Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 6 Introduction of Financial Statement of Company
RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 6 Textbook Questions
RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Financial statements are prepared at the time of:
(a) inception of business
(b) end of accounting year
(c) winding up of business
(d) None of these
Answer:
b
Question 2.
The statement which depicts the financial position of a company :
(a) balance sheet
(b) cash flow statement
(c) statement of profit and loss
(d) statement of changes in equity
Answer:
a
![]()
Question 3.
For which of the following company, it is necessary to prepare cash flow statement?
(a) inactive company
(b) public company
(c) one person company
(d) small company
Answer:
b
Question 4.
Owners of the company are :
(a) shareholders
(b) loan providers
(c) creditors
(d) all of these
Answer:
a
Question 5.
Financial statements are useful for :
(a) employees
(b) managers
(c) shareholders
(d) all of these
Answer:
d
Question 6.
For a company financial year ends :
(a) on 30 June
(b) on 30 September
(c) on 31 December
(d) on 31 March
Answer:
d
![]()
Question 7.
General reserves will be shown under which head of the Balance Sheet?
(a) Short Term Provisions
(b) Share Capital
(c) Miscellaneous Expenses
(d) Reserves and Surplus
Answer:
d
Question 8.
Number of main heads under ‘Equity and Liabilities’ part of Balance Sheet of a company is :
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
d
Question 9.
When accounting income exceeds taxable income, it leads to :
(a) deferred tax liability
(b) deferred tax assets
(c) long term loan
(d) None of these
Answer:
a
Question 10.
Which of the following is not employee benefits expenses?
(a) salary
(b) provident fund contribution
(c) repairs of factory machine
(d) payment of gratuity
Answer:
c
RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 6 Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by financial statements?
Answer.
Financial statements are the end products of accounting process. They provide information about the probability and financial
position of a business.
Question 2.
Name the two financial statements prepared by a company.
Answer.
- Balance sheet
- Profit and Loss statement.
![]()
Question 3.
Write the name of the major heads of the assets of the balance sheet of a company.
Answer.
- Non Current Assets
- Current Assets
Question 4.
Why are financial statements called as historical document?
Answer.
Financial statement called as a historical document because they related past period information.
Question 5.
What is operating cycle?
Answer.
An operating cycle is the time between the acquisition of assets for processing and their realization in cash or cash equivalents. Where the normal operating cycle cannot be identified it is assumed to have a duration of 12 months.
Question 6.
Define trade payables.
Answer.
A payable shall be classified as a “Trade payable” if it is in respect to the amount due on account of goods purchase as service received in the normal course of business. It include both ‘Sundry creditors’ and bills payable.
Question 7.
What is meant by statement of profit and loss ?
Answer.
By which statement in selected period calculate the net profit and loss and know that processing of a business is going well or not thats called profit and loss statement.
![]()
Question 8.
What is meant by current liabilities?
Answer.
Current Liabilities: Current liabilities are those liabilities which are:
(a) expected to be settled in company’s normal operating cycle.
(b) due to the settled within 12 months after the reporting date.
(c) held primarily for the purpose of being trade.
(d) there is no unconditional right to defer settlement for at least 12 months after the reporting date.
Question 9.
How are calls-in-arrears shown in balance sheet?
Answer.
Calls in arrears are shown in balance sheet by deducting in subscribed capital.
Question 10.
What is meant by ‘share application money, pending allotment’?
Answer.
Such amount received by the company on share application but not yet allotted share at the date of preparation of balance sheet so its called ‘share application money pending allotment.
RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 6 Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Which statement are included in the financial statements under Section 2(40) of the Companies Act, 2013?
Answer.
As per Section 2 (40) of the Companies Act, 2013, “Financial Statements” in relation to a company include the following:
- A balance sheet as at the end of the financial year
- A statement of profit and loss for the financial year
- Cash flow statement for the financial year
- A statement of changes in equity, if applicable, and
- Explanatory notes.
Question 2.
Write main characteristics of financial statements.
Answer.
Characteristics of Financial Statements:
- Financial statements are related to past period and hence are historical documents.
- They are expressed in terms of money.
- Financial statements show profitability through statement of profit and loss and financial position through balance sheet.
![]()
Question 3.
Write four objectives of financial statements.
Answer.
Four objectives of financial statements are as follows :
- To available financial data of assets and liabilities of a company.
- To present a true and fair view of the financial performance of the business.
- To assist to make a future plan, decision and activities.
- To present company’s future guess to earn profit, comparison and evaluation by balance sheet. Profit and loss statement and financial activities.
Question 4.
What is meant by current assets ?
Answer.
Current Assets : An asset shall be classified as current when it satisfies any of the following criteria:
- It is expected to be realised in or is intended for sale or consumption in the company’s normal operating cycle.
- It is held primarily for the purpose of being traded.
- It is expected to be realised within twelve months after the reporting date.
Question 5.
Explain meaning of trade receivables.
Answer.
Trade Receivables: Trade receivables refer to the amount receivable on account of sale of goods or services rendered by the company in the normal course of business. They are classified as current assets if the amount is expected to be realised within a period of 12 months from the date of balance sheet or within the operating cycle of the business.
Question 6.
Write four items under the head of ‘Reserves and Surplus’ of Balance Sheet.
Answer.
These are:
- Capital Reserve
- Security Premium
- Capital Redemption Reserve
- Debenture redemption Reserve.
![]()
Question 7.
What is ‘share options outstanding account’? Explain.
Answer.
Share Options Outstanding Account: It is a reserve which represents the difference between the market value and issue price of shares issued to employees under Employees Stock Option Scheme i.e., ESOR For example, if the shares are issued to employees at Rs 60 per share whereas the market price is Rs 100 per share, the difference i.e., Rs 40 should be credited to this reserve.
Question 8.
Write the names of five sub-heads comparing under the heads ‘Non-Current Assets’.
Answer.
The are
- Fixed Assets
- Non Current Investment
- Long term loan and Advances
- Other non current assets
- Differed tax assets.
Question 9.
Explain cash equivalents.
Answer.
The short term most liquid investment which can be quickly changed in cash and the risk of changing in its value is equal to nothing called cash equivalents. Any investment is considered cash equivalents only then when its maturity period is minimum means three months or less than it from the receiving date.
RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 6 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by financial statements? Describe characteristics and objectives of these.
Answer.
Meaning of Financial Statements : Financial statements are the end products of accounting process. They provide information about the profitability and the financial position of a business. As per Section 2 (40) of the Companies Act, 2013, “Financial Statements” in relation to a company include the following:
- A balance sheet as at the end of the financial year
- A statement of profit and loss for the financial year
- Cash flow statement for the financial year
- A statement of changes in equity, if applicable, and
- Explanatory notes.
![]()
One person company, small company and dormant company are exempted from preparing cash flow statement with their financial statements.
Section 129 (1) of the Companies Act, 2013, requires that the financial statement of a company.
- shall give a true and fair view of the state of affairs of the company.
- shall comply with the accounting standards noticed under Section 133.
- shall be in the prescribed form given in Schedule III.
The prescribed form for the preparation of balance sheet has been given in Part I of Schedule III and prescribed form for the preparation of statement of profit and loss has been given in Part II of Schedule III.
The Board of Directors shall present the financial statements before the shareholders for their approval at every Annual General Meeting of the Company. The auditor’s report and director’s report must be attached to the financial statements of the company.
Objectives of Preparing Financial Statements:
- To present a true and fair view of the financial performance {i.e., profit/loss) of the business.
- To present a true and fair view of the financial position {i.e., assets/equity and liabilities) of the business.
Characteristics of Financial Statements:
- Financial statements are related to past period and hence are historical documents.
- They are expressed in terms of money.
- Financial statements show profitability through statement of profit and loss and financial position through balance sheet.
Question 2.
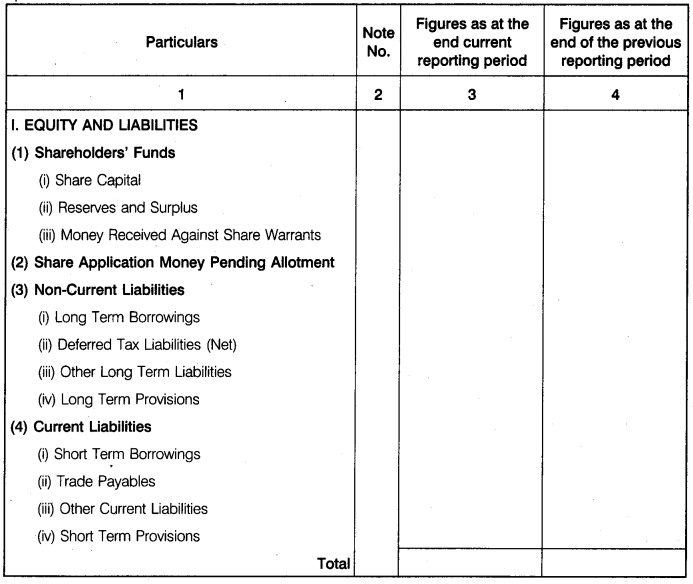
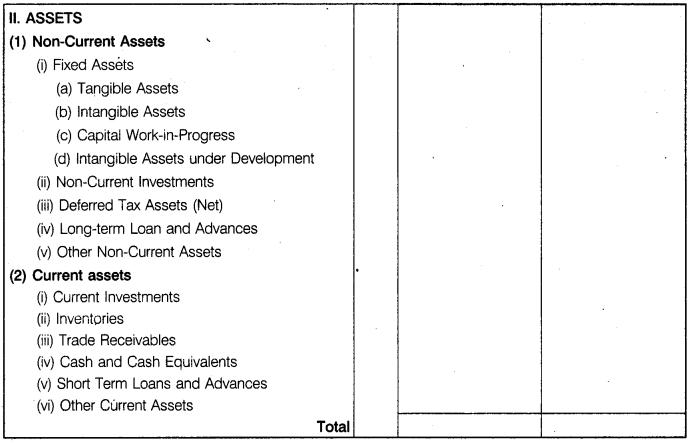
What do you mean by balance sheet ? Give its format.
Answer.
Balance Sheet of a Company: Balance sheet is a financial statement that summarizes company’s equity (shareholders’ funds), liabilities and assets at a specific point of time. These three balance sheet segments, i.e., equity (shareholders’ funds), liabilities and assets show what the company owns and what is owes. Balance sheet of a company is prepared following the same principles as are followed in preparation of balance sheet of a sole proprietorship or partnership firm. However, it differs from them in presentation. Balance sheet of a company is prepared in the prescribed format i.e., Schedule III, Part I of Companies Act, 2013.
![]()
Part-I
Format of Balance Sheet
Name of the Company
Balance Sheet .
as at….
![]()
Question 3.
What is meant by profit and loss statement? Give its format.
Answer.
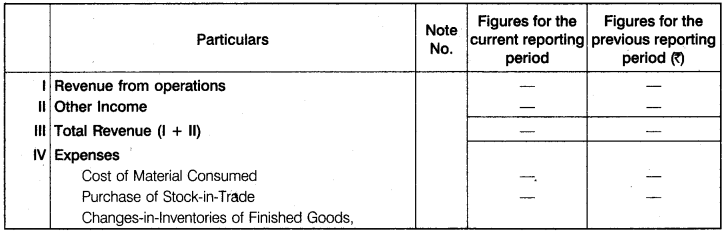
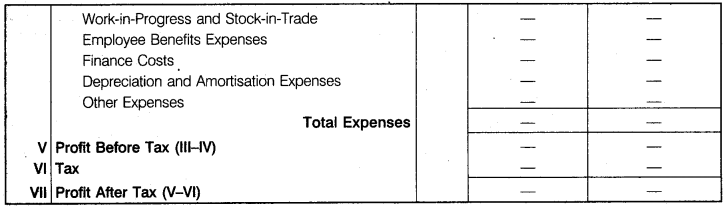
By which statement, is selected period calculate the net profit and loss and know that a processing of a business is going well or not that called profit and loss statement.
Part-II
Format of Statement of Profit and Loss
Important Note
As per revised syllabus major headings and sub-headings of statement of profit and loss are also a part of syllabus for board examination.
Format of statement of profit and loss is specified in Part II Schedule III of the Companies Act, 2013 (format given in C.B.S.E. circular no. 43 dated 2nd July, 2013 for Board Examination is given below) .
Form of Statement of Profit and Loss
Name of the Company
Profit and Loss Statement
for the year ended …. (in….)
Question 4.
Explain contingent liabilities and commitments.
Answer.
Contingent Liabilities and Commitments
(i) Contingent Liabilities: Contingent liabilities are those liabilities which may or may not arise because they are dependent on a happening in future. For example, a claim is filed against the company in a consumer court by a customer. The court may hold the company at fault and may impose penalty. It may happen otherwise, also whether the company has a liability or not is dependent on court order. Thus, it is contingent liability.
Contingent liability is not recorded in the books of account but it is disclosed in the notes to accounts for the information of the users. It is to be classified into:
(a) Claims against the company not acknowledged as debt.
(b) Guarantees given by the company.
(c) Other money for which the company is contingently liable.
![]()
(ii) Commitments: Commitment is defined as an agreement to perform a particular activity at a certain time in the future under certain circumstances. Commitments shall be classified as:
(a) Estimated amount of contracts remaining to be executed on capital account and not provided for.
(b) Uncalled liability on shares and other investment partly paid. If the company hold partly paid shares of other companies as investment. The uncalled amount on these shares is a commitment as it will have to be paid when called.
(c) Other commitments (specify nature) such as; arrears of dividends on cumulative preference shares.
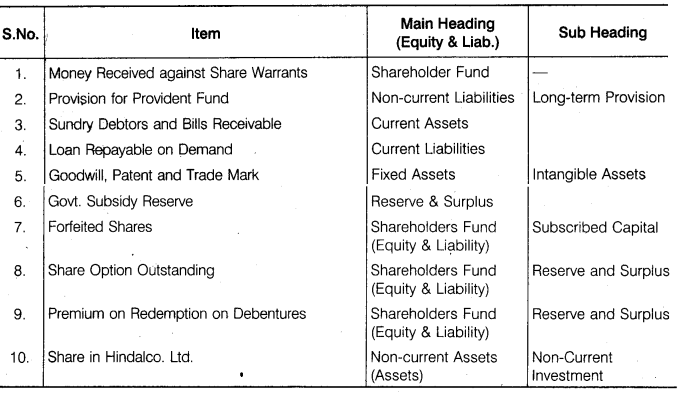
Question 5.
Under which heads will you show the following items in the Balance Sheet of a company?
- Money received against share warrants,
- Provision for provident fund,
- Sundry debtors and B/R,
- Loan repayable on demand,
- Goodwill, patents and trademarks,
- Government subsidy reserves,
- Forfeited shares,
- Shares options outstanding,
- Premium on redemption of debentures,
- Shares in Hindalco Ltd.
Answer.
Question 6.
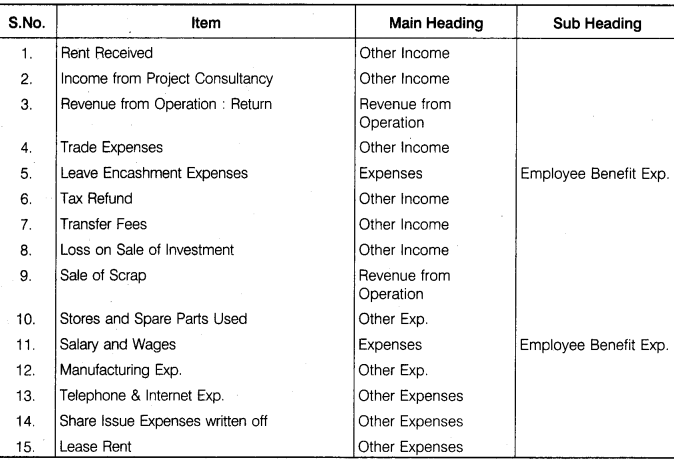
Under which major head will you show the following items in the Statement of Profit and Loss of a company ?
(1) Rent received,
(2) Revenue from project consultancy,
(3) Revenue from operations : Return,
(4) Trade expenses,
(5) Leave encasement expenses,
(6) Refund of income tax,
(7) Transfer fees,
(8) Loss on sale of investment,
(9) Sale of scrap,
(10) Stores and spares parts used,
(11) Salary and wages,
(12) Manufacturing expenses,
(13) Telephone and internet expenses,
(14) Share issue expenses written off,
(15) Lease rent
Answer:
![]()
RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 6 Numerical Questions
Question 1.
From the following information, calculate Revenue from operations, Other Income and Total Revenue of Non-financial Company :
Revenue from Sales Rs 30,00,000; Sales Return Rs 6,50,000; Sale of Scrap Rs 1,50,000; Interest on Bank Deposit Rs 2,00,000; Interest earned on Debentures Rs 50,000.
Answer.
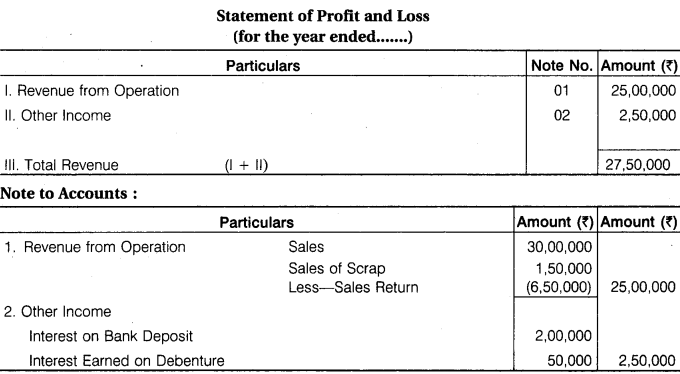
Question 2.
From the following information of Religare Ltd. (a financial company), calculate Revenue . from Operations, Other Income and Total Revenue :
Profit on Sale of Investments Rs 5,00,000; Profit on Sale of Building Rs 4,50,000; Miscellaneous Income Rs 50,000; Dividend Received Rs 4,00,000; Interest on Loans Rs 25,00,000.
Answer.
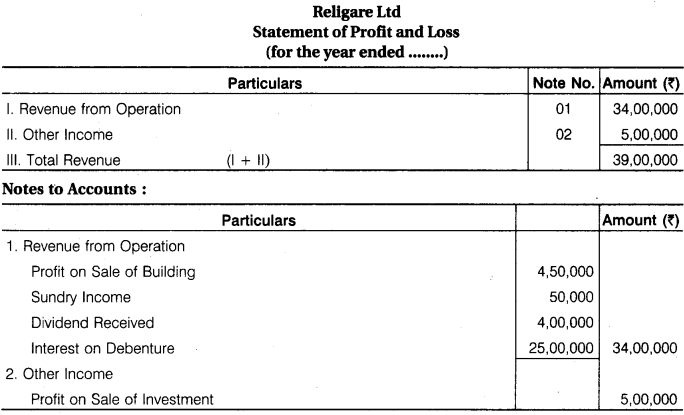
![]()
Question 3.
The following balances are taken from trial balance of a company :
Loan from IDBI Rs 5,00,000; Land and Building Rs 3,70,000; Plant and Machinery Rs 2,58,000; Furniture Rs 45,000; Investments Rs 2,47,000; Dr. Balance of P & L Statement
Rs 50,000; Trade Receivables Rs 2,25,000; Inventory Rs 1,75,000; Cash and Cash Equivalents Rs 51,000.
You are required.to draw up assets side of Balance Sheet as per Companies Act, 2013.
Answer.
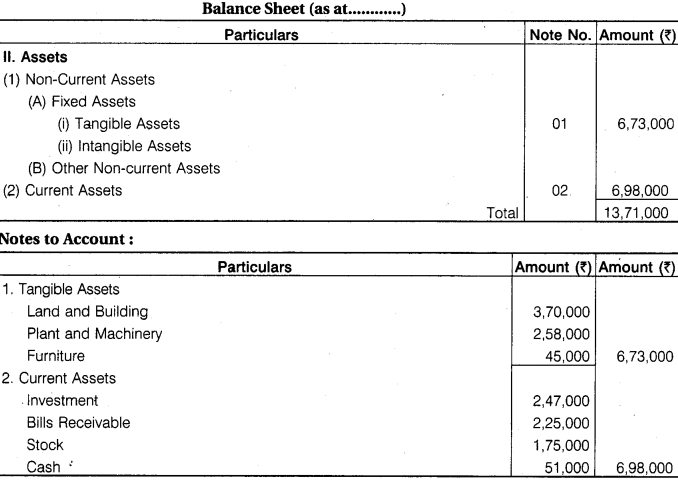
![]()
Question 4.
The following balances are taken from trial balance of a company :
1,20,000 Equity Share of Rs 10 each fully called up Rs 12,00,000; Calls-in-arrears on 5,000 shares @ Rs 2 each Rs 10,000; General Reserve Rs 5,80,000; Preliminary Expenses Rs 20,000; Provision for Provident Fund Rs 1,20,000; Trade Payables Rs 3,00,000; Loan from Bank Rs 5,00,000; Provision for Doubtful Debt Rs 40,000.
You are required to prepare Equity and Liabilities side of Balance Sheet as per Companies Act, 2013.
Answer.
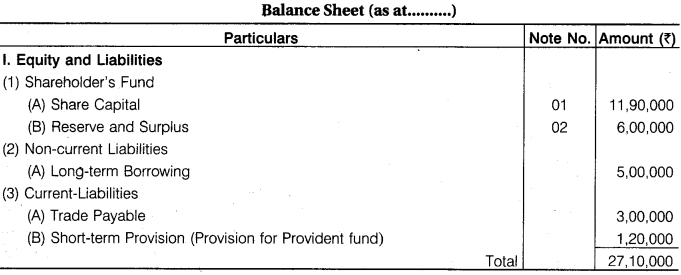

Question 5.
Prepare Notes to Accounts on Employee Benefits Expenses from the following information for the year ended 31 March, 2017 :
(i) Entertainment Expenses Rs 1,50,000,
(ii) Staff Welfare Expenses Rs 2,70,000,
(iii) Travelling Expenses Rs 80,000,
(iv) Bonus Rs 5,50,000;
(v) Salaries Rs 18,70,000;
(vi) Wages Rs 25,20,000.
Answer.
Notes to Accounts

[Note—(i) Entertainment Exp., (ii) Travelling Exp.
Employee’s benfit expenses are not included those are shown in P & L statement in other expenses.]
![]()
Question 6.
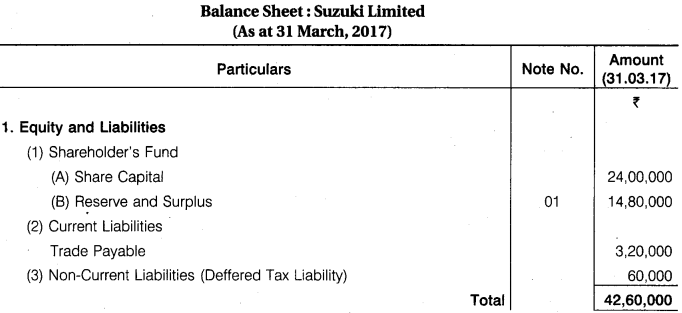
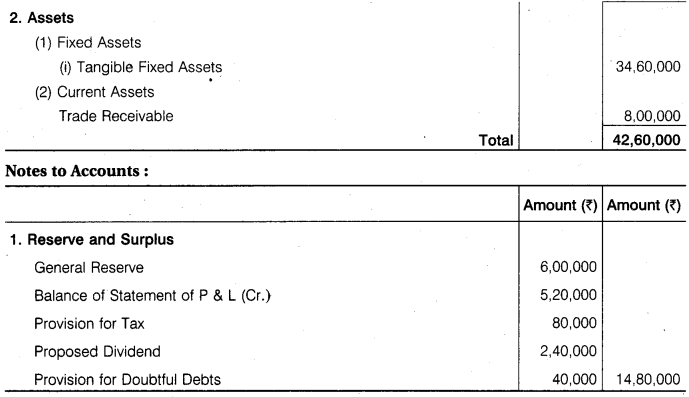
From the following information prepare Balance Sheet of Suzuki Ltd. as at 31st March, 2017 : Share Capital Rs 24,00,000; Deferred Tax Liabilities Rs 60,000; General Reserve Rs 6,00,000; Balance of Statement of Profit & Loss (Cr.) Rs 5,20,000; Tangible Fixed Assets Rs 34,60,000; Trade Receivables Rs 8,00,000; Provision for Doubtful Debts Rs 40,000; Trade Payables Rs 3,20,000; Provision for Tax Rs 80,000; Proposed Dividend Rs 2,40,000.
Answer.
![]()
Question 7.
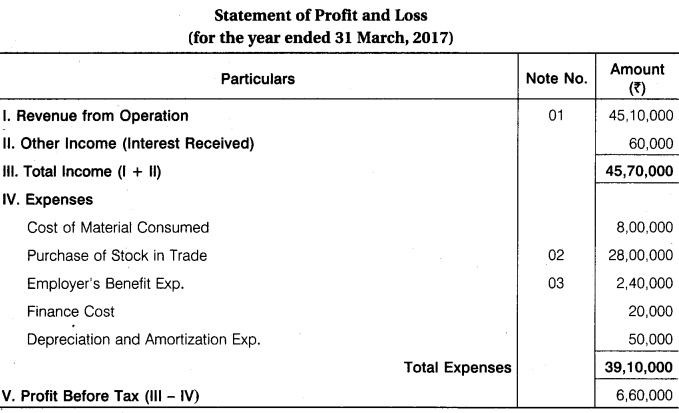
From the following information, prepare statement of Profit & Loss of Shubham Ltd., for the year ending 31 March, 2017 :
Sales Rs 45,00,000; Cost of Material Consumed Rs 8,00,000; Purchase of Stock-in-Trade Rs 30,00,000; 10% Debentures (Issued on 01-04-2016) Rs 2,00,000; Depreciation on Machinery Rs 50,000; Interest received Rs 60,000; Wages Rs 1,80,000; Salaries Rs 60,000; Sales of Scrap Rs 10,000; Opening Stock-in-Trade Rs 3,00,000; Closing stock-in-Trade Rs 5,00,000.
Answer.

![]()
Question 8.
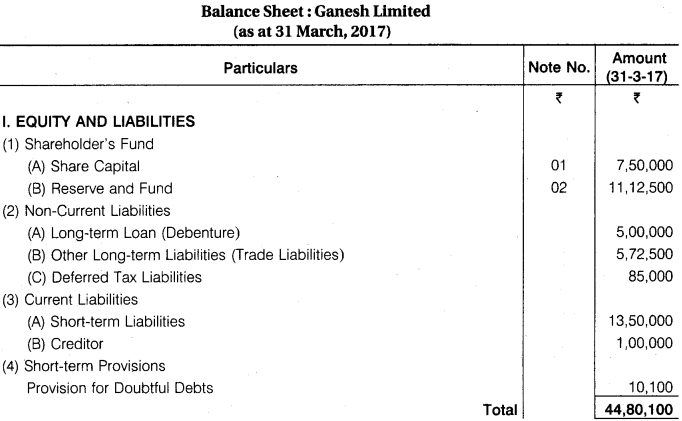
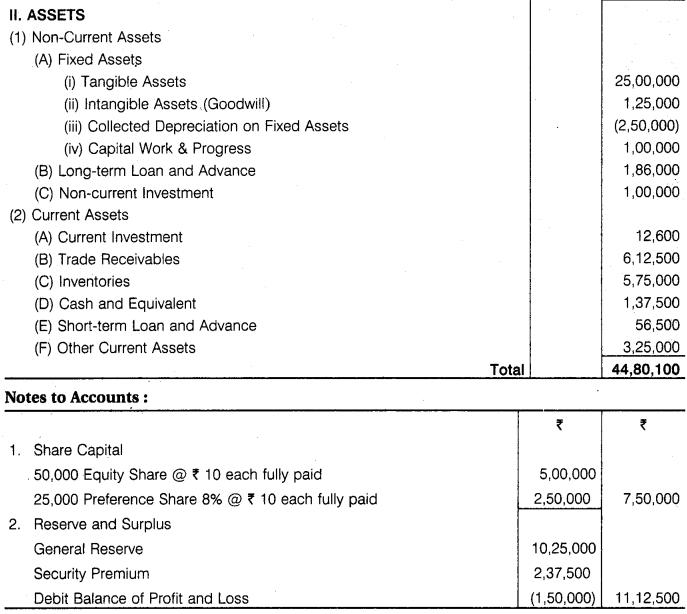
From the following information, prepare Balance Sheet of Ganesh Ltd as at 31 March, 2017.
Fully paid 50,000 Equity Shares Rs 10 each Rs 5,00,000; 25,000 8% Preference Shares Rs 10 each fully paid up Rs 2,50,000; 7% Debentures Rs 5,00,000; Trade Creditors Rs 5,72,500; Cash and Cash Equivalents Rs 1,37,500; Provision for Tax Rs 85,000; Goodwill at Cost Rs 1,25,000; . Balance of Statement of Profit & Loss (Dr.) Rs 1,50,000; Provision for Doubtful Debts Rs 10,100; Tangible Fixed Assets at Cost Rs 25,00,000; Other Current Assets Rs 3,25,000; General Reserves Rs 10,25,000; Short-term Loans Rs 13,50,000; Long-term Advances Rs 1,86,000; Short-term Advances Rs 56,500; Securities Premium Rs 2,37,500; Non-Current Investments Rs 1,00,000; Current Investments Rs 12,600; Sundry Debtors Rs 6,12,500; Creditors for Expenses Rs 1,00,000; Closing Stock : Store Rs 2,00,000; and Finished Goods Rs 3,75,000 (Total Rs 5,75,000); Capital Work-in-Progress Rs 1,00,000; Accumulated Depreciation on Fixed Assets Rs 2,50,000.
Answer.