Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 22 Concept of Ecosystem
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 22 Text Book Questions
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 22 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Who first propounded the word bio – diversity?
(a) E.O. Wilson
(b) David Tillman
(c) Norman Meyers
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) E.O. Wilson
Question 2.
How many bio – diversity hot – spots have been identified in the world?
(a) 12
(b) 20
(c) 25
(d) 34
Answer:
(c) 25
Question 3.
The number of national parks in India is:
(a) 103
(b) 72
(c) 89
(d) 96
Answer:
(c) 89
Question 4.
The propounder of the word ‘ecosystem’ is:
(a) A. G. Tansley
(b) Fassberg
(c) E.P. Odum
(d) Peter Hagate
Answer:
(a) A. G. Tansley
Question 5.
Which statement is true in relation to ecology?
(a) Study of environmental effects on ecological organisms.
(b) Ecology is the study of pollution of air, water and soil.
(c) Ecology is the study of human environment.
(d) The study of the inter-relationships of ecological organisms and the environment.
Answer:
(d) The study of the inter-relationships of ecological organisms and the environment.
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 22 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
On what percentage of the entire earth is the lithosphere present?
Answer:
About 29 per cent of the entire earth is the lithosphere.
Question 2.
Biosphere is the result of which activities?
Answer:
Biosphere is the result of the complex activities of the biotic and abiotic components found on the Earth’s surface.
Question 3.
What percentage of plant diversity of the whole world is found in our country?
Answer:
In our country, 8 per cent of the world’s total plant diversity is present.
Question 4.
Write the name of green matter found in plants.
Answer:
In plants, green matter present is called chlorophyll.
Question 5.
According to Odum, how much insolation per day per square meter is obtained from sunlight?
Answer:
According to Odum, insolation of an average of 3000 kilo calories per day per square meter is obtained from sunlight.
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 22 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define the term biosphere.
Answer:
The study of living organisms in the lithosphere, atmosphere and hydrosphere is included in the biosphere. The interaction of the organisms found in these three divisions and their mutual relationships are considered to be the integral part of the biosphere. Generally, the ecosystem is a cover around the surface of the earth, under which vegetation and animal life becomes possible without any protective device. According to Stroller, “All living organisms on earth and the environment, which interacts with these organisms, together create the biosphere.”
Question 2.
Write a comment on bio – diversity in India.
Answer:
India is the country with the highest bio – diversity in the world, next only to Brazil. Due to geographical and climatic variations in our country, there is a wide variety of bio – diversity of – flora and fauna. India has 6.5 percent of animal species and 8 per cent of plant species of the world. There are approximately 46,000 plant species and 81,000 animal species found in India. In India, two bio – diversity hot – spots are found. Western Ghats hot spots and Eastern Himalayas hot spot.
Question 3.
Explain the objectives of establishing national parks and sanctuaries.
Answer:
The main purpose of establishing National Parks and Sanctuaries is to conserve wild life, ban hunting of wild animals and ban illegal trade of wildlife products and to develop ecology in the proximity of national parks and sanctuaries so that the bio – diversity of different plants and organisms can be maintained.
Question 4.
According to Tansley, write the definition of ecosystem.
Answer:
According to A.G. Tansley, “The system in which the biotic and abiotic factors of the environment are inter – connected is called the ecosystem”. The use of the term ‘ecosystem’ in the study of biosphere by Tansley, had attracted the attention of the entire world.
Question 5.
Define energy flow.
Answer:
The biotic and abiotic components of an ecosystem are controlled by the ecology of that system and they remain active in a certain process. Energy is required to stay active. This energy makes an ecosystem dynamic. This entire process is called energy flow. This energy flow keeps the environment naturally controlled. As a result, the balance in that ecosystem is maintained.
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 22 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Write an article on the concept of ecosystem.
Answer:
The Concept of ecosystem:
A systematic and orderly study of organisms living in a geographic unit and the inter-relations of that unit is called ecological mechanism. According to A.G. Tansley(1935), “The system in which the biotic and abiotic factors of the environment are inter – related, is called the ecosystem”.
Other definitions related to ecosystem are given as follows:
According to R.L. Lindeman (1942):
“The system that is produced by physical – chemical – biological processes in a particular time unit of any magnitude, is called the ecosystem”.
According to Fasbert (1963):
“The ecosystem is a functional and interactive system, whose structure is formed by one or more organisms and their effective environment”.
According to Odum (1971):
“The ecosystem is the basic functional unit of such organisms and their environment, which constantly interacts with other ecosystems and their components”
According to Peter Haggett (1975):
“Ecosystem is such an ecological system in which plants and organisms are linked to their environment through the nutritional chain.”
According to Arthur N. Strahler (1976):
“The ecosystem is a group of components that interact with groups of organisms. This activity involves investing in substances and energy, which create biological structures.”
According to Park (1980):
“The ecosystem is the gross of all the natural organisms and elements within a certain area.”
An ecosystem is the basic unit of ecological study whose size and extent can vary. For example, if one ecosystem is an entire global supplemental ecosystem, then the second ecosystem may be as small as a cage built in a zoo or limited to a lake. Ecosystems can be either natural or man-made.
Question 2.
Write an article on energy flow in the ecosystem.
Answer:
The biotic and abiotic components of an ecosystem are controlled by the ecology of that system and remain active in a certain process. Energy is required to stay active. This energy makes an ecosystem dynamic. This entire process is called energy flow. This energy flow keeps the environment naturally controlled, which results in balance in that ecosystem. There may be a crisis in this ecosystem if there is a slight change due to human or natural reasons in this process.
Continuous energy flow is required to keep any ecosystem moving smoothly. Sun is the main source of energy on Earth, but infact, very subtle amount of solar energy can only be used in the ecosystems. Just 0.02 percent of solar energy is converted into chemical energy by plants and some part can be used in other functions of the ecosystem. This micro part of solar energy is able to make an ecosystem dynamic.
The green pigment found in plants (chlorophyll) absorbs solar energy and turns it into organic particles. This process is called photosynthesis. With the help of carbon – dioxide and water, the plants work to convert solar energy into food (starch) by the process of photosynthesis. The plant develops with the help of glucose and carbohydrates and oxygen and water vapor is released into the atmosphere by the respiratory action of plants.
The accumulated chemical energy in plants is obtained by herbivores as food. Energy is lost during its transfer from plants to herbivores. After this, carnivorous organisms eat the herbivorous organisms, and even then, there is loss of energy. Thus, energy continues to flow from one nutritional level to another nutritional level. Along with this transfer of energy, it also gets lost. Thus, the quantity of energy at every consumer level decreases continuously.
According to odum, an average daily energy of 3000 k cal per square meter is obtained by insolation. Out of this, 1500 k cal energy is absorbed by plants, of which only 1% (15 k cal) is converted into chemical energy. At secondary and tertiary nutritional levels, it decreases to 1.5 k cal and 0.3 k cal respectively.
Usually, most of the energy is lost while transferring from one nutritional level to another nutritional level, but its quality increases. Energy is neither created nor destroyed, although the nature of energy can change. Thus the amount of inherent and outflow of energy in an ecosystem remains the same.
Question 3.
Explain the effect of industrialisation on eco – system in detail.
Answer:
The effects of industrialization on the ecosystem are visible as given below:
1. As a result of industrialization, environmental pollution has increased rapidly.
2. Industrial Units are a major source of air and water pollution. On one hand, due to the poisonous gases emerging from these units, the atmosphere is constantly being polluted, and on the other hand, chemical waste water from many industrial units pollutes the rivers, underground water and sea water.
3. Due to the pollution of rivers and underground water, the problems of drinking water in the adjoining areas of industrial cities has become acute.
4. The emergence of chemically-polluted water in tube – wells of Pali city is a proof of this.
5. Due to the effect of toxic gases, the ozone layer is thinning and acid rain near the industrial areas has become frequent.
6. Solid waste from industrial units is reducing the fertility of the land, which has adverse effects on the agricultural produce and productivity.
7. Smoke emitted from industrial units is frozen in the form of a layer in the atmosphere which is proving to be a barrier in the reflection of terrestrial radiation.
8. Industrial units emit carbon – dioxide which is responsible for global warming, and this is causing a steady increase in global temperature.
9. The contribution of industrial units in the process of climate change has been, thereby impacting the bio – diversity and ecosystem. All these processes indirectly influence the ecosystem adversely.
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 22 Other Important Questions
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 22 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The word ‘ecology’ has originated from which language?
(a) from French language
(b) from Greek language
(c) from German language
(d) from Hindi language
Answer:
(b) from Greek language
Question 2.
Whose idea was that “earth is not a material substance”?
(a) Odum’s
(b) Humboldt’s
(c) Ritter’s
(d) Tansley’s
Answer:
(b) Humboldt’s
Question 3.
Those organisms who are dependent on other creatures for their survival, are called:
(a) Holozoics
(b) Saprophytes
(c) Parasites
(d) Consumers
Answer:
(c) Parasites
Question 4.
Which of the following, is different from the other three.
(a) Eagle
(b) Frog
(c) Fox
(d) Dog
Answer:
(a) Eagle
Question 5.
Which of the following is an abiotic component?
(a) Cow
(b) Lion
(c) Fish
(d) Rain
Answer:
(d) Rain
Question 6.
According to Forest Report 2015, what is the total geographical area of forests in India?
(a) 19.02%
(b) 20.15%
(c) 22.02%
(d) 24%
Answer:
(c) 22.02%
Question 7.
Water Cess Act was implemented:
(a) In 1971
(b) In 1981
(c) In 1977
(d) In 1986
Answer:
(c) In 1977
Question 8.
Which of the following is not a Key – stone species:
(a) Elephant
(b) Frog
(c) Fox
(d) Cow
Answer:
(d) Cow
Matching Type Questions
Question A.
Match column A with column B:
| Column A (Bio – species) | Column B (Tropic status) |
| (i) Algae | (a) Carnivorous |
| (ii) Goats | (b) Decomposer |
| (iii) Cat | (c) Herbivorous |
| (iv) Fungus | (d) Auto – trophical components |
Answers:
- (d)
- (c)
- (a)
- (b)
Question B.
Match column A with column B:
| Column A (Name of species) | Column B (Nutritional Level) |
| (i) Grass | (a) Quadratic Level |
| (ii) Grasshopper | (b) Primary Level |
| (iii) Lizard | (c) Secondary level |
| (iv) Eagle | (d) Tertiary Level |
Answers:
- (b)
- (c)
- (d)
- (a)
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 22 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Who used the word ecology for the first time and for whom?
Answer:
The term ecology was firstly used for the regions of vegetation by Haikal (1989).
Question 2.
How has the word ecology originated?
Answer:
Ecology has originated from the Greek word ‘Oikos’ means habitation and ‘Logos’ means studies.
Question 3.
What did Ritter write about ecology?
Answer:
Ritter wrote that there is co – ordination in the regional distribution of different elements on the surface. These elements are inter – related, so that they give a specificity to that area.
Question 4.
What is meant by ecosystem ?
Answer:
A timely and sequential study of the organisms living in a geographic unit and the inter-relations of that unit is called ecosystem.
Question 5.
How has Odum defined ecosystem ?
Answer:
According to Odum:
“The ecosystem is the basic functional unit of such organisms and their environment, which constantly interacts with other ecosystems and their components”.
Question 6.
On the basis of the source of energy, ecosystem is divided into how many parts?
Answer:
On the basis of the source of energy, there are two types of ecosystem:
- Natural ecosystem
- Man – made or Artificial ecosystem.
Question 7.
What is meant by Natural Ecosystem?
Answer:
The ecosystem which develops in natural conditions is called natural ecosystem.
Question 8.
Which is the largest and permanent ecosystem?
Answer:
The largest and permanent ecosystem is the marine ecosystem.
Question 9.
What is a man – made ecosystem?
Or
What is artificial ecosystem?
Answer:
Man – made and evolved system is called artificial ecosystem.
Question 10.
What forms the structure of the ecosystem?
Answer:
The ecosystem is composed of the interactions of biotic and abiotic components of the environment.
Question 11.
What is meant by biotic components ?
Answer:
All the living organisms of an ecosystem are the biotic constituents of that system; all these organisms are inter-related by different interactions.
Question 12.
On the basis of nutrition, into how many parts are biotic components divided?
Answer:
On the basis of nutritional potential, biotic components have been divided into autotrophic components and heterotrophic components.
Question 13.
What is meant by hetero – trophic components?
Answer:
The components that take the food provided by auto – trophic primary producers are called hetero – trophic components.
Question 14.
Heterotrophic components are divided into how many parts?
Answer:
Heterotrophic components are divided mainly into three parts:
- saprophytic
- parasitic
- holozoic components.
Question 15.
What are saprophytic components?
Answer:
Saprophytic components survive by obtaining organic compounds derived from plants and animals in liquid form.
Question 16.
On the basis of functioning, into how many parts are biotic components divided ?
Answer:
On the basis of functions, biotic components have been divided into producers, consumers, and decomposers.
Question 17.
What does the term decomposition mean?
Answer:
The micro – organisms and fungi that feed on organic matter, including dead plants and animals, decompose them. This is called decomposition.
Question 18.
How many types of Abiotic components are there?
Answer:
The abiotic components are mainly of three types:
- Climatic elements.
- Organic substances.
- Inorganic substances.
Question 19.
What is meant by food chain ?
Answer:
All the organisms in the ecosystem that come under the category of producers and consumers are arranged in a sequence or series. This systematic series of organisms, by which the transfer of food energy and nutrients takes place, is called food chain.
Question 20.
What is meant by nutritional level ?
Answer:
Each level or link in the food chain is called nutritional,level.
Question 21.
What is meant by ecological pyramid?
Answer:
The pyramidal structure representing the formulation of the amount of rectangles biomass and energy flow of producers, carnivores and herbivores through their rectangles, is known as ecological pyramid.
Question 22.
Which human activities are responsible for climate change?
Answer:
Afforestation, industrialization and invention nuclear power is considered to be accountable for climatic change.
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 22 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-I)
Question 1.
How did the concept of ecology emerge?
Answer:
Although the word ecology may be the gift of the 19th century, yet the concept of ecology is very ancient in terms of Indian culture. Since ancient times, Indian sages and intellectuals have linked ecological components to different kinds of symbols of religion, social norms and conduct in order to make the inter – relationship of nature and organism a part of the public masses.
For example, the cow was granted the status of a mother. For thousands of years, mutually beneficial interaction existed between humans and environment, but the desire of humans to conquer nature in the modern era has provided only material pleasures as the basis of life while sacrificing these eternal laws and conduct. There was a distortion in the inter-relationship of the organisms, which led to the emergence of the concept of ecology.
Question 2.
Explain the ecological system.
Answer:
Ecology is a system that is the result of the interaction of the organism and the environment. This system is developed under natural rules. Therefore, in the study of ecology, the secrets of this system are traced. This system is so complex that as the scholars are searching for these secrets, new discoveries are emerging.
Although the scientific man, in the field of scientific achievements and technological advances, has started accepting that he is not a slave of nature. He is free to use and consume natural bounties as he wishes. The adverse consequences of this trend of human beings have now started to appear in various forms of environmental degradation.
Question 3.
Describe the main features of an ecosystem.
Answer:
The ecosystem has the following characteristics:
- An ecosystem is the basic unit of ecological studies.
- The size and extent of the ecosystem can vary.
- The ecosystem may be natural or man – made.
- Ecosystem may be spread across the entire globe or may be as small as a cage built in the zoo or limited to a lake.
Question 4.
What is the difference between Biotic and Abiotic components?
Answer:
The following differences are found between Biotic and Abiotic components:
| Biotic Components | Abiotic Components |
| 1. All living organisms of any ecological system are the biotic components of that svstem. | 1. All the inanimate (non – living) components of an ecosystem are the abiotic components of that system. |
| 2. Biotic components are inter-related by mutual interactions. | 2. There is no reciprocal interaction between abiotic components. |
| 3. Human components, organisms and vegetation are included in biotic components. | 3. Abiotic components include elements of the climate, organic matter and inorganic materials. |
| 4. Biotic components are components that change. | 4. Abiotic components are often unchanging components. |
Question 5.
Consumers are divided into how many parts?
Answer:
There are three types of consumers:
1. Primary consumers:
These are also called herbivores. All living beings, such as rabbits, deer, goats, cows, insects, which get food from plants or their products come in this category.
2. Secondary consumers:
These are also called carnivorous consumers. They kill the herbivores and obtain their food from their flesh. These include frogs, cat, fox, dog, lion etc.
3. Tertiary Consumers:
They are also called omnivorous consumers. They get their food by eating plants, herbivores and carnivores. This category includes humans, eagles, lions and fish.
Question 6.
Why does the quantity of energy at each consumer level continue to decrease?
Answer:
The accumulated chemical energy in plants is received by the herbivores in the form of food. Degradation of energy occurs during its transfer from plants to herbivores. After that, carnivorous organisms eat the herbivorous organisms, and at that time also there is degradation of energy. Thus, from one nutritional level to another, the energy flows and transfer of energy occurs. Thus, the quantity of energy at every consumer level decreases continuously.
Question 7.
Explain the contribution of wild life in natural balance.
Answer:
Wild life has its distinct balancing role and importance in maintaining natural balance. Wild life maintains ecological balance in nature and once the balance gets disturbed, its direct impact is on mankind. For example, if the carnivorous wild life is eliminated by the predators, the herbivores will increase in number to such extent, that they will eat up all the trees and vegetation in the forest and eventually entire forest regions will be erased.
This will result in absence of rainfall, the production of crops will not be sufficient and the human beings will have to suffer financially. From all these facts it is clear that wild life plays an important role in balancing the nature.
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 22 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-II)
Question 1.
Explain the types of ecosystem.
Answer:
The ecosystem has been classified on various bases. This has been clarified through the following table:
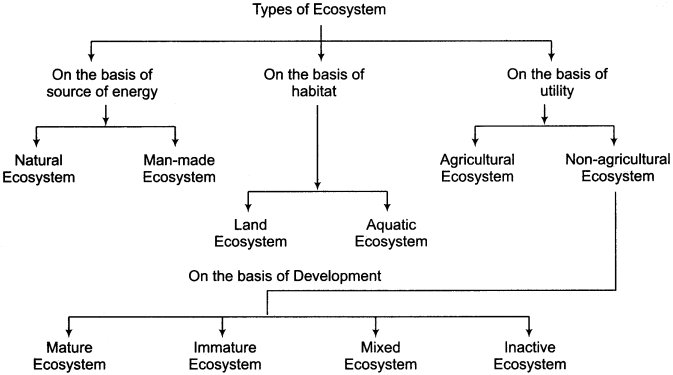
On the basis of source of energy ecosystems are of two types:
1. Natural ecosystem:
The ecosystem that has developed in natural conditions is called natural ecosystem, these systems can be of both types:
- Terrestrial
- Aquatic
In the terrestrial natural ecosystem, forests, grasslands, ponds, rivers, deserts, mountain, areas, etc. are included, marine ecosystem is the largest and permanent ecosystem. Forests, grasslands, deserts, open sea etc. are natural ecosystems.
2. Man – made or artificial ecosystem:
Man – made and developed ecosystem is called artificial ecosystem, such as fields, parks, kitchen – gardens, zoos, aquariums, etc.
3. On the basis of housing:
- Terrestrial ecosystem
- Aquatic ecosystem
4. On the basis of usage:
- Agricultural ecosystem
- Non – agricultural ecosystem
5. On the basis of development:
- Mature ecosystem
- Immature ecosystem
- Mixed ecosystem
- Inactive ecosystem
Question 2.
Explain the heterotrophs.
Answer:
Heterotrophs, are those organisms which cannot produce their own food, and which obtain the food provided by the primary producers. As heterotrophs use food produced by autotrophs, they are also called consumers. On the basis of on the process of obtaining food, they can be divided into three types:
- Saprophytic
- Parasitic
- Holozoic
1. Saprophyte:
Saprophyte components survive by obtaining organic compounds derived from plants and animals in liquid form.
2. Parasite:
These components depend on other living organisms for their food and survival.
3. Holozoic:
These component consume food through their mouth. All the major animals, including humans come in this category.
Question 3.
Explain the adverse effects of agricultural activity on the ecosystem.
Answer:
For the solution of the problems arising due to the rapid growth of the population, where humans developed the expansion of agricultural land, chemical fertilizers, advanced varieties of seeds, agricultural implements and equipment, they have adverse effects on the ecosystem, such as human has cleared the forests and grasslands for the expansion of agricultural land, which has an adverse impact on the wildlife, the pastures and the marine ecosystem.
Similarly, using chemical fertilizers and pesticides for more production of food grains has not only made the land unfit for agriculture, but it also has done the work of polluting ground water due to chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Continuous use of ground water for irrigation has led to a decline in the level of ground water, due to which drinking water crisis has arisen in various regions such as Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, etc.
Question 4.
What adverse effects does deforestation have on the ecology?
Answer:
The adverse effect of human activities of uncontrolled deforestation for agriculture, urbanisation and other economic activities can be seen clearly on the ecosystem’s climate, soil, wild life, birds, etc. As a result of deforestation, the climate starts heating up; the amount of rainfall decreases, the erosion of the land starts and the destruction of wildlife occurs.
As a result of uncontrolled harvesting of forests today, in many parts of the world, in which India is also included, many wild life species have become extinct or they are on the verge of extinction. This has made the forest ecosystem imbalanced, because natural vegetation is the main basis of the forest ecosystem.
Question 5.
Explain the role of the key-stone species in the balance of nature.
Answer:
“Key – stone species are such species that affect most ecosystems of a particular region.” Key-stone species provide sustainability to ecosystem and in their absence there are changes in which the nature of ecosystem changes completely and the chances of elimination also remain. Thus the role of Key – stone species in ecosystem is highly significant. Key – stone species mainly include predatory species, and these species have a major impact on ecosystems.
Increase in the number of predators is an indicator that they keep the number of prey species limited by consuming them in the form of food. Due to the lack of predatory species there will be an increase in the number of prey species and due to this situation, the possibility of destruction of all ecosystems will arise. These types of key-stone species determine the number of other species in the community. Elephants and frogs are such keystone species that balance the ecosystem.
RBSE Class 11 Physical Geography Chapter 22 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the structure of the ecosystem.
Answer:
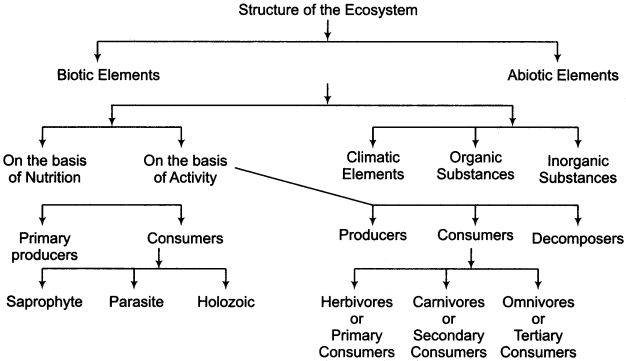
The structure of an ecosystem is the result of the reciprocal interaction of Biotic and Abiotic components of the environment. The structure of a typical ecosystem has been shown by the following table:
The brief description of the nature of all these components is as follows:
Biotic components:
All living organisms of an ecosystem are called Biotic components of that system; all these organisms are connected to each other through various interactions. Biotic components can be classified as follows on the basis of their nutritional potential and functioning:
1. Classification of Biotic components on the basis of nutritional potential:
Biotic components are divided into two categories based on nutritional potential:
(i) Auto – trophic components:
Auto – trophic components, also known as primary producers, obtain food from solar energy through the process of photosynthesis and from the soil through their roots, and provide food to herbivores.
(ii) Heterotrophic components:
These are the Heterogeneous living components which obtain the food provided by the autonomous primary producers. As heterotrophs use food produced by auto – trophs, they are also called consumers.These can be divided into three types depending on the process of consuming food :
(A) Saprophyte:
Saprophytic components survive by obtaining organic compounds derived from plants and animals in liquid form.
(B) Parasite:
These components depend on other living organisms for their food and survival.
(C) Holozoic:
These components feed through their mouth. Most living beings, including humans, come into this category.
2. On the basis of functionality:
Biotic components are divided into three types:
(i) Producers:
Those species which make their own food from solar energy by the process of photosynthesis and from the soil through their roots are included in this, and they are known as primary producers. The plants, animals and humans which depend on these auto – trophs are called secondary producers.
(ii) Consumers:
These are the heterotrophs, which consume food derived from Auto – trophs. These are of three types:
(a) Herbivores or primary consumers:
All organisms receiving food from plants or their products; like various kinds of mollusks in aquatic ecosystem, rabbits, deer, goats, cows, insects.
(b) Carnivorous or secondary consumers:
These kill the herbivores and obtain their food. They are also called secondary consumers. Such as frogs, cat, fox, dog, lion, etc.
(c) Omnivorous or Tertiary Consumers:
In this category, those creatures are included, who get their food by eating plants, herbivores and carnivorous organisms. These include humans, hawks, vultures, fishes, lions, etc. Therefore, they are called tertiary consumers or high class consumers.
(iii) Decomposers:
It consists primarily of micro-organisms and fungi, which decay biological substances including dead plants and animals and decompose them.These organisms rearrange the biotic elements while feeding or their prey in the process of decomposition and make it available for the use of primary producers.
All the components are collectively helpfull in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
Abiotic components:
There are three types of abiotic components:
1. Climatic elements:
such as sunlight, temperature, rainfall, humidity, water vapor, etc.
2. Organic substances:
such as protein, carbohydrate, fat, liquid substances, etc. They are called body – building substances.
3. Inorganic materials:
such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen, carbon, sulphur, calcium, minerals, salts, etc.
These elements play an important role in the cycling of matter in the ecosystem and give strength to the organisms.
Question 2.
Explain the adverse impact of humans on the ecosystem.
Or
How is mankind affecting the ecosystem adversely?
Answer:
Adverse effects of mankind are more significant and pronounced than favorable effects on the ecosystem, due to which environmental problems have become visible in the present time. If these problems are not controlled in time, then one day human life will be eliminated from the earth. The adverse effects of human impact on the ecosystem can be explained under the following heads:
1. Adverse effects of agricultural activity:
In order to expand agricultural land, mankind has not only cleared the forests and grasslands, but it has also made efforts to reclaim land from the ocean, and this has directly and adversely impacted the wild life, pastures and on the oceanic ecosystem.
Similarly, the indiscriminate use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides for more production of food grains has not only made the land unfit for agriculture, but it also has done the work of polluting the ground water by the addition of chemical fertilizers and insecticides. Continuous use of ground water for irrigation has led to a decline in level of ground water, due to which drinking water crisis has arisen in various regions such as Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, etc.
2. Adverse effects of deforestation:
The adverse effects, of uncontrolled deforestation done by mankind for urbanization and various economic activities can be seen clearly on the ecosystem’s climate, soil, wild life, birds, etc. As a result of the deforestation, the climate starts heating up, the amount of rainfall decreases, the erosion of land starts and the destruction of wild life occurs.
As a result of uncontrolled harvesting of forests today, in many parts of the world, in which India is also included, many wild life species are extinct or on the verge of extinction. This has made the forest ecosystem imbalanced, because natural vegetation is the main basis of the forest ecosystem.
3. Adverse effects of mining operations:
Along with industrial and technological progress, the mining process has also increased, but it has created many environmental problems. Under the mining process, the land is dug in a wide area, due tc which huge pits are formed on the ground’s surface and destruction of natural vegetation and creatures of that area results.
Land area of millions of square kilometers becomes unusable. Underground explosions done for mining activity increase the amount of dust particles in the atmosphere, which has direct and adverse effect on the health of its residents. As a result, imbalances in the ecosystem of such areas are created.
4. Adverse effects of industrialization:
Due to industrialization, environmental pollution is increasing. Water and air pollution is increasing due to the industrial units. Various types of toxic gases are being introduced in the atmosphere from these units. Chemical waste and effluents released from industrial units is polluting the rivers and ground water. Ozone layer deplection and phenomenon of acid rain have emerged due to the effect of toxic gases emanating from industrial areas.
5. Adverse effects of climate change:
The process of climate change is taking place due to the process of deforestation, industrialization and invention of nuclear power by humans. Irregularities of rainfall, increase in temperature, ozone depletion, etc. reflects the changes in climate.
6. Adverse effect of natural disasters:
As a result of human activities, natural calamities like flood, drought, famine, landslide, etc. have increased. The construction of large dams on rivers has resulted in an increase in activities such as earthquake. The Koyna dam is considered to be responsible for the earthquake of Later in Maharashtra.
In the 1980’s, due to natural calamities in the world, an average of 2 billion dollars were lost through loss of property, whereas in the 1990’s, this average increased to 12 billion dollars. On December 26, 2004, more than 2 lakh people became victims of tsunami waves. The height of sea level has increased at Andaman Nicobar Coast. It is therefore clear that natural disasters lead to an imbalance in the ecosystem.
Question 3.
Explain the adverse effects of climate change.
Answer:
Climate controls any ecosystem. Since the Industrial Revolution, there is a change in the climate through many actions of human beings, which is also affecting the ecosystem indirectly. The following activities of human beings are considered as important factors responsible for the change of climate:
1. Deforestation:
Mankind is excessively exploiting the forests for its convenience and benefits, which has resulted in irregularity in rainfall and increased temperature.
2. Industrialisation:
Toxic gases emitted from indiustrial units not only pollute the air, but due to their impact, the ozone layer starts to deplete. The ozone layer prevents the ultraviolet and infrared rays coming from the sun to reach the earth and absorbs them before reaching the surface. As a result of the toxic gases, there has been an unprecedented increase in the incidence of skin and respiratory diseases in the world.
3. The invention of nuclear power:
The most devastating scientific invention of humans is the discovery of nuclear bombs, due to which the climate is affected by the underground or oceanic explosions. After the Pokhran blast, abnormal rainfall in the Barmer area is an example of this. Whatever is being done by scientists in the name of development, all that is directly impacting the climate and indirectly impacting the ecological system.
From December 6 to 17, 2004, a climate change meeting held in Buenos Aires did not reach any consensus on the changes in the weather and determining the reasons behind this and the efforts needed to control them. The reason for this is the uncompromising attitude of developed countries such as the United States, the Soviet Union, Italy, etc. Not only that, countries such as Saudi Arabia, Oman and Qatar are also opposed to curbing carbon emissions, because doing so could cause a crisis for their economy.
Today, the behavior of the weather in every country of the world is unusual. It appears as if there is no definite season of rain. There is no fixed place for the snowstorm, because snow fall has taken place in Dubai. There is no definite season for blooming of flowers, when the summer season will stat and what temperature will be reached, it is not possible to determine. The main reason for this unusual behavior of weather is the increase in global temperature.
The Inter – governmental Manual on Climate Change has warned about global warming, that if it is not stopped, there will be a large number of storms and floods, temperature will increase and the number of people killed by Loo and hot storms will also increase. The only way to reduce it is to reduce the emission of greenhouse gases by 50% to 70% from the 1990 level.
In June 2004, the Government of India released the first National Communication Report on climate change. In which for the first time according to this report, an increase of 0.4 degree Celsius in the average temperature in the last 100 years has resulted in an increase in rainfall of 10 – 12% in the west, north – western part of the country and northern Andhra Pradesh.