Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 General Introduction of Partnership Questions and Answers
RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 Textbook Questions
RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 Multiple Choice Questions
RBSE Solutions For Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 Question 1.
In the absence of partnership deed, the interest on loan payable at is :
(a) 6% p.a.
(b) 0.50% p.a.
(c) 5% p.a.
(d) 4% p.a.
Answer:
(a)
General Introduction Of Partnership Question 2.
In the absence of partnership deed, profit sharing ratio is :
(a) in capital ratio
(b) equally
(c) sacrificing ratio
(d) as decided by the partners
Answer:
(b)
RBSE Solutions Accountancy Class 12 Question 3.
Calculate the interest on Ram’s drawings @ 10% if he withdrawn Rs 24,000 during the year.
(a) Rs 1,200
(b) Rs 1,800
(c) Rs 2,400
(d) Rs 1,600
Answer:
(a)
RBSE Solutions For Class 12 Accountancy Question 4.
In absence of partnership deed :
(a) interest on capital is given
(b) interest on drawings discharged
(c) salary is given
(d) provided share in profits
Answer:
(d)
RBSE Solutions Of Class 12 Accountancy Question 5.
In a firm maximum number of partners are :
(a) 2
(b) 10
(c) 20
(d) 50
Answer:
(d)
RBSE Solutions For Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 Question 6.
Partners are not entitled to receive ……… in the absence of partnership agreement.
(a) salaries
(b) interest on capital
(c) fees and commission
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d)
RBSE Solutions For Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 In Hindi Question 7.
The balance of partners’ capital account will reduce with :
(a) interest on capital
(b) interest on drawings
(c) salaries
(d) interest on partners loan
Answer:
(b)
RBSE Solution Class 12 Accountancy Question 8.
Partnership deed is the agreement between the partners in :
(a) oral
(b) written
(c) implied
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b)
RBSE Solutions For Class 12th Accountancy Question 9.
The persons who forms the partnership are individually known as :
(a) firm
(b) partners
(c) sale trader
(d) co-ventures
Answer:
(b)
RBSE Solutions For Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 In Hindi Question 10.
Interest on drawings is …… of firm.
(a) income
(b) expenses
(c) income and expense both
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a)
RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 Very Short Answer Questions
RBSE Solutions For Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 Question 1.
What is the minimum and maximum limit on number of partners in a firm?
Answer.
In a firm minimum number of partner’s can be 02 and maximum number of partner’s can be 50.
RBSE Solutions For Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 Question 2.
What do you understand by partnership firm?
Answer.
Partners are the persons who have agreed to carry on a business and share its profits and losses, partners carrying on the business are collectively known as partnership firm.
RBSE Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Question 3.
What do you mean by profit and loss appropriation account?
Answer.
In which account net profits and losses show distribution amount to partners called profit and loss appropriation account. It is a nominal nature account.
Class 12 RBSE Accounts Solutions Question 4.
Give two circumstances in which fixed capital of partners may change.
Answer.
- Introduced extra capital by partner.
- Withdrawn of capital by partner.
RBSE Solutions For Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 Question 5.
What account are opened?
(a) When the capitals are fixed.
(b) When the capitals are fluctuating.
Answer.
(a) When the capital are fixed:
- Partners capital account,
- Partners current account
(b) When the capitals are fluctuating:
- Partners capital account.
RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Solutions Question 6.
What is meant by unlimited liabilities of partner?
Answer.
Unlimited liabilities of partners means to the legal obligations general partners and sole proprietors because they are liable for all business debts it the business cannot pay its liabilities. In other words, general partners and sole proprietors are responsible for paying off all of the firms debts personally if the firm cannot makes its payments.
RBSE 12 Accounts Solutions Question 7.
State any three items of charges on profits.
Answer.
- Managers commission
- Interest on loan of partner’s
- Rent of building in which business runs.
RBSE 12th Commerce Accountancy Book Solutions Question 8.
State any two points regarding need of partnership.
Answer.
- To remove the problem of ‘limited capital’.
- To remove the risk taking capacity.
Accountancy Class 12 Chapter 1 Question 9.
What items shown on the credit side of fluctuating capital account?
Answer.
- Additional capital brought by partner’s
- Interest on capital
- Salary and commission payable to partners
- Partner’s share in net profit.
Partnership Accounting Questions And Answers Pdf Question 10.
What items shown on the debit side of fluctuating capital account?
Answer.
- Withdrawn of capital by partner.
- Drawing
- Interest on drawing
- Share of loss
RBSE Solutions Class 12 Question 11.
Name any two items which are shown the credit of profit and loss appropriation account.
Answer.
- Interest on drawings
- Partner’s share in net loss.
Final Accounts Without Adjustments Questions And Answers Pdf Question 12.
Name any two items which are shown the debit of profit and loss appropriation account.
Answer.
- Interest on capital
- Salary of partner
RBSE Solutions Class 12 Accountancy Question 13.
Shipra and Shruti are partners in a firm. After preparing the final account, it was found that salary of Rs 2,000 was not given to Shipra. Give journal entry for rectification.
Answer.
P & L Adjustment A/c Dr. 2,000
To Shipra’s Capital A/c 2000
(Salary not given to Shipra now rectified.)
RBSE Solution Class 12th Accountancy Question 14.
The firm of A, B and C earned a profit of Rs 20,000 during the year which was distributed among the partners in the ratio of 2 : 1 : 1, whereas it should be in the ratio of 1 : 2 : 2. Give a journal entry for rectification.
Answer.
A’s Capital A/c Dr. 6,000
To B’s Capital A/c 3,000
To C’s Capital A/c 3,000
(To profit wrongly distributed now rectified.)
RBSE Solutions For Class 12 Commerce Question 15.
Write the names of methods regarding adjustment in closed partnership accounts.
Answer.
- By Single Entry
- By opening Profit and Loss Adjustment A/c
Class 12 Accountancy RBSE Solutions Question 16.
How would you calculate interest on drawings of equal amounts drawn in the middle of every month?
Answer.

RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 Short Answer Questions
RBSE Solutions For Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 Question 1.
Name any two items which are shown the credit of profit and loss appropriation account.
Answer.
Two item which are shown the credit of profit and loss appropriation account are as follows:
- Net profit of current year
- Interest on drawings.
RBSE Solutions 12th Accounts Question 2.
In the absence of partnership deed, what are the rules relating to :
(a) Interest on partners capital
(b) Interest on partners drawings
(c) Interest on partners loan
(d) Partners’ profit sharing ratio
(e) Salaries of partners
Answer.
In the absence of partnership deed the provision affecting of Indian partnership act, 1932 are applicable the important rules are as follows:
(a) Interest on partners capital — No Interest on capital is to be paid
(b) Interest on partners drawings — No Interest on drawing is to be charged
(c) Interest on partners loan — Interest on loan is to be given at 6% per annum
(d) Partners profit sharing ratio — Profit and losses are to be shared equally
(e) Salaries of partners — No salary is payable to partners
RBSE Solutions For Class 12 Accounts Question 3.
Rashmi and Ashish are two partners of a firm. Rashmi withdrawn Rs 1,000 at the beginning of each month. Whereas, Ashish withdrawn Rs 2,000 at the end of each month during the whole year. Interest on drawings is charged @ 12% per annul. Calculate the amount of interest at the end of the year.
Answer.
Total drawings by Rashmi = 100×12 = Rs 12,000
Interest on drawings = 12,000 x \(\frac { 65 }{ 12 }\) x \(\frac { 12 }{ 100 }\) = Rs 780
Total drawings by Ashish=2,000 x 12 = Rs 26,000
Interest on drawings=24,000 x \(\frac { 55 }{ 12 }\) x \(\frac { 12 }{ 100 }\) = Rs 1,320
Accounts Class 12 RBSE Solutions Question 4.
What is meant by guarantee of profit to a partner?
Answer.
Guarantee of Profit to a Partner: Sometimes, a partner is admitted into the firm who is having a specialized knowledge in a particular field, e.g., sales and marketing, professional efficiency of specific type, etc. Such type of partner wants a minimum guaranteed amount as share in the profits of the business from the other partners. Such a guarantee is given either by
(a) one of the old partner or
(b) all the partners in a certain ratio. Such type of guarantee can be given in four ways as follows:
- Guarantee by the firm
- Guarantee by a partner
- Guarantee by a partner to the firm
- Guarantee by a partner to the firm and guarantee by firm to a partner So, it is called guarantee of profit to a partner.
RBSE Accounts Solutions Class 12 Question 5.
For how much period, interest on drawings will be calculated if the equal amounts are drawn for 6 months ending on
- 1st date of every month,
- End of every month,
- Middle of every month?
Answer.
Interest will calculate as follows:
- 1st day of every month: \(\frac { N+1 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { 6+1 }{ 2 }\) = 3.5 month
- Last day of every month: \(\frac { N-1 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { 6-1 }{ 2 }\) = 2.5 month
- Middle day of every month: \(\frac { N }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { 6 }{ 2 }\) = 3 month
RBSE Class 12th Accounts Solution Question 6.
Chandra, Surya and Kiran are partners in a firm, during the year 2017, their drawings were as follows :
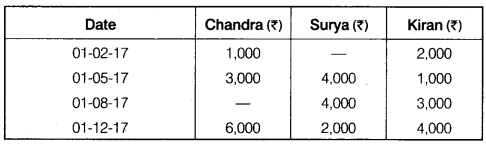
Calculate the interest on drawings @ 6% p.a. for the year ending on 31st December, 2017 by ‘Product Method’.
Solution.
Calculation of Interest of Drawing of Chandra:
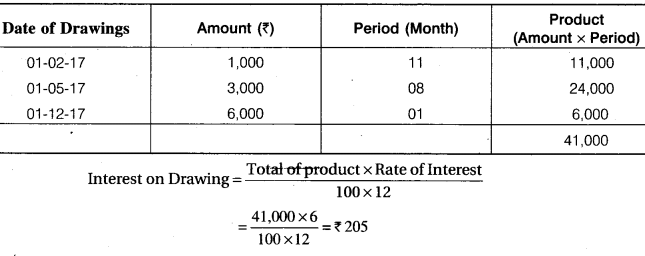
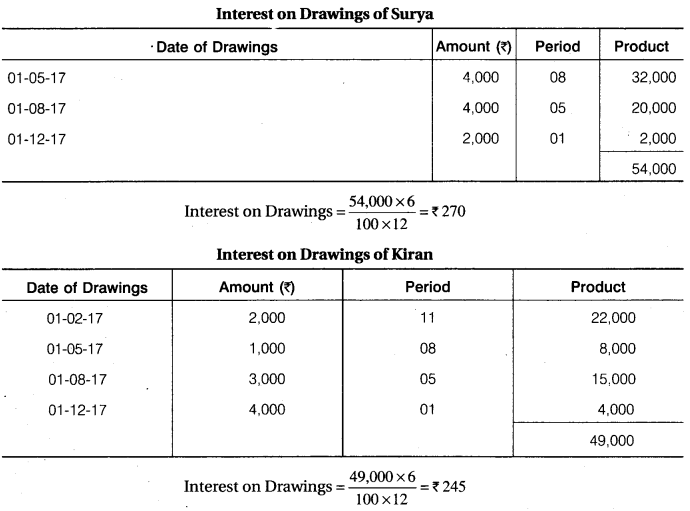
12th Accountancy 1st Chapter Question 7.
Ram, Rahim and Roja are partners sharing profit and loss in the ratio of 3 : 2 : 1. As per partnership deed, Roja’s minimum profit will be Rs 10,000 p.a. The profit for the half year ending on 31st March, 2017 was Rs 24,000. Pass necessary Journal Entries for the distribution of the profit and prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
Solution.
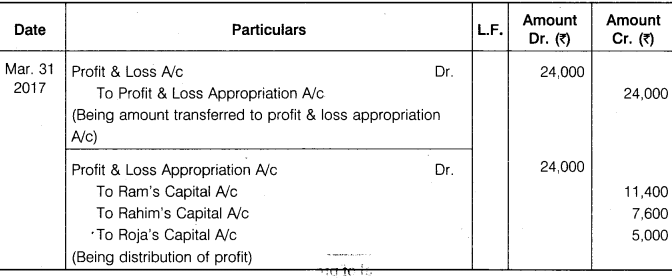
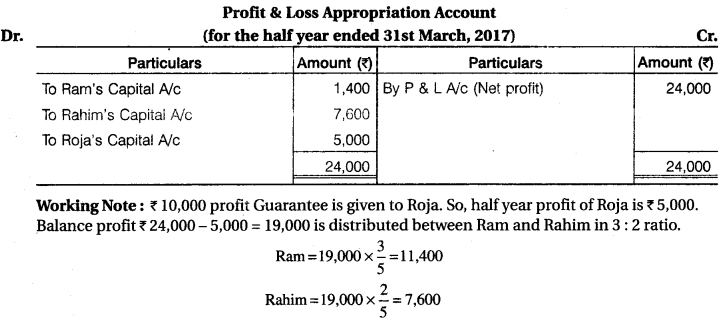
RBSE 12th Accountancy Solution Question 8.
X, Y and Z have capital of Rs 40,000, Rs 30,000 and Rs 20,000. For the year 2016, interest was credited to them @ 12% p.a. instead of @ 10% p.a. with what amount you will pass the adjustment entry.
Solution.
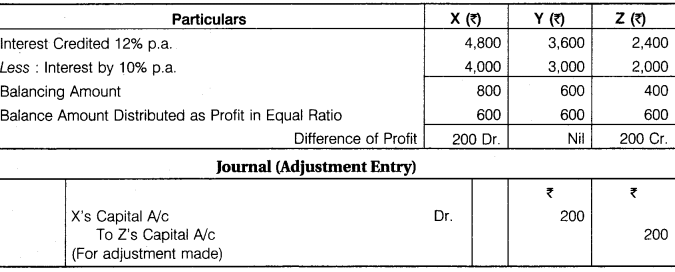
RBSE Solution Class 12 Accountancy Question 9.
X, Y and Z are partners’ sharing profit in ratio 5 : 3 : 2. Z gives guarantee to firm of minimum Rs 1,20,000 earnings but Z could earn only Rs 80,000 for the firm. Total profit earned by the firm is Rs 2,00,000. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account for distribution of profit among partners.
Solution.
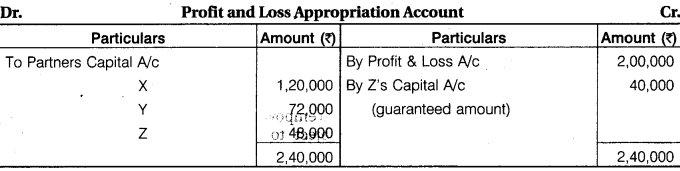
Note : Z’s share of profit should only 48,000 – 40,000 = 8,000. Because his guarantee amount deficiency 1,20,000 – 80,000 = 40,000 is charge from his capital account.
RBSE 12th Accounts Solution Question 10.
P, Q and R are partners, sharing profit in ratio 3 : 2 : 1. It was agreed that
1. R would get minimum profits Rs 3,00,000,
2. Q made guarantee to the firm that he would earn minimum Rs 4,80,000, firm earned Rs 15,20,000 for the current year it included Rs 3,20,000 earned by Q. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account for distribution of profit among partners.
Solution.
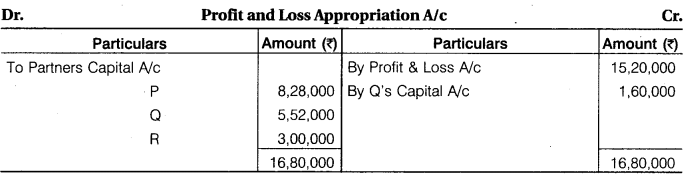
Note:
(1) Q guaranteed to earn minimum Rs 4,80,000. But he earn only Rs 3,20,000. So, balance Rs 1,60,000 is charged from his capital account.
(2) Total profit of firm = 15,20,000 + 1,60,000 = Rs 16,80,000
R guaranteed by firm for 3,00,000 profit. So, Balance profit 16,80,000 – 3,00,000 = Rs 13,80,000 will distributed between P and Q in 3:2 ratio.
RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 Essay Type Questions
12th Accountancy Chapter 1 Question 1.
Define partnership and discuss it’s characteristics.
Answer.
Meaning and Definition of Partnership
As per accounting viewpoint, partnership firm is treated as a separate business entity distinct from its partners. However, as per legal viewpoint, a partnership firm is not a separate legal entity. In other words, it has no existence separate from its partners. It means that in case of bankruptcy of the partnership firm private estates of the partners would be liable to meet the firm’s debts. Partnership is an association of two or more persons who have agreed to share profits or losses of a business in certain proportion.
According to Section (4) of the Indian Partnership Act, 1932, “Partnership is the relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all or any one of them acting for all.” The persons who have established the business are individually called Partners and collectively a firm.
Characteristics of Partnership
The essential characteristics of partnership are:
1. Two or More than Two Persons: There must be atleast two persons to form a partnership and all such persons must be competent to contract. According to Indian Act, 1872, every person except the following is competent to contract:
- Minor
- Persons of unsound mind
- Persons disqualified by any law.
Section 464 of the Companies Act, 2013 empowers the government to prescribe maximum numbers of partners in a firm subject to be 50 wide rule 10 of the Companies (Miscellaneous) Rules, 2014.
2. Agreement Among Partners: Partnership is the result of an agreement. It must come into existence by an agreement and not by the operation of law. On the contrary, a Hindu undivided family comes into existence by the operation of law and not by an agreement. Such an agreement can be either oral or in written. The agreement forms the basis of mutual rights and duties of partners.
3. Sharing of Profit: The agreement between/among the partners must be to share profits or losses of the business. It is not essential the all the partners must share losses also. There may be a provision in the partnership deed that a particular partner or partners shall not bear the losses.
4. Carrying of Business: Agreement among partners should be for carrying on of a business the purpose of which should be to share profits. To be a co-owner of a property is not a partnership.
5. Business Carried on by All or Any one of them Acting for All: It means that each partner can participate in the conduct of business and each partner is bound by the the acts of other partners in respect to the business of the firm.
6. Responsibility of Partners: Every partner is liable jointly and separately for all the acts of the firm. The liability of all partners cannot limited.
7. Relationship of Principal and Agent: Each partner is an agent as well as a partner of the firm. An agent, because he can bind the other partners by his acts and a principal because he himself can be bound by the acts of the other partners.
8. Mutual Agency : The business of a partnership concern may be carried on by all the partners or any one of them acting for all. This statement has two important implications. First, every partner is entitled to participate in the conduct of the affairs of its business. Second, that there exists a relationship of mutual agency between all the partners. Each partner carrying on the business is the principal as well as the agent for all the other partners. He can bind other partners by his acts and also is bound by the acts of other partners with regard to business of the firm. Relationship of mutual agency is so important that can one say that there would be no partnership if the element of mutual agency is absent.
9. Unlimited Liabilities: In partnership each partner has unlimited liabilities.
10. No separate Existence: There is no separate existence of partners from partnership. So, all agreements of the firm/related to the firm apply on the firm as well as on each partner individually or collectively
RBSE Class 12 Accounts Solution Question 2.
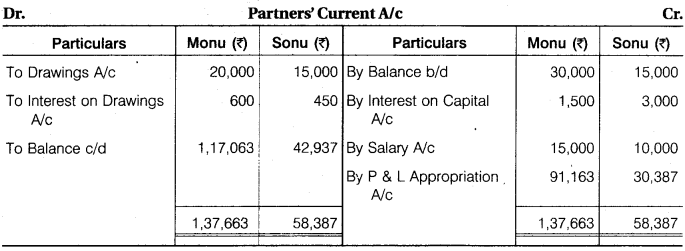
What do you mean by fixed and fluctuating capital accounts? Point out the differences between the fixed and fluctuation capital accounts. Prepare partners’ current account by using imaginary figures.
Answer.
Partners Capital Account
1. Fixed Capital Account Method : Fixed capital means capital of the partners are fixed. When fixed capital account method is followed, two accounts i.e., a capital account and a current account for each partner are maintained.
Capital Account : Fixed capital means that the capital remains unaltered i.e., fixed unless additional capital is introduced or withdrawal is made from the existing capital. Thus, if fresh capital is not introduced or capital is not withdrawn, capital account of a partner will continue to show same balance year after years.
Current Account: Current account is maintained to record transactions other than introduction and withdrawal of capital, such as interest on capital, interest on drawings, salary or commission to a partner, share of profits/losses. As a result, the balance of current account fluctuates with every transaction with the partner.
Current account of each partner is debited with:
(a) Drawings made by him
(b) Interest on drawings
(c) Share of loss
(d) Transfer of any amount to capital account permanently.
Similarly, current account of each partner is credited with:
(a) Interest on capital
(b) Salary or commission
(c) Share of profit
(d) Transfer of any amount from capital account permanently.
Normally, partners’ current account has a credit balance but if a partner has drawn more than his or her share of the profits, then it will have a debit balance.
The balances of the partners capital account are shown on the liabilities side of the balance sheet, as that much amount is due on them.
Credit balance in current account is shown on the liabilities side and debit balance on the assets side of balance sheet.
2. Fluctuating Capital Account Method : Under fluctuating capital account method, only one account namely “Capital Account” is maintained for each partner.
All transactions of a partner (e.g., salary or commission, interest allowed on capital, drawings, interest charged on drawings, share of profit or share of loss etc.) are recorded in his capital account. As a result, balances in the capital account fluctuates with every transaction.
Capital account having credit balances are shown on the liabilities side while capital accounts having debit balances are shown on the assets side of the balance sheet, Fluctuating capital method is normally followed for maintaining capital accounts and therefore, in the absence of any instruction, this method should be followed for maintaining the partners’ capital account.
Difference between Fixed Capital Account & Fluctuating Capital Account Method
| Basis | Fixed Capital Account | Fluctuating Capital Account |
| Change in capital | When the capitals are fixed, the balances in capital accounts usually remain unchanged during the life time of business except when capital is introduced or withdrawn permanently. | When the capitals are fluctuating, the balances in capital accounts go on changing from time to time. |
| Number of Accounts | When the capitals are fixed each partner has two accounts namely, capital account and a current account. | When the capitals are fluctuating each partner has only one account namely capital account. |
| Recording of Transactions | When the capitals are fixed transactions relating to drawings, interest on capital, interest on drawings, salary, share of profit or loss etc., are not made in capital accounts but are entered in separate current account. | In this case all transactions relating to partners are made directly in the capital accounts itself. |
| Can a capital account show a negative balance | Fixed capital account can never show a negative balance. | Fluctuating capital account can show a negative balance. |
Class 12th RBSE Accounts Solution Question 3.
What is partnership deed? What points are included in it from accounting point of view?
Answer.
Partnership Deed: Since partnership is the outcome of an agreement, it is essential that there must be some terms and conditions agreed upon by all the partners. Such terms and conditions may be either oral or written. The law does make it compulsory to have a written agreement. However, in order to avoid all misunderstandings and disputes, it is always the best course to have a written agreement duly signed and registered under the act. Such a written document which contains the terms of agreement is called “Partnership Deed”. It is also called “Articles of Partnership”. The partnership deed should contain the following points :
- The name and address of the firm
- Name and address of the partners
- The type and nature of the business the firm proposes to do
- Amount of capital to be contributed by each partner
- Interest on capital
- Amount of drawings
- Interest on drawings
- Profit sharing ratio
- Salary commission, bonus of the partner
- Goodwill
- Accounting period of firm
- Method of recording of firm’s accounts
- Auditing
- Date of commencement of partnership
- Duration of partnership
- Bank accounts operation
- Rules to be followed in case of admission of a partner
- Rules to be followed while settling the accounts on retirement
- Settlement of disputes
- Death of a partner
- Methods and conditions of dissolution of the firm
- Use of the decision of Garner vs. Murray.
12th RBSE Accountancy Solutions Question 4.
Describe various types of partnership.
Answer.
Types of Partnership
1. Limited and Unlimited Partnership: When liability of a partner is limited to the extent of his contribution in the firm, it is called Limited Partnership. On the other hand, when all the partners of the firm are individually and collectively responsible for discharging the liabilities of the firm then it is called Unlimited Partnership.
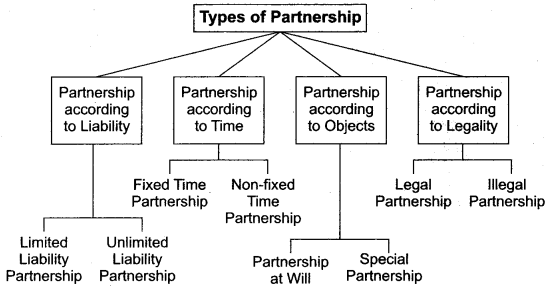
2. Fixed Time Partnership and Non-fixed Time Partnership: When a partnership is formed for some specific period, for example; for 2 years, 5 years or so on, it is called Fixed Period Partnership. In this case, the partnership is dissolved as soon as that specific period expires. When no period is fixed for partnership, it is called Non-fixed Time Partnership.
3. Partnership at Will and Special Partnership : When a partnership is formed to carry on business for an uncertain period, it is called Partnership at Will. Such partnership may be dissolved with the consent of all the partner or by any one partner giving notice for dissolution.
When a partnership is formed for a specific purpose or specific work, it is called Specific or Special Partnership. The partnership under this case the partnership, is automatically dissolved as soon as the work is completed. For example, to undertake construction of road, dam, bridge etc.
4. Legal and Illegal Partnership : Although, registration of a partnership is not compulsory yet is has to carry on its business as per the Provisions of Partnership Act. For example; minimum number of partners must be 2 and maximum number 50 in a firm. When a partnership firm carries on its business in accordance with the provisions of the act, it is called Legal Partnership.
On the other hand, the partnership is called Illegal in the following cases:
- When number of partners exceed 50 in a firm.
- When the object of partnership is illegal.
- When the business of partnership is against the public code of conduct.
- When any one or more than one partner belongs to enemy country.
12th Commerce Account Chapter 1 Question 5.
What do you mean by guarantee of profit to a partner? Explain the two types of such guarantee.
Answer.
Sometimes a partner is admitted into the fifth Who is having a specialized knowledge in a particular field, e.g., sales and marketing, professional efficiency of specific type, etc. Such type of partner wants a minimum guaranteed amount as share in the profits of the business from the other partners. Such a guarantee is given either by (a) one of the old partner or (b) all the partners in a certain ratio. Such type of guarantee can be given in four ways as follows:
(i) Guarantee by the firm
(ii) Guarantee by a partner
(iii) Guarantee by a partner to the firm
(iv) Guarantee by a partner to the firm and guarantee by firm to a partner
(i) Guarantee by the Firm: This situation arises when profit of the firm is not adequate or in case of loss, therefore, the payment of minimum guarantee profit is not possible to the partner who has been given such a guarantee. In such situation, minimum guaranteed amount or any shortfall in it would be borne by remaining partners. However, in case his share in profits is over and above the guaranteed amount, he would get share in profit as per profit ratio agreed among partners at the time of his admission.
(ii) Guarantee by a Partner: First of all distributable profits of the firm will be distributed to the partners in their profit sharing ratio. Afterwards, if there is any share shortfall in the guaranteed amount, the required profit would be adjusted by deducting from the share of profit of the partner who has given such guarantee. The same adjusted amount would be added in the share of guaranteed partner.
RBSE Solution Class 12 Accounts Question 6.
How would you adjust the omission disclosed after closing the partnership accounts?
Answer.
Adjustment in Closed Partnership Accounts : Sometimes partnership accounts are closed without taking care of conditions given in the partnership deed in respect of interest on capital, interest on drawings, partners’ salary, commission, interest on loan, etc. Similarly, sometimes partners’ decide some new arrangements in respect of aforesaid adjustments or profit sharing ratio applicable with retrospective effect after close of partnership accounts. Under such circumstances, rectification may be done.
- By means of one adjustment entry or
- By means of profit and loss adjustment account.
1. By One Adjustment Entry
- An analysis table is prepared in which the names of all the partners are horizontally written with debit and credit, two columns for every partner.
- The amount payable to partners are written in credit columns of partners and anything chargeable are written in debit columns. Similarly, one column of the firm is also drawn with debit and credit columns.
- Thereafter, debit and credit columns of every partner is totaled. The amount of difference is ascertained if the firm’s debit and credit columns, which will reveal either profit or loss.
- The amount of profit or loss will be divided among the partners in profit sharing ratio. Lastly every partner’s debit and credit columns are totaled and difference is ascertained, then one entry will be passed at the beginning of next accounting year by debiting or crediting partners’ current account or capital account, as the case may be.
2. By Opening Profit and Loss Adjustment Account
This account is a nominal account. In case of loss to the firm, this account is debited and partners capital or current account credited. In case of profit to the firm, reverse entry is passed
- With the amount of interest on capital, salary, bonus and commission to partners
Profit and Loss Adjustment A/c Dr.
To Partners Capital/Current A/c - With the amount of interest on drawings
Partners’ Capital/Current A/c Dr.
To Profit and Loss Adjustment A/c - Then prepare profit and loss adjustment account and balance will be transferred to partners capital/current account in profit sharing ratio.
(a) If debit balance
Partners’Capital A/c Dr.
To Profit and Loss Adjustment A/c
(b) If credit balance
Profit and Loss Adjustment A/c Dr.
To Partners’ Capital A/c
(Reverse the above entry.)
RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 Numerical Questions
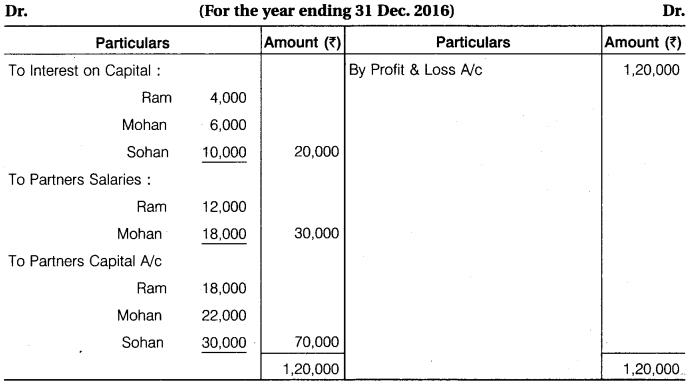
RBSE Solution Class 12th Commerce Accountancy Question 1.
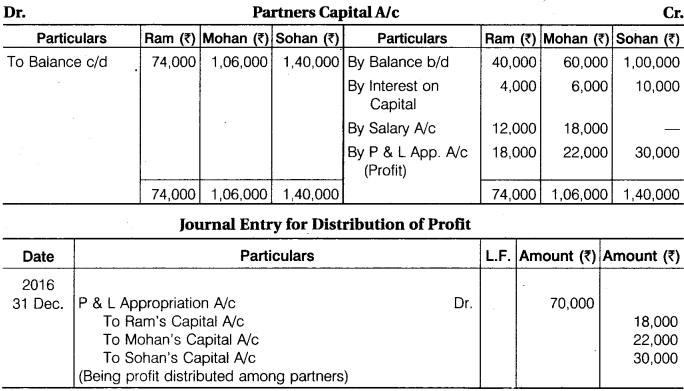
Ram, Mohan and Sohan were partners. Their capital on 1st January, 2016 were Rs 40,000, Rs 60,000 and Rs 1,00,000 respectively. Before division of profit, Ram is entitled for salary of Rs 12,000 and Mohan Rs 18,000 per annum. Interest is allowed on capital @ 10% per annum. Out of net divisible profits, first Rs 40,000 will be divided in their capital ratio and the balance of profits is to be divided equally. The profit of the firm for the year ending on 31st December, 2016 amounted to Rs 1,20,000 before making all the above adjustments. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account and Partners’ Capital Account on 31st December, 2016 and pass a Journal Entry for distribution of profit.
Solution.
Profit and Loss Appropriation A/c
RBSE Solutions For Class 12 Question 2.
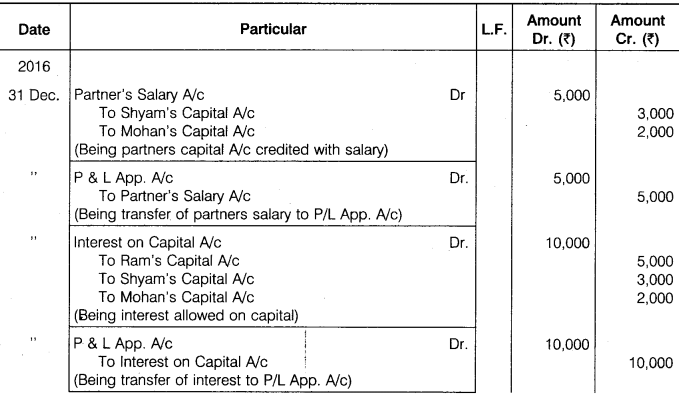
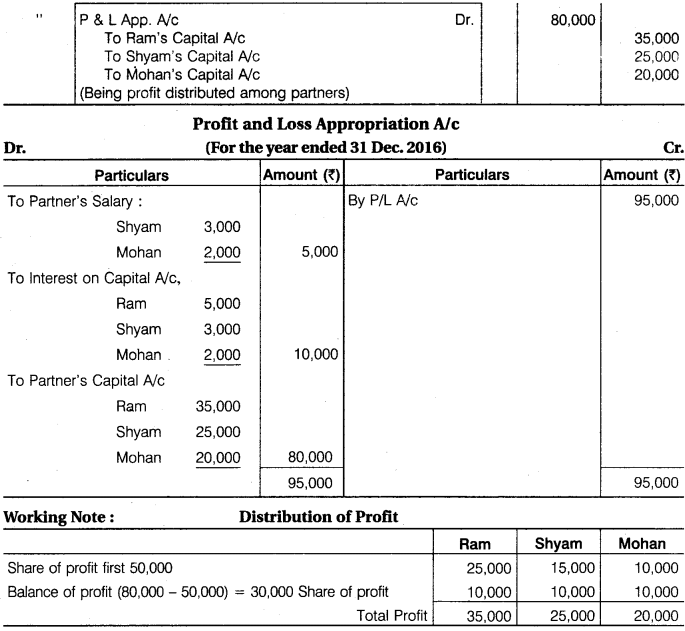
Ram, Shyam and Mohan were partners, their capital on 1st January, 2016 were Rs 50,000, Rs 30,000 and Rs 20,000 respectively. Before division of profit, Shyam is entitled for salary of Rs 3,000 and Mohan Rs 2,000 per annum. Interest is allowed on capital @ 10% per annum. Out of net divisible profits, first Rs 50,000 will be divided in their capital ratio and the balance of profits is to be divided equally. The profit of the firm for the year ending on 31st December, 2016 amounted to Rs 95,000 before making all the above adjustments.
Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account and give Journal Entries.
Solution.
Journal Entries
12 Commerce Account Chapter 1 Question 3.
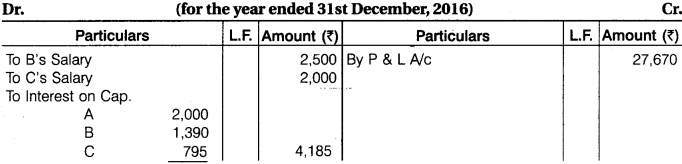
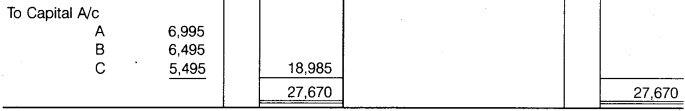
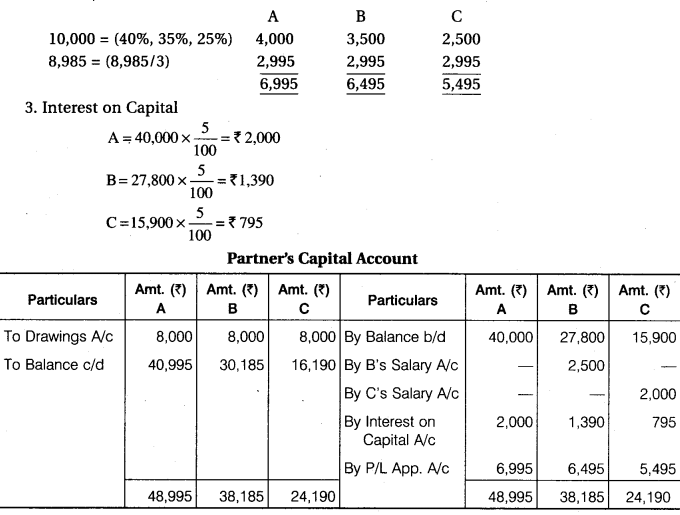
A, B and C were partners, their capital as on 1st January, 2016 was Rs 40,000, Rs 27,800 and Rs 15,900 respectively. Before division of profit, B is entitled for salary of Rs 2,500 and C for Rs 2,000 per annum. Interest is allowed on capital @ 5% per annum. Out of net divisible profits, first Rs 10,000, A will receive 40%, B 35% and C 25%. Profits in excesses to that are shared equally. For the year ending on 31st December, 2016 after debiting salary but before charging interest the profits were Rs 23,170. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
Solution.
Profit and Loss Appropriation Account
Working Note:
1. Profit shown in the question is after deducted of salary. Before deduction of salary, profit will be 23,170 + 2,500 + 2,000 = Rs 27,670.
2. First of all interest on capital will charge from profit after that Balance of Profit 23,170 – 4,185 = 18,985 will distributed among partners. Within 18,985, Rs 10,000 will distributed 40%, 35% and 25% and Balance of Profit 18,985 -10,000 = Rs 8,985 will distributed equally. Hence,
Introduction To Partnership Class 12 Question 4.
P and S started a partnership firm on 1st January, 2016 with a capital of Rs 1,000, Rs 10,000 respectively. On 1st March, 2016, P introduced additional capital of Rs 4,000. On that day S withdrawn Rs 3,000 from his capital. C entered in the firm on 1st July, 2016 with a capital of Rs 15,000. On that day P and S introduced additional capital of Rs 6,000 and Rs 5,000 respectively. Profit-Loss are distributed in capital ratio. The profit for the year 2016 was Rs 29,800. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account by giving detailed calculations.
Solution.
Profit and Loss Appropriation A/c (31 Dec. 2016)
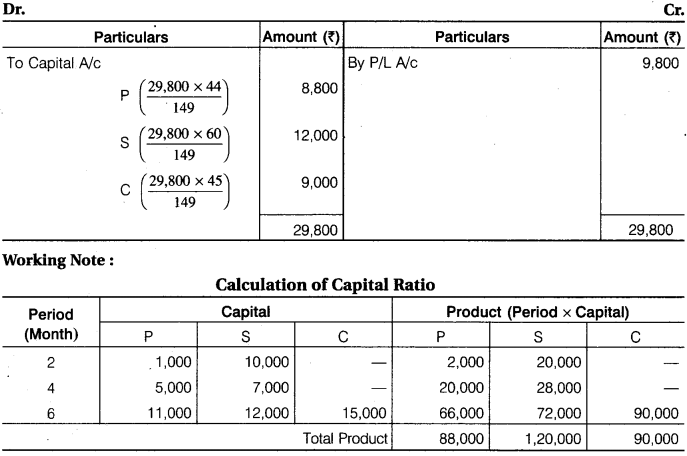
Ratio of Profit = 88,000 : 1,20,000 : 90,000 = 44 : 60 : 45
12th Accountancy Chapter 1 Exercise Sums Question 5.
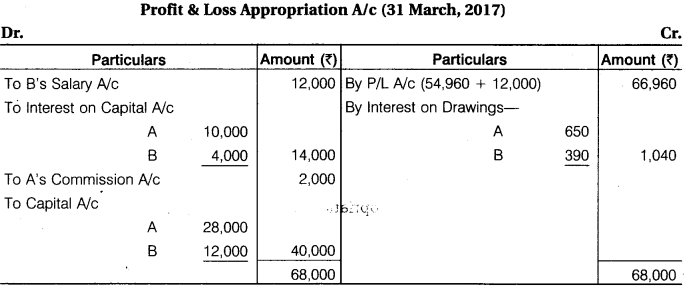
A and B were partners sharing profits in the ratio of 7 : 3. On 1st April, 2016, their capitals were Rs 1,00,000, Rs 40,000 respectively. Interest is to be charged on capital and drawings at 10% per annum. B is to be allowed salary Rs 1,000 per month. A and B withdrawn Rs 1,000 and Rs 600 per month respectively on the first day of every month. The profits for the year, prior to calculation of interest on capitals and drawings, but after charging B’s salary, amounted to Rs 54,960. A provision for A’s commission at 5% on net profit (after charging such commission) is to be made. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account for the year ending 31st March, 2017.
Solution.
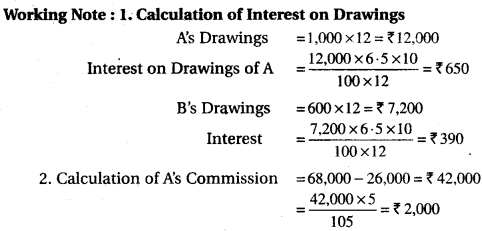
12th Accountancy RBSE Solutions Question 6.
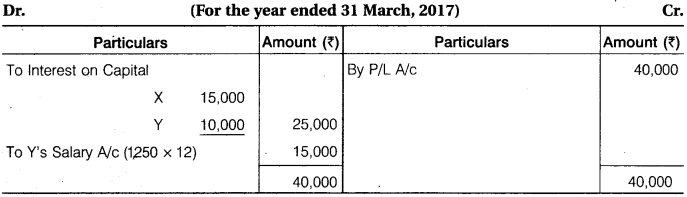
X and Y were partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2. On 1st April, 2016, their capital were Rs 3,00,000 and Rs 2,00,000 respectively. The partnership deed provided interest on capital @ 10% p.a. and salary to Y as Rs 1,250 p.m. The net profit before providing interest on capital and salary amounts to Rs 40,000 for the year ended 31st March, 2017. Show the distribution of profit for the year.
Solution.
P/L Appropriation A/c
Question 7.
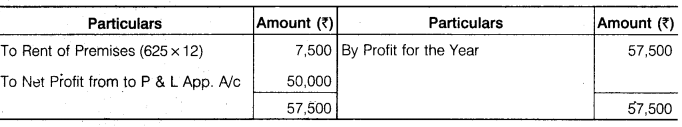
Ruchi and Prashant were partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 1. On 1st April, 2016, their capitals were Rs 50,000 and Rs 40,000 respectively. During the year ended 31st March, 2017, the profit of the firm amounted to Rs 57,500 before taking into consideration the following :
1. Interest on capital is to be allowed @ 5% p.a.
2. Ruchi will get commission of 2% on sales. Sales for the year were Rs 1,25,000.
3. Prashant will get a salary of Rs 250 p.m.
4. Prashant is entitled to a rent of Rs 625 per month for the use of his premises by the firm.
5. 10% of the divisible profit is to be transferred to general reserve. You are required to prepare the Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
Solution.
P & L A/c
(31st March, 2017)
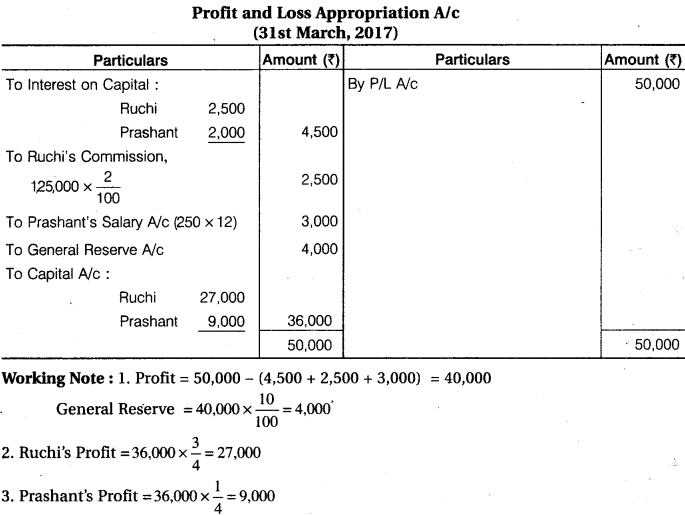
Question 8.
A, B and C are partners, sharing profit and loss in 3 : 2 : 1 ratio. A withdrawn Rs 2,000 at the beginning of every month, B withdrawn Rs 1,500 in the middle of every month, whereas C withdrawn Rs 1,000 at the end of every month. Interest on capital and drawings is to be charged @ 10% p.a. C is also to be allowed a salary of Rs 800 per month. After deducting salary but before allowing all types of interest, the profit for the year ending 31st December, 2016 was Rs 1,22,150. Prepare Profit and Loss Account and Capital Account and Current Account to the Partners from the additional information given below :
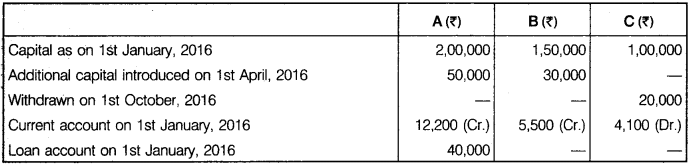
Solution.
Profit & Loss App. A/c
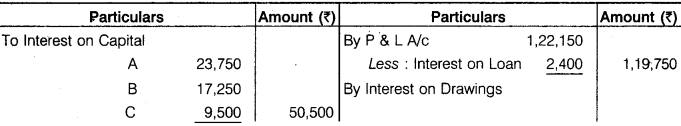
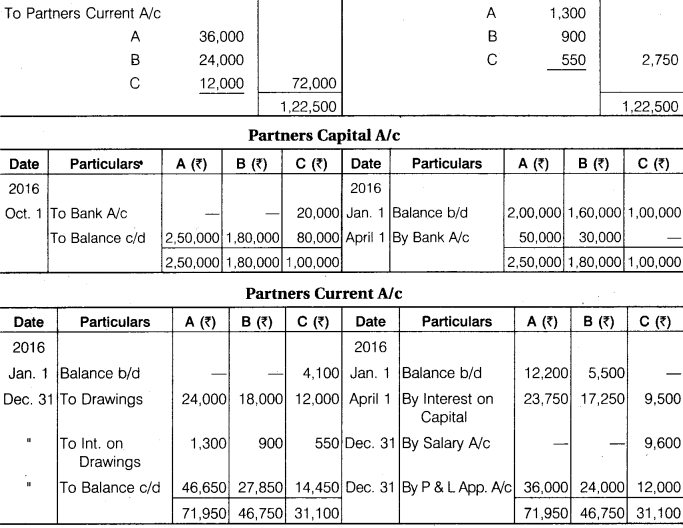
Question 9.
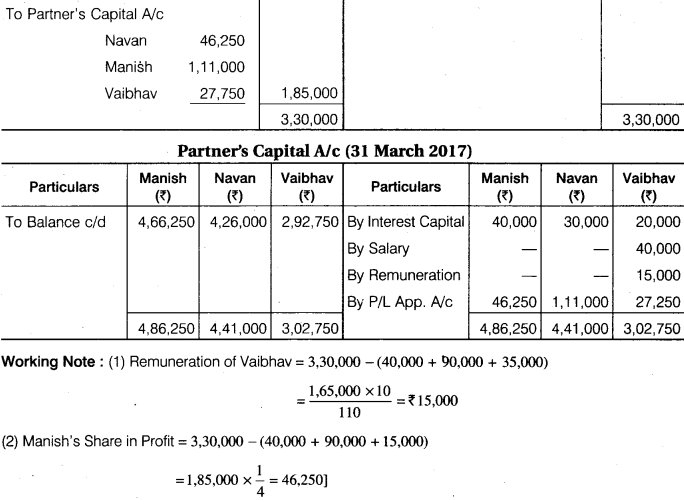
Manish, Navan and Vaibhav are partners in a firm, balance of their capital account as on 1st April, 2016 were Rs 4,00,000, Rs 3,00,000 and Rs 2,00,000 respectively. The partnership agreement provides – A. Vaibhav shall be credited for Rs 40,000 of salary per annum. B. After providing Vaibhav salary, 10% p.a. interest on capital to all partners and extra remuneration to Vaibhav as provided in this paragraph ‘B’, Vaibhav shall be entitled to 10% of all profits in excess of Rs 35,000 p.a. C. Navan is to have one-third of the profits after charging all amount under ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’. D. The balance is to be divided between Manish and Vaibhav in the ratio 4 : 1. The profits for the year ended 31st March, 2017 (before making any provision for the above) was Rs 3,30,000. You have to prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account and Partners’ Capital Account for the year ending 31st March, 2017. During the year Manish, Navan and Vaibhav withdrawn the amount for personal use Rs 20,000, Rs 15,000 and Rs 10,000 respectively.
Solution.
P & L Appropriation A/c (31 March 2017)
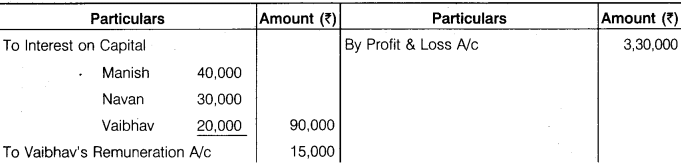
Question 10.
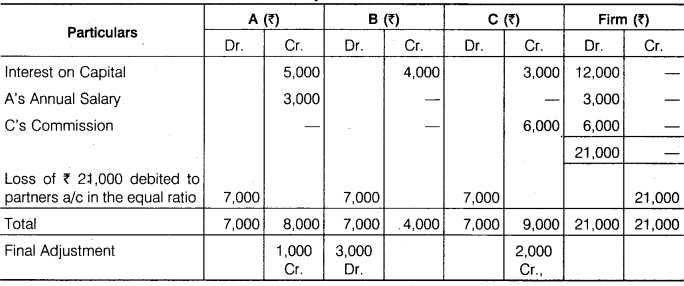
A, B and C are equal partners in a firm. Their capitals on 1st January, 2016 were Rs 50,000, Rs 40,000 and Rs 30,000 respectively. After closing the accounts of the year 2016, it was found that according to the partnership agreement interest at 10% per annum on partners capital, a salary of Rs 3,000 per year to A and a commission of Rs 6,000 to C were not provided before distribution of profits. It was agreed among the partners to make the adjustment entry at the beginning of the next year rather than to alter the balance sheet. Pass one Journal Entry in the books of the firm showing the working of adjustment assuming that capitals are fixed.
Solution.
Analytical Table
Adjustment Entry
B’s Current A/c Dr. 3,000
To A’s Current A/c 1,000
To C’s Current A/c 2,000
(Adjustment of partners A/c made)
Question 11.
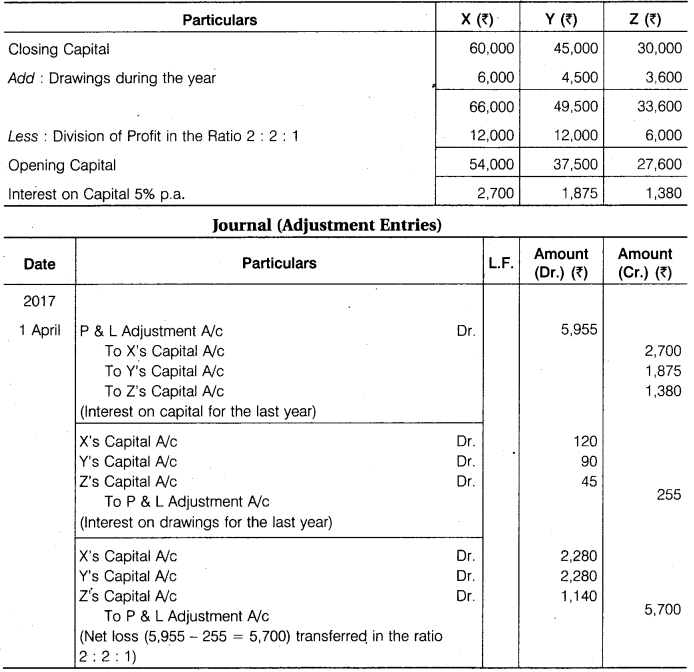
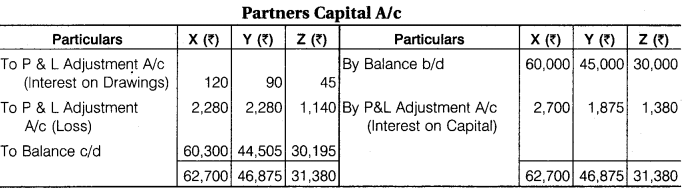
X, Y and Z are partners in a firm, sharing profit and loss in the ratio of 2 : 2 : 1. On 31st March, 2017 after recording drawings and distribution of profits Rs 30,000, their capitals were Rs 60,000, Rs 45,000 and Rs 30,000 respectively. After this it was found that 5% interest on capital and interest on drawings was omitted to be recorded. Drawings were as follows : X Rs 6,000, Y Rs 4,500 and Z Rs 3,600. Interest on which is to be charged Rs 120, Rs 90 and Rs 45 respectively. Pass necessary Journal Entries for the above omissions and prepare Adjusted Partners’ Capital Account.
Solution.
Calculation of Opening Capital
Question 12.
P, Q and R partners in a firm. Their capital accounts stood at Rs 90,000 Rs 45,000 and Rs 45,000 respectively on 31st March, 2017.
1. R was to be allowed a remuneration of Rs 9,000 p.a.
2. Interest at 5% p.a. was to be provided on capitals.
3. Profits were to be divided in the ratio of 2 : 2 : 1. Ignoring the above items, net profit of Rs 54,000 for the year ended 31.03.2017. It was divided among the three partners equally. Make Journal Entry for rectification and show workings.
Solution.
Analytical Table
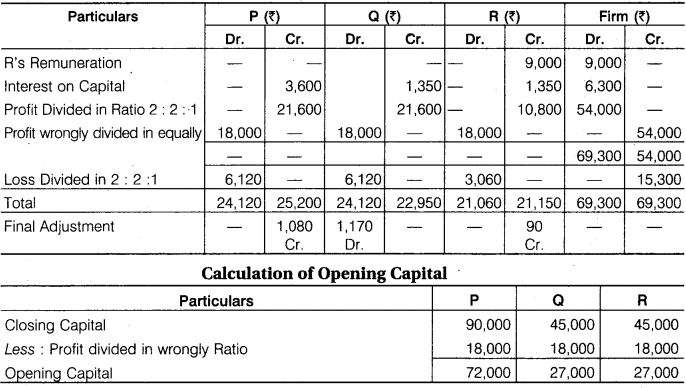
Adjustment Entry
Q’s Capital A/c Dr. 1,170
To P’s Capital A/c 1,080
To R’s Capital A/c 90
(Adjustment of partners A/c made)
Question 13.
Satish, Nitin and Ajay are partners with a fixed capital Rs 1,00,000, Rs 75,000 and Rs 75,000 respectively. Their current account balances were Satish Rs 5,000 (Cr.), Nitin Rs 4,000 (Cr.) and Ajay Rs 2,500 (Dr.). The partnership deed provided as under :
1. Interest on capital @ 5% p.a.
2. Nitin was entitled for rent @ Rs 500 p.m. for providing his premises to the firm.
3. Ajay was entitled to a salary of Rs 1,000 p.m.
The profits of the firm were to be distributed as follows :
A. The first Rs 20,000 in proportion to their capital.
B. Next Rs 20,000 in the ratio 2:2:1.
C. Remaining profits to be shared equally.
The net profit before the above adjustments for the year was Rs 85,500. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account, Capital Account and Current Account of the partners.
Solution.
Profit and Loss A/c
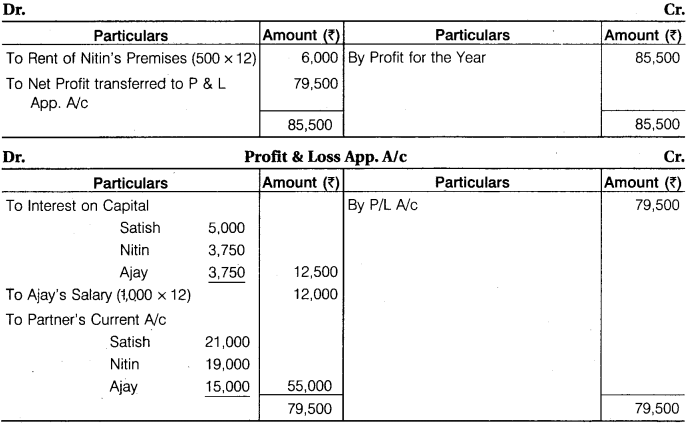
Working Note: Calculation of Profit:
Profit for Distribution = 79,500 – (12,500 + 12,000) = Rs 55,000
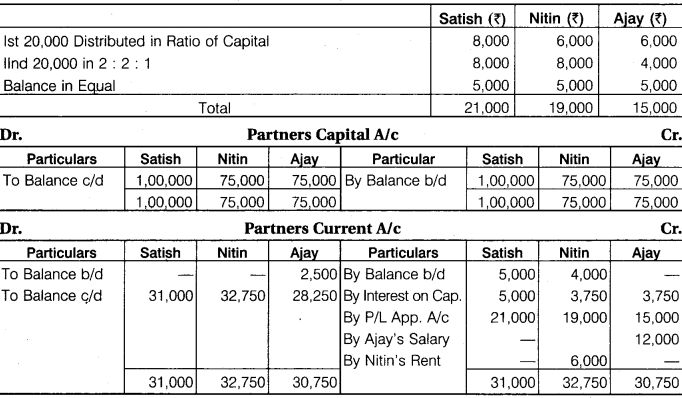
Question 14.
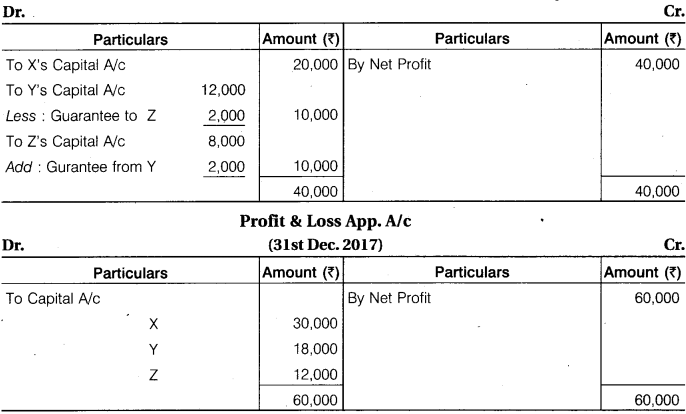
X, Y and Z are partners in a firm. Their profit sharing ratio is 5 : 3 : 2. However, Z is guaranteed a minimum amount of Rs 10,000 as share of profit every year. Any deficiency arising on that account shall be met by Y. The profit for the two years ending 31st December, 2016 and 2017 were Rs 40,000 and Rs 60,000 respectively. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account for the two years.
Solution.
Profit & Loss App. A/c (31st Dec. 2016)