-west India also in the winter, there is rainfall caused by cyclones.

RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 15 Other Important Questions
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 15 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
At an average, the percentage of humidity in the atmosphere is found to be:
(a) 2%
(b) 3%
(c) 4%
(d) 5%
Answer:
(a) 2%
Question 2.
The solid form of water is called:
(a) water vapor
(b) ice
(c) water
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) ice
Question 3.
The temperature at which the air is saturated is called:
(a) Freezing point
(b) Melting point
(c) Dew point
(d) Boiling point
Answer:
(c) Dew point
Question 4.
How many calories are needed to convert 1 gm of water into vapor?
(a) 79 Calories
(b) 165 Calories
(c) 405 Calories
(d) 607 Calories
Answer:
(d) 607 Calories
Question 5.
Where does highest evaporation take place on the oceans?
(a) Between 5° to 10° latitudes
(b) Between 10° to 20° latitudes
(c) Between 30° to 40° latitudes
(d) Between 60° to 80° latitudes
Answer:
(b) Between 10° to 20° latitudes
Question 6.
The solidification of water vapor in the form of snowflakes instead of the formation of dew is called:
(a) dew
(b) frost
(c) fog
(d) cloud
Answer:
(b) frost
Question 7.
Cirrus clouds are found at a height of:
(a) 8000 – 12000 meters
(b) 4000 – 7000 meters
(c) 2000 – 4000 meters
(d) Less than 2000 meters
Answer:
(a) 8000 – 12000 meters
Question 8.
What kind of rain is the highest in the world?
(a) convectional rainfall
(b) orographic rainfall
(c) cyclonic rainfall
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) orographic rainfall
Matching Type Questions
Question A.
Match column A with column B.
| Column A (Types of clouds) | Column B (Height) |
| (i) Cirrus Cloud | (a) 4000 – 7000 meters |
| (ii) Cumulus Cloud | (b) 2500 – 3000 meters |
| (iii) Stratus Cloud | (c) closest to the surface |
| (iv) Nimbus Cloud | (d) 8000 – 12000 meters |
Answers:
- (d)
- (a)
- (b)
- (c)
Question B.
Match column A to column B.
| Column A (Belt of Rain) | Column B (Latitudinal extent) |
| (i) Equatorial Rainfall Belt | (a) From 60° latitude to the poles |
| (ii) Rain belt of Trade winds | (b) Between 40° to 60° latitude |
| (iii) Subtropical rain belt | (c) Between 30° to 40° latitude |
| (iv) Mediterranean rain belt | (d) 10° latitudes from the equator |
| (v) Mid-latitudinal rain belt | (e) Between 10° to 20° latitude |
| (vi) Polar less rainfall belt | (f) between 20° to 30° latitude |
Answers:
- (d)
- (e)
- (f)
- (c)
- (b)
- (a)
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 15 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which are the different states of water?
Answer:
Like every substance, there are three states of water – solid, liquid and gas. Water is found in the form of ice in the solid state, in the form of water in liquid state, and in the form of water vapor in gaseous state.
Question 2.
What is water vapor ?
Answer:
Change the state of water due to the effect of insolation results in it turning from liquid to gaseous state, which is called water vapor.
Question 3.
How is water cycled?
Answer:
The waters in the oceans, the atmosphere and the continents continue to be exchanged through transpiration, evaporation, condensation and precipitation.
Question 4.
What does saturated air mean ?
Answer:
When a volume of air at a given temperature holds the maximum amount of water vapor, it is called saturated air.
Question 5.
What is dew point?
Answer:
The temperature at which the air is saturated is called the Dew Point.
Question 6.
Which formula is used to calculate relative humidity?
Answer:
We use the following formula to calculate relative humidity :
![]()
Question 7.
On what does the amount of evaporation depend?
Answer:
The amount of evaporation depends primarily upon temperature, air dryness, expanse of water area, clouds and wind velocity.
Question 8.
When does condensation take place ?
Answer:
If the temperature of the air goes below the dew point or if the amount of water vapor Increases, condensation takes place. For this, the following conditions are responsible.
- The degree of heat loss.
- Increase in humidity.
Question 9.
What is the meaning of clouds?
Answer:
The giant mass of water particles or snowflakes formed by the condensation of water vapor in the open air at very high altitude in the atmosphere is called cloud.
Question 10.
Which conditions are necessary for rain?
Answer:
For rain, it is necessary to have the following conditions:
- Sufficient water vapor in the air.
- Presence of such conditions by which the vaporized air can condense.
Question 11.
How many types of rainfall are there?
Answer:
Rainfall on the earth is divided on the basis of origin, into the following three types:
- Convectional rainfall
- Orographic rainfall
- Cyclonic rainfall
Question 12.
Where does convectional rainfall mainly take place ?
Answer:
Convectional rainfall mainly takes place in the equatorial linear regions. Such areas mainly include Indonesia, the Philippines, the Congo Basin and the Amazon Basin area.
Question 13.
What is the rain shadow area?
Answer:
Under orogrophic rainfall on the mountains, there is more rainfall on the mountair slopes towards the windward side, but on the other hand, there is a lack of rainfall on the other side. This rain less area is called rain shadow area.
Question 14.
Why does rain occur in India in the winter season?
Answer:
Rainfall of winter season in north-western India is mainly caused due to temperate cyclones.
Question 15.
Name the factors influencing rainfall.
Answer:
The factors influencing rainfall mainly include latitude, elevation, prevailing winds water currents, distance from sea, water and land conditions and direction of mountain ranges.
Question 16.
Which are the factors affecting distribution of rainfall?
Answer:
Factors affecting the distribution of rainfall include temperature, land – water distribution, direction of wind, mountains, etc.
Question 17.
Explain trade winds rainfall belt.
Answer:
The extension of this belt is found between 10 0 to 20 0 latitudes on both side of the equatorial. Here, the rain is caused in the eastern parts of the continents due to trade winds Monsoon rains also occur in this belt.
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 15 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-I)
Question 1.
Explain the importance of water vapor.
Answer:
Water vapor is an important component of the atmosphere, its utility has been clarified through the following points:
- Depending on the amount of water vapor, the air is moist or dry.
- The condensation of water vapor determines the form of rainfall, hailstone ant snowfall.
- Water vapor is present in the atmosphere due to the process of transpiration. Based on the quantity of this water vapor, the atmospheric temperature is less or more.
- Due to water vapor, different forms of condensation occur.
- Due to the presence of water vapor, conditions of rainfall emerge, which is the basis o the life on the earth.
Question 2.
Explain the process of evaporation.
Answer:
Evaporation is a process by which the liquid water changes into gaseous water vapor Humidity is obtained by the atmosphere through evaporation. The amount and rate o evaporation, depends on the speed of the wind, the temperature the dryness of air and the expanse of water surface. Evaporation is more on the oceans than land. To convert 1 gram of ice to water, 79 calories are required, whereas 607 calories are needed to convert 1 gm of water into vapor. At high latitudes, the amount of evaporation is often found to be less.
Question 3.
Explain the difference between dew and frost.
Answer:
The following differences are found between dew and frost:
| Basis of difference | Dew | Frost |
| The cause of the origin | The formation of dew takes place due to the cooling down of earth’s surface and the decline in the temperature of air coming in its contact. | The origin of the frost is due to the very low temperature of the air. |
| Temperature conditions | During the formation of dew, the temperature is indeed low, but it always above freezing point. | The temperature in the formation of frost often drops to 0 ° or less. |
| State of matter | Dew is the liquid state of water. | Frost is the solid state of water. |
| Necessary condition | For the formation of dew, along with the presence of water vapor in the air, it is necessary to have less temperature so that the vapor condenses. | For frost, it is necessary for the temperature to rapidly fall for a long period of time and to reach the freezing point. |
Question 4.
Describe the Cumulus Clouds.
Answer:
- These clouds are very extensive and deep dark – coloured and dense.
- These clouds cause heavy rain, hail and thunderstorms.
- These clouds are shaped like cauliflowers.
- The height of these clouds ranges from 4000 to 7000 meters.
- They are found in ideal form due to convection currents in tropical areas.
Question 5.
Describe the features of the Mediterranean rain belt.
Answer:
The Mediterranean rain belt has the following characteristics:
- Expanse of this rain belt is found in both the hemispheres between 30° to 40° latitudes.
- Rainfall in this belt occurs in the winter season.
- Rainfall in this belt occurs by westerlies winds.
- Rainfall in this belt is simple and cyclonical.
- This rain belt has an average rainfall of 100 centimeters.
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 15 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-II)
Question 1.
Explain the process of precipitation.
Answer:
The total amount of rainfall measured by rain – gauge in a certain place in a fixed period of time, which consists of snow, hail and water droplets falling from the clouds. When water vapor present in the atmosphere gets converted into liquid or solid state due to condensation, it is called precipitation. When precipitation occurs in the form of water, it is called rainfall.
When the temperature is less than 0°, rainfall takes place in the form of snow particles, and it is called snowfall. Hail, snow and water all the three can be included under rainfall. The meaning of rainfall is commonly taken from the average rainwater fall. For this, it is necessary to have two things sufficient water vapor content in air-and sufficient temperature drop.
Question 2.
What is the difference between extreme rainfall and drought in orographic rainfall ?
Answer:
The following differences are there in extreme rainfall and drought:
| Extreme Rainfall | Drought |
| 1. In the Orographic rain, the windward slope is the slope which is facing the wind. | 1. In Orographic rain, the Leeward slope is the slope opposite to the direction of the flowing of the winds. |
| 2. There is extreme rainfall along the windward slope. | 2. The area with leeward slope is the region of drought. |
| 3. Extreme Rainfall due to excessive moisture on the windward slope due to the height of the mountain peak. | 3. Drought conditions emerge due to lack of moisture in the clouds on the leeward slope. |
Question 3.
What is the difference between Orographic and Cyclonic Rainfall?
Answer:
The following differences are there in Orographic and Cyclonic Rainfall:
| Orographic Rainfall | Cyclonic Rainfall |
| 1. This type of rain takes place due to the cooling down and condensation of air containing vapor which rises up along the mountain. | 1. This type of rainfall is caused due to the evaporated air proceeding from the sea coming in contact with cold air and due to the cooling down of hot air. |
| 2. In Orographic rain, there is more rainfall in the region facing the air current, whereas in the opposite part, there is less rainfall. | 2. The cyclonic rain is in the form of light showers distributed uniformly. |
| 3. This type of rainfall occurs in mountainous regions. | 3. This type of rainfall mainly takes place in areas with cyclonic conditions. |
| 4. The Orographic rain is caused by a temperate air mass being cooled down by rising up. | 4. Cyclonic rainfall is the result of meeting of two different types of air masses and their competitive process. |
Question 4.
What is the difference between the Equatorial rain belt and the Mediterranean rain belt?
Answer:
| Equatorial Rain belt | Mediterranean Rain belt |
| 1. Rainfall occurring in this belt is called equatorial rain. | 1. The rainfall occurring in this belt is called Mediterranean rain. |
| 2. Convectional rainfall takes place here due to the receipt of more heat in this belt. | 2. This belt receives cyclonic rainfall due to temperate conditions. |
| 3. Rainfall in this belt is of torrential nature. | 3. Rainfall in this belt is in the form of light showers. |
| 4. The annual rainfall of this belt takes place at an average of 175 cm. to 200 cm. | 4. In this belt, the average annual rainfall is 100 centimeters. |
| 5. The expansion of this rain belt is found in the Amazon Basin, Congo Basin, New Guinea, Philippines, Madagascar and Indonesia. | 5. This belt extends in California, Central Chile, South – western part of South Africa, and in the south – western part of Western Australia. |
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 15 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by cloud? State the types of clouds.
Answer:
Meaning of cloud:
When the temperature of the air blowing upwards in the atmosphere falls below the dew point, the water vapor present in the air cools down and it turns into micro-water particles or snowflakes. Such water – particles or snowflakes suspended in the form of agglomerates in the atmosphere are called clouds.
Types of clouds:
Clouds are divided into the following types depending on their altitude, size, density and transparency:
1. Cirrus clouds:
These clouds are found at greatest height (8000 to 12000 meters). The climate and the sky remain usually clear due to these and there is no rainfall. They are spread across the entire sky, like a white sheet. On their arrival, haloes are formed around the sun and the moon, which is indicative of the arrival of cyclone.
2. Cumulus clouds:
These are very extensive and dark – coloured and dense clouds. These clouds cause heavy rains, hail and thunderstorms. They look similar Jo cotton and their height ranges from 4000 to 7000 meters. Their shape is like cauliflower.
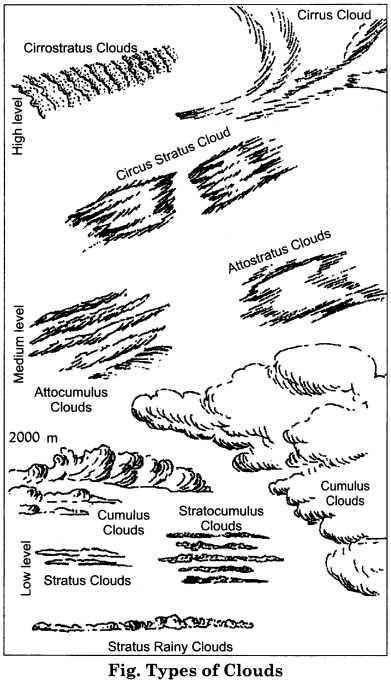
3. Stratus clouds:
These clouds look like fog and are found nearest to the surface. They are composed of many similar layers. They are formed in the cold winter in the temperate zone due to the presence of two opposite – natured winds. Their colour is light brown and some times pink or purple. The sky is blurred due to their shade. The possibility of drizzling is there due to these.
4. Nimbus clouds:
These clouds are thick and dark. As they are dense, darkness prevails and there is heavy rain. They are situated at the lowest height. From distance, it looks as if they are touching the earth. These clouds cause the maximum rainfall.
Question 2.
Explain the distribution pattern of rainfall in the world.
Answer:
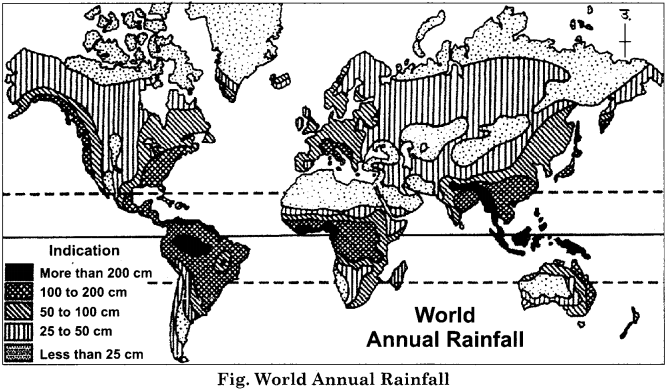
The amount of rainfall varies in different regions on the earth’s surface. Distribution of rainfall on the surface is very uneven. In some places, the rainfall is more than 200 centimeters, while at other places, it is less than 20 centimeters. Important factors influencing the distribution of rainfall are temperature, land-water distribution, direction of winds, direction of mountains, etc. There are six belts of rainfall on the Earth:
1. Equatorial excess rainfall belt:
The extension of this belt is found between 10° latitudes on both side of the equatorial line. In this, the Amazon Basin of South America, the Congo Basin, the windward coastal part of Central America, New Guinea, Philippines and Madagascar are included. Here, the annual rainfall is about 175 centimeters to 200 centimeters. Rainfall is mainly of convection type. There is rain in the afternoon with thunder and lightning every day.
2. Rainfall belt of trade winds:
The extension of this belt is found between the latitudes of 10° to 20° on both sides of the equator. Here, the rain takes place in the eastern parts of the continents due to trade winds. Monsoon rains also occur in this belt.
3. Sub – tropical rainfall belt:
This belt is located in the both hemispheres between 20° to 30° latitudes. It is a high pressure belt, in which winds descend from top to bottom. So, anticyclonic conditions are found. In Sahara, and Thar deserts, the annual rainfall is less than 25 centimeters.
4. Mediterranean belt:
Its expanse is found in both the hemispheres between 30° to 40° latitudes. It includes California, Central Chile, South – western part of South Africa, and South – western part of Western Australia. In winter, there is a lot of rain due to westerlies winds. Rainfall is simple and cyclonic. The annual rainfall averages 100 cm. Dry summers are characteristic of this belt because at this time this belt remains under the influence of dry trade winds.
5. Belt of moderate latitudinal rainfall:
This belt is found between 40° to 60° latitudes on both side of the equator. Here, more rainfall takes place in the western parts of the continents. Due to the excess of the aquatic part, the northern hemisphere experiences more rain as compared to the southern hemisphere. Here, there is cyclonic rainfall due to the conjunction of polar and westerlies winds. Here, the annual rainfall averages from 100 to 125 cm.
6. Polar low rainfall belt:
It extends from 60° latitude to poles in both hemispheres. The amount of rainfall towards the poles decreases. Most of the rainfall here is in the form of snow. Here, the annual rainfall is up to 25 centimeters.
The status of the rain received in the world is represented by the following map: