Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 38 Human Population
RBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 38 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Who has first of all given the “Theory of Population” in context to the human population.
(a) Malthus
(b) Lamarck
(c) Bodenhamer
(d) Darwin
Answer:
(a) Malthus
![]()
Question 2.
What percentage of the population is contributed by India globally?
(a) 12.4%
(b) 17.85%
(c) 16.2%
(d) 15.13 %
Answer:
(b) 17.85%
Question 3.
The main reason for the increasing world population is –
(a) Increased Natality
(b) Improvement in living standard
(c) Global warming
(d) Decreased Mortality
Answer:
(d) Decreased Mortality
Question 4.
If there are a number of old persons in population it becomes –
(a) Increase in future
(b) Decrease in future
(c) Stationary
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Decrease in future
![]()
Question 5.
Which is not a contraceptive?
(a) Condom
(b) Saheli pill
(c) Vault
(d) Steroid pill
Answer:
(d) Steroid pill
RBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 38 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define Population.
Answer:
A group of animals of a species at a specific place and at a specific time is called a population.
Question 2.
What is the population growth curve?
Answer:
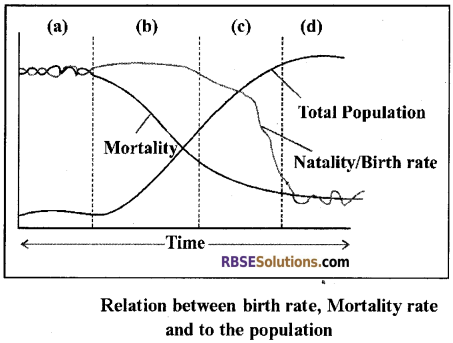
Population growth in animals exhibits a fixed pattern which can be exhibited by a population growth graph. The population growth graph is drawn between population size and time.
![]()
Question 3.
Write anyone important factor for decreased mortality in India?
Answer:
Advanced medical facilities and time bond vaccination.
Question 4.
What will happen if the population if natality and mortality rate will be equal?
Answer:
The size of the population of that species will be stationary.
Question 5.
What is IUD in contraception devices?
Answer:
Intra-Uterine Device (IUD):
- Intra-uterine devices are small devices that are inserted into the uterus by doctors.
- Examples:
- Non-Medicated IUD – Lippes Loop.
- Copper Releasing IUD – Cut, Cu7, Multiload 375 etc.
- Hormone Releasing IUD – LNG 20, Protestant etc.
- These devices promote phagocytosis of sperms to prevent fertilization. They are used to delay pregnancy. Cut, Cu7 are devices containing copper. The release of copper ions inhibits the motility of sperms & fertilisation. These are considered as ideal contraceptives for females. IUD hormones prevent implantation in the uterus two children IUD is an ideal method. It is widely used in India.
![]()
Question 6.
What are contraceptive pills?
Answer:
Contraceptive Pills:
- These Pills are used as oral contraceptives. These pills contain small doses of estrogen or progesterone or a combination of both. These oral contraceptives should be taken for a period of 21 days.
- After a gap of 7 days, that is, at the time of menstruation, these pills should be avoided. After this gap, these pills should be taken again in the same pattern until and unless female desires conception or fertilization.
- Progesterone or combination with estrogen may also be given to females via injections. They work similarly to orally taken pills.
- Saheli is a new oral contraceptive without any steroids hormone. It contains a chemical called centchroman. It is a highly effective contraceptive pill.
- Emergency pills Contain a chemical called Levenorgastril. This pill is to be taken after forced sex or unplanned sex within 72 hours. It prevents ovulation. It is also called a pill – 72.
Question 7.
What is Vasectomy?
Answer:
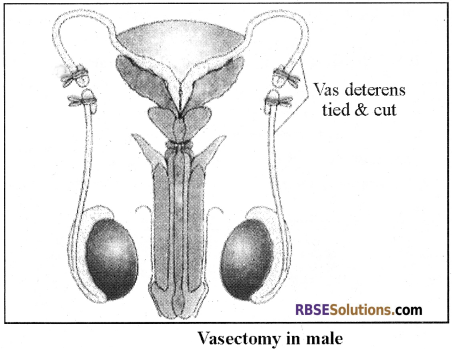
Vasectomy:
- Vasectomy is one of the methods used in males. In this method, a small incision is made and vas deferens get tied.
- It is commonly known as “Male Nasbandi”.
![]()
Question 8.
What is Tubectomy?
Answer:
Tubectomy:
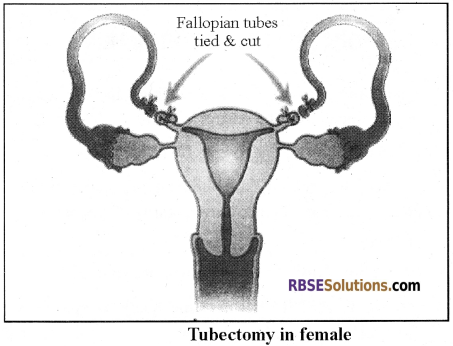
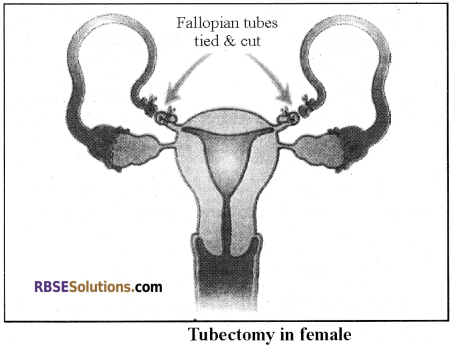
- Similarly, in females, Tubectomy is done. In tubectomy, a small part of Fallopian tube is removed via an incision or it gets tied.
- This techniques are effective and have reversibility. These techniques are commonly known as “female Nasbandhi”.
RBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 38 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write the difference between mortality and natality.
Answer:
Natality or Fertility:
- It determines the growth of any population. In a population, the ability to produce a new baby from active reproducing organisms is called fertility. In growing, population natality is one of the important factors.
- The birth rate is the number of births per 1000 individuals per year. It can be calculated by the following formula –
N = \(\frac { B }{ t } \)
where N = Natality/Birth rate
B = Birth of children per 1000 people
t = Time period in a year - Bodenheimer divided the human population into 3 groups –
- Pre-reproduction population: Population below 18 years of age.
- Reproductive population: Population between 18 to 45 years of age.
- Post-reproductive population: Population above 45 years of age.
- A number of the reproductive population indicates an increase in population growth. Similarly, number post-reproductive population indicates a decrease in the population growth.
Mortality:
- Mortality or Death rate is the number of deaths per thousand persons in a year.
M = \(\frac { D }{ t } \)
where M = mortality, D = Number of death in one thousand persons and t = time in years. - In many countries, a decline in death rates is recorded which resulted in an increase in population. This could be because of the following reasons:
- Developed medical facility including Immunization vaccination.
- Level of cleanliness has increased.
- Awareness towards personal health & cleanliness has increased.
- Availability of food and water is in a sufficient amount.
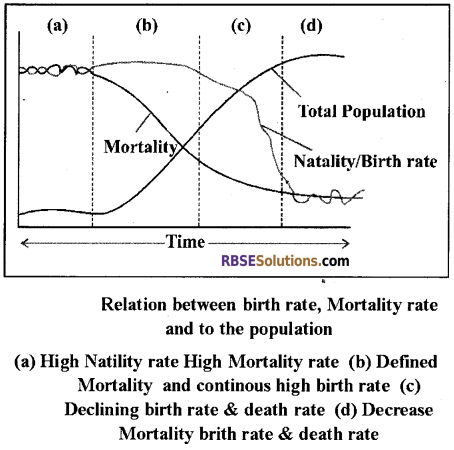
- Mortality and Natality are the important factors which determine the population. In other words, using mortality and natality rate, population pattern of any country can be determined.
- Crude Birth Rate: The crude birth rate is the rate of births among a population of 1000.
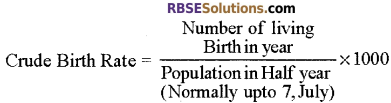
- Crude death Rate: It is the rate of death among a population of 1000.
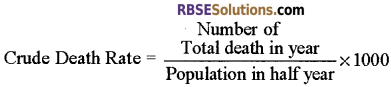
- Annual Rate of Natural Increase/Growth:
- Difference between mortality and natality is called Annual growth rate.
- Annual growth rate = Natality/Birth rate – Mortality rate.
- Crude Birth Rate: The crude birth rate is the rate of births among a population of 1000.
If mortality and natality are equal, population shape is stationary means the growth rate of the population will be zero. However, it occurs very rarely. It can be seen in some developed society.
![]()
Question 2.
Define population density. Write the methods to determine it.
Answer:
Population Density:
- Population density is a measurement of the population of organisms in per unit area or unit volume. Population density is a numerical expression.
- For Example, 100 trees per acre or 200 fishes per km or 50 billion diatoms m3.
- It shows the total number of individuals of specific species lived in a habitat. It can be calculated using the formula –
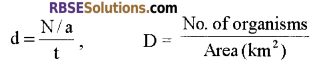
where d = density, N = No. of organisms, a = Area, t = Time
- The population is changing from time to time i.e. it is not permanent. Change in population causes a change in density.
Types of Population Density:
Population Density is of two types:
- Crude Density:
Crude density includes all the organisms within the land range. For example, if 1000 rabbit lived in 1 mile than population density will be 1000 rabbit per mile. It is calculated in per mile, per acre, or per meter. It is also known as Habitat density. - Ecological Density:
Ecological density includes only that portion of land which is actually colonized by the species. For example, if 500 rabbits are lived in the one-mile area but they needed only half mile to live than ecological density will be 1000 rabbit per mile.
Determination of Population Density:
Population density can be calculated by several methods, some of them are as follows –
1. Direct count method:
- This method is used to count big size organisms which live in groups. This method is suitable for birds and big sized mammals (elephant, panther, and rabbit are counted by this method).
- In this method, every individual is counted. This method showed an exact population density of species.
- Human Population census is the best example of it. In India, the human population is counted in every 10 years.
2. By Sampling Method:
- This method is used to determine population density in ecological habitat. In this method, samples have been collected from different parts and the number is counted. Average of all the samples is calculated to know the population density.
- Example 1: To calculate the population of the density of paramecium, the Culture medium of Paramecium is shaken well and Paramecium is counted in cm on a watch glass. Sum of the result is counted and the average of that is calculated in per 1 cc.
- Example 2: To calculate the population density of terrestrial animals, Quadrats may be used to determine population size and density. Each quadrat marks off an area of the same size – typically, a square area, within the habitat. In the end, the data can be used to estimate the population size and population density within the entire habitat. Sum of all the results is calculated and the average is to be taken out. This method indicates the almost correct population density.
3. By marking and recapture Method:
- For organisms that move around, such as mammals, birds, or fish, rabbit, a technique mark-recapture method is often used to determine population size.
- This method involves capturing a sample of animals and marking them using tags, bands, paint, or other body markings. Then, the marked animals are released back into the environment and allowed to mix with the rest of the population.
- Later, a new sample is collected. This new sample will include some individuals that are marked and some individuals that are unmarked. Using the ratio of marked to unmarked individuals, scientists can estimate how many individuals are in the total population.

- Suppose, we capture 100 organisms and release them back into the forest after marking. After some time, the second sample is taken and find that 10 are already marked. We can formulate the following relationship:
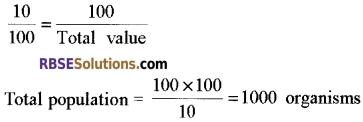
4. By Indirect Method:
In a laboratory, the population density is calculated using an indirect method. Such as:
On the basis of consumption of O2 and release of CO2.
- On the basis of the consumption quantity of food.
- On the basis of the remaining food material present in the stomach.
- On the basis of dead animal remaining of carnivorous animals.
5. By Sample Plot Method:
- In ecological habitat, this is the most simple and commonly used method.
- In this method, the area in which density is to be determined is divided into an equal plot.
- Numbers of organisms are counted in some plot and average of number is taken out.
- The average number is multiplied by a total number of plots which indicate the population density of that area.
- For example, We have to calculate population density in 100 km2. Now, 100km2 is divided into 100 plots of 1Km2. Suppose the average of 5 plots is 125 than the average of 1 plot is 25. Population density of 100Km2 field is 25 × 100 ⇒ 2500.
![]()
Question 3.
Write the different methods to determine population density.
Answer:
Determination of Population Density:
Population density can be calculated by several methods, some of them are as follows –
1. Direct count method:
- This method is used to count big size organisms which live in groups. This method is suitable for birds and big sized mammals (elephant, panther, and rabbit are counted by this method).
- In this method, every individual is counted. This method showed an exact population density of species.
- Human Population census is the best example of it. In India, the human population is counted in every 10 years.
2. By Sampling Method:
- This method is used to determine population density in ecological habitat. In this method, samples have been collected from different parts and the number is counted. Average of all the samples is calculated to know the population density.
- Example 1: To calculate the population of the density of paramecium, the Culture medium of Paramecium is shaken well and Paramecium is counted in cm on the watch glass. Sum of the result is counted and the average of that is calculated in per 1 cc.
- Example 2: To calculate the population density of terrestrial animals, Quadrats may be used to determine population size and density. Each quadrat marks off an area of the same size – typically, a square area, within the habitat. In the end, the data can be used to estimate the population size and population density within the entire habitat. Sum of all the results is calculated and the average is to be taken out. This method indicates the almost correct population density.
3. By marking and recapture Method:
- For organisms that move around, such as mammals, birds, or fish, rabbit, a technique mark-recapture method is often used to determine population size.
- This method involves capturing a sample of animals and marking them using tags, bands, paint, or other body markings. Then, the marked animals are released back into the environment and allowed to mix with the rest of the population.
- Later, a new sample is collected. This new sample will include some individuals that are marked and some individuals that are unmarked. Using the ratio of marked to unmarked individuals, scientists can estimate how many individuals are in the total population.

- Suppose, we capture 100 organisms and release them back into the forest after marking. After some time, the second sample is taken and find that 10 are already marked. We can formulate the following relationship:

4. By Indirect Method:
In the laboratory, the population density is calculated using an indirect method. Such as:
On the basis of consumption of O2 and release of CO2.
- On the basis of the consumption quantity of food.
- On the basis of the remaining food material present in the stomach.
- On the basis of dead animal remaining of carnivorous animals.
5. By Sample Plot Method:
- In ecological habitat, this is the most simple and commonly used method.
- In this method, the area in which density is to be determined is divided into an equal plot.
- Numbers of organisms are counted in some plot and average of number is taken out.
- The average number is multiplied by the total number of plots which indicate the population density of that area.
- For example, We have to calculate population density in 100 km2. Now, 100km2 is divided into 100 plots of 1Km2. Suppose an average of 5 plots is 125 than the average of 1 plot is 25. Population density of 100Km2 field is 25 × 100 ⇒ 2500.
![]()
Question 4.
Write a note on
- ‘S’ – shaped growth form
- Factors affecting population
- Natality and Mortality
Answer:
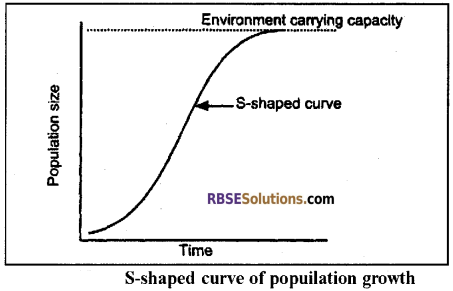
1. ‘S’ – Shaped Growth or Sigmoid growth curve:
It is also called a sigmoid curve.
It has 3 phases:
1. Early or Lag phase: There is little or no growth.
2. Middle or Log or Exponential phase: There is fast growth in the population.
3. Stationary or Zero or Plateau phase:
- The population growth is zero.
- Mortality and natality are equal.
- The population becomes equal to the environmental carrying capacity.
In S (sigmoid) form, the population increases slowly at first, then more rapidly but it soon slows down gradually as the environment resistance increases.
2. Factors affecting Population Growth:
- The population of any country is effected by 4 factors
- Natality
- Mortality
- Migration
- Age Distribution
- More natality in any country and less mortality increases population and the vice versa. Similarly, if human Immigration is more than migration, the population will increase and vice versa.
1. Natality or Fertility:
- It determines the growth of any population. In a population, the ability to produce a new baby from active reproducing organisms is called fertility. In growing, population natality is one of the important factors.
- The Birth rate is the number of births per 1000 individuals per year. It can be calculated by the following formula –
N = \(\frac { B }{ t } \)
where N = Natality/Birth rate
B = Birth of children per 1000 people
t = Time period in a year - Bodenheimer divided the human population into 3 groups –
- Pre-reproduction population: Population below 18 years of age.
- Reproductive population: Population between 18 to 45 years of age.
- Post-reproductive population: Population above 45 years of age.
- A number of the reproductive population indicates an increase in population growth. Similarly, the number of post-reproductive population indicates a decrease in population growth.
2. Mortality:
- Mortality or Death rate is the number of deaths per thousand persons in a year.
M = \(\frac { D }{ t } \)
where M = mortality, D = Number of death in one thousand persons and t = time in years. - In many countries, a decline in death rates is recorded which resulted in an increase in population. This could be because of the following reasons:
- Developed medical facility including Immunization vaccination.
- Level of cleanliness has increased.
- Awareness towards personal health & cleanliness has increased.
- Availability of food and water is in a sufficient amount.
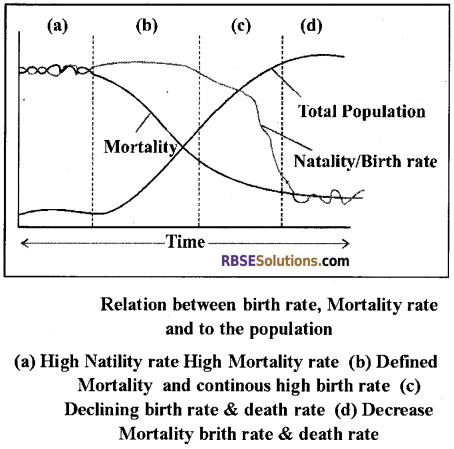
- Mortality and Natality are the important factors which determine the population. In other words, using mortality and natality rate, population pattern of any country can be determined.
- Crude Birth Rate: The crude birth rate is the rate of births among a population of 1000.

- Crude death Rate: It is the rate of death among a population of 1000.
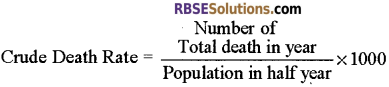
- Annual Rate of Natural Increase/Growth:
- Difference between mortality and natality is called Annual growth rate.
- Annual growth rate = Natality/Birth rate – Mortality rate.
- If mortality and natality are equal, population shape is stationary means the growth rate of the population will be zero. However, it occurs very rarely. It can be seen in some developed society.
- Crude Birth Rate: The crude birth rate is the rate of births among a population of 1000.
3. Migration:
- The movement by humans from one area to another is known as Migration. The humans who undergo migration are called Migrants.
- The people who migrate into a territory are called immigrants, and they’re conveyed as Immigration.
- Similarily the people who leave a territory are called Emigrants. and movement is Emigration. However, migrations can occur in different places in the same country. Only migrations between 2 countries affect the population.
- Due to Emigration population density gets decreased and due to immigration, it increases. Due to migration increase in population is called Net Immigration. It can be calculated by –
- Net Immigration = Immigration – Emigration
- Net Immigration can be positive, zero or negative.
4. Age Distribution:
- The age distribution is an important factor. It affects both Mortality and Natality. Distribution of various age groups in the population is called Age Distribution.
- Natality and Mortality vary according to age. In a similar way reproduction also depend on age. Population growth depends on the ratio of all these factors. This ratio determines the future of any population.
- On the basis of the economy, the human population is divided into 2 groups
- Dependent age group (DAG): It includes children of 18 – 20 years of age which are economically dependent on their parents.
- Productive age group (PAG): The population which is capable of earning.
- The ratio of DAG & PAG is called a dependency ratio (DR)
- DR ⇒ Number of DAG/Number of PAG
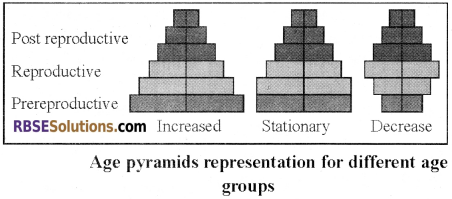
Age Pyramids:
- An age pyramid is a graphical illustration that shows the distribution of various age groups in a population. Population pyramids often contain continuous stacked histogram bars, making it a horizontal bar diagram.
- In ecology, 3 types of a pyramid can be imagined:
- A pyramid with Broad Base: In this type of pyramid, the base part is wide. In these types of a pyramid, the natality rate is high and the population grow rapidly. A number of an organism in each generation increase from the previous generations. This types of pyramids are found in Yeast, Paramecium, housefly.
- A Bell-shaped Polygon: In this type of population growth rate is slow and become stationary. Pre reproductive and reproductive age groups are an almost equal number. Post reproductive age groups will remain small. This type of population is bell-shaped.
- An Urn Shaped Pyramid: In this pyramid child population is very less. The birth rate becomes very low. Since post – productive is dominating, the diminishing age pyramid is urn-shaped.
3. Natality or Fertility:
- It determines the growth of any population. In a population, the ability to produce a new baby from active reproducing organisms is called fertility. In growing, population natality is one of the important factors.
- The birth rate is the number of births per 1000 individuals per year. It can be calculated by the following formula –
N = \(\frac { B }{ t } \)
where N = Natality/Birth rate
B = Birth of children per 1000 people
t = Time period in a year - Bodenheimer divided the human population into 3 groups –
- Pre-reproduction population: Population below 18 years of age.
- Reproductive population: Population between 18 to 45 years of age.
- Post-reproductive population: Population above 45 years of age.
- A number of the reproductive population indicates an increase in population growth. Similarly, the number of post-reproductive population indicates a decrease in population growth.
Mortality:
- Mortality or Death rate is the number of deaths per thousand persons in a year.
M = \(\frac { D }{ t } \)
where M = mortality, D = Number of death in one thousand persons and t = time in years. - In many countries, a decline in death rates is recorded which resulted in an increase in population. This could be because of the following reasons:
- Developed medical facility including Immunization vaccination.
- Level of cleanliness has increased.
- Awareness towards personal health & cleanliness has increased.
- Availability of food and water is in a sufficient amount.
- Mortality and Natality are the important factors which determine the population. In other words, using mortality and natality rate, population pattern of any country can be determined.
- Crude Birth Rate: The crude birth rate is the rate of births among a population of 1000.
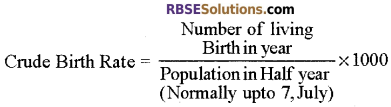
- Crude death Rate: It is the rate of death among a population of 1000.
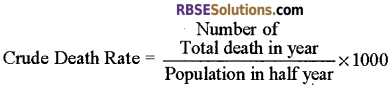
- Annual Rate of Natural Increase/Growth:
- Difference between mortality and natality is called Annual growth rate.
- Annual growth rate = Natality/Birth rate – Mortality rate.
- If mortality and natality are equal, population shape is stationary means the growth rate of the population will be zero. However, it occurs very rarely. It can be seen in some developed society.
![]()
Question 5.
Write a note on age composition in any population.
Answer:
Age Distribution:
- The age distribution is an important factor. It affects both Mortality and Natality. Distribution of various age groups in the population is called Age Distribution.
- Natality and Mortality vary according to age. In a similar way reproduction also depend on age. Population growth depends on the ratio of all these factors. This ratio determines the future of any population.
- On the basis of the economy, the human population is divided into 2 groups:
- Dependent age group (DAG): It includes children of 18 – 20 years of age which are economically dependent on their parents.
- Productive age group (PAG): The population which is capable of earning.
- The ratio of DAG & PAG is called a dependency ratio (DR)
- DR ⇒ Number of DAG/Number of PAG
Question 6.
What is age Pyramid?
Answer:
Age Pyramids:
- An age pyramid is a graphical illustration that shows the distribution of various age groups in a population. Population pyramids often contain continuous stacked histogram bars, making it a horizontal bar diagram.
- In ecology, 3 types of a pyramid can be imagined:
-
- A pyramid with Broad Base: In this type of pyramid, the base part is wide. In these types of a pyramid, the natality rate is high and the population grow rapidly. A number of the organism in each generation increase from the previous generation. This types of pyramids are found in Yeast, Paramecium, housefly.
- A Bell-shaped Polygon: In this type of population growth rate is slow and become stationary. Pre reproductive and reproductive age groups are an almost equal number. Post reproductive age groups will remain small. This type of population is bell-shaped.
- An Urn Shaped Pyramid: In this pyramid child population is very less. The birth rate becomes very low. Since post – productive is dominating, the diminishing age pyramid is urn-shaped.

-
![]()
Question 7.
Describe the various method of contraception used by females.
Answer:
Family Planning Welfare:
- Population control can effectively be done by using family planning technique. It is nowadays called “Family Welfare”.
- It involves the use of contraceptives and by making the public families aware of the methods of conceptions that they can decide when to give birth to young and what number they want.
- The various family planning methods are as follows:
1. Barrier Methods:
1.1. Condom:
- In this method, the process of fertilization between sperm and ovum is restricted using a physical barrier such as a condom. Condoms are barriers made up of rubber or latex sheath that are used to cover the penis in male and vagina in the female. This method is used to prevent semen from entering the female vagina.
- The use of condoms had increased since the last few years. For males, the brand “Nirodhi”, a condom is very popular.
- Use of condom also prevents sexually transmitted diseases such as AIDS besides preventing pregnancy.
- Both male and female condom has to be discarded after use. It can be used by an individual by its own and in this way, it can remain personal.
1.2. The diaphragm, Cervical Cap & Vault:
- The diaphragm, Uterus convex cap, vault, rings etc., are other contraceptives made of rubber and which are put into female reproductive tract to cover Uterus cervix and they stop the entry of sperm into the female tract.
1.3. Spermicidal:
- Spermicidal serum, jelly and foam are also used as contraceptive measures.
2. Intra-Uterine Device (IUD):
- Intra-uterine devices are small devices that are inserted into the uterus by doctors.
- Examples:
- Non-Medicated IUD – Lippes Loop.
- Copper Releasing IUD – Cut, Cu7, Multiload 375 etc.
- Hormone Releasing IUD – LNG 20, Protestant etc.
- These devices promote phagocytosis of sperms to prevent fertilization. They are used to delay pregnancy. Cut, Cu7 are devices containing copper. The release of copper ions inhibits the motility of sperms & fertilisation. These are considered as ideal contraceptives for females. IUD hormones prevent implantation in the uterus two children IUD is an ideal method. It is widely used in India.
3. Contraceptive Pills:
- These Pills are used as oral contraceptives. These pills contain small doses of estrogen or progesterone or a combination of both. These oral contraceptives should be taken for a period of 21 days.
- After a gap of 7 days, that is, at the time of menstruation, these pills should be avoided. After this gap, these pills should be taken again in the same pattern until and unless female desires conception or fertilization.
- Progesterone or combination with estrogen may also be given to females via injections. They work similarly to orally taken pills.
- Saheli is a new oral contraceptive without any steroids hormone. It contains a chemical called centchroman. It is higly effective contraceptive pill.
- Emergency pills Contain a chemical called Levenorgastril. This pill is to be taken after forced sex or unplanned sex within 72 hours. It prevents ovulation. It is also called a pill – 72
4. Surgical methods:
- Surgical methods are also being used to control birth. These methods are also known as Surgical methods. These methods are used to terminate any further pregnancy. These methods block gamete transfer and thus prevent conception.
- They are two types:
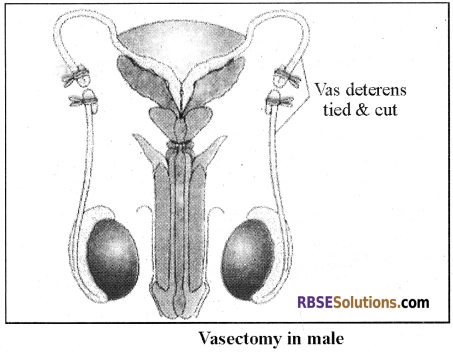
1. Vasectomy:
- Vasectomy is one of the methods used in males. In this method, a small incision is made and vas deferens get tied.
- It is commonly known as “Male Nasbandi”.
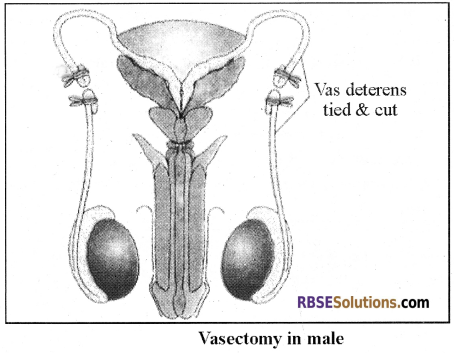
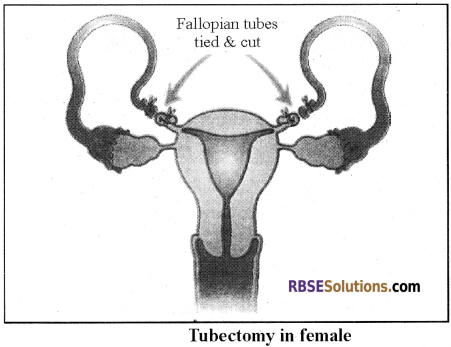
2. Tubectomy:
-
- Similarly, in females, Tubectomy is done. In tubectomy, a small part of Fallopian tube is removed via an incision or it gets tied.
- This techniques are effective and have reversibility. These techniques are commonly known as “female Nasbandhi”.
![]()
Question 8.
Give an account of castration.
Answer:
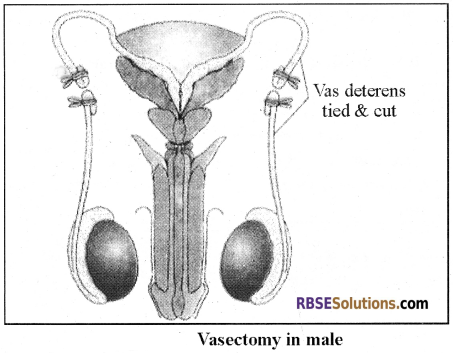
Vasectomy:
-
- Vasectomy is one of the methods used in males. In this method, a small incision is made and vas deferens get tied.
- It is commonly known as “Male Nasbandi”.
RBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 38 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
An increasing population in India is a big problem. Write your opinion.
Answer:
Population in India:
- India is the second-largest country in the world concern to the human population. The India population was 134 crore as on Nov. 2017. Maximum population is found in China which was 141 crore in Nov. 2017.
- In India, the population is increasing at a rate of 1.2%. If this growth in the population continues, India will become the country of the largest human population by 2030. India harbours 17.85% of the world population.
- Population in Western countries is decreasing. On the country, it is increasing in India and other Asian countries.
- In India, out of a total population, 69.7 crores are males and 65.2 crores are females. The sex ratio in India is 945 females per 1000 males. 50% of Indian population is in age slot of 0 – 25 years. 72.2% population inhabiting rural area and about 27.8% population living in an urban area.
![]()
Question 2.
Write a note on
- Human age pyramid
- The male and female ratio in Indian population
Answer:
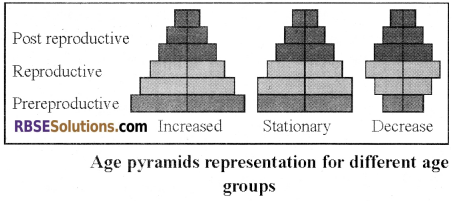
1. Age Pyramids:
- An age pyramid is a graphical illustration that shows the distribution of various age groups in a population. Population pyramids often contain continuous stacked histogram bars, making it a horizontal bar diagram.
- In ecology, 3 types of a pyramid can be imagined:
- A pyramid with Broad Base: In this type of pyramid, the base part is wide. In these types of a pyramid, the natality rate is high and the population grow rapidly. A number of an organism in each generation increase from previous generations. This types of pyramids are found in Yeast, Paramecium, housefly.
- A Bell-shaped Polygon: In this type of population growth rate is slow and become stationary. Pre reproductive and reproductive age groups are an almost equal number. Post reproductive age groups will remain small. This type of population is bell-shaped.
- An Urn Shaped Pyramid: In this pyramid child population is very less. The birth rate becomes very low. Since post – productive is dominating, the diminishing age pyramid is urn-shaped.
2. The male and female ratio in Indian population:
- In India, out of a total population, 69.7 crores are males and 65.2 crores are females. The sex ratio in India is 945 females per 1000 males. 50% of Indian population is in age slot of 0 – 25 years. 72.2% population inhabiting rural area and about 27.8% population living in an urban area.
Question 3.
Describe the different population growth curve.
Answer:
Population Growth Form:
- The population of either human or organisms always increases and the increase is more when the population reproduces actively. The population growths always grow in a particular manner which is called Growth Curve.
- The growth curves are of two types:
- ‘S’ Shaped Growth Curve
- ‘J’ shaped Growth Curve
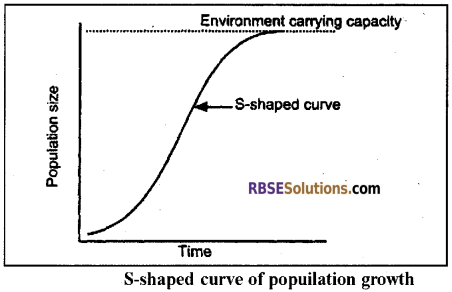
1. ‘S’ – Shaped Growth or Sigmoid growth curve:
It is also called a sigmoid curve.
It has 3 phases:
1. Early or Lag phase: There is little or no growth.
2. Middle or Log or Exponential phase: There is fast growth in the population.
3. Stationary or Zero or Plateau phase:
- The population growth is zero.
- Mortality and natality are equal.
- The population becomes equal to the environmental carrying capacity.
In S (sigmoid) form, the population increases slowly at first, then more rapidly but it soon slows down gradually as the environment resistance increases.
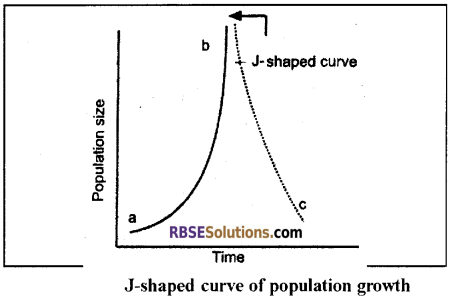
2. ‘J’ – shaped curve:
- It is J – shaped.
- It is exhibited by the populations of insects & human beings.
- It is also called abiotic potential curve.
- According to it, the population grows speedily and this growth is more in large populations in comparison to small populations.
- J – shaped curve has 3 phases –
- Lag or Establishment phase
- Exponential phase
- Crash phase
- The human population is in its exponential phase. The crash phase is yet to come.
![]()
Question 4.
Write the various factors involved to control the population.
Answer:
Factors to Control Population:
- Increasing population in India has raised several socio-economical problems. We have to control this problem otherwise our economic growth will slow down and we will face the problem of food and place. Population control can be achieved in the following ways:
1. Increase Age of Marriage:
- To control population child marriage should be strictly controlled and age of female and male should be increased to 21 and 24 years respectively for marriage.
2. Education:
- The population problem can also be controlled by educating the people that poverty, scarcity of resources and low standard living are because of population explosion.
- People should be made aware of the planned family & its benefits. Sex education should be included in an educational system.
3. Natural Method:
- This technique works on the principle of stopping fusion of ovum and sperm. One of the methods is Abstinenea is a particular period. Couples avoid sexual intercourse between 10 to 17 days in which there is an ovulation process. In this period the chance of fertilization and pregnancy is more.
- Coitus interruptus, withdrawal or pull – out method, is also a good method of birth control in which a man during sexual intercourse, withdraws his penis from a woman’s vagina prior to orgasm (ejaculation) and then directs his ejaculate (semen) away from the vagina in an effort to avoid insemination.
- Lactational amenorrhea is the temporary postnatal infertility that occurs when a woman is amenorrheic (not menstruating) and fully breastfeeding. The time period is 46 month & the chance of pregnancy is zero. This technique is effective only until six months of child age.
4. Family Planning Welfare:
- Population control can effectively be done by using family planning technique. It is nowadays called “Family Welfare”.
- It involves the use of contraceptives and by making the public families aware of the methods of conceptions that they can decide when to give birth to young and what number they want.
- The various family planning methods are as follows:
1. Barrier Methods:
1.1. Condom:
- In this method, the process of fertilization between sperm and ovum is restricted using a physical barrier such as a condom. Condoms are barriers made up of rubber or latex sheath that are used to cover the penis in male and vagina in the female.
- This method is used to prevent semen from entering the female vagina. The use of condoms had increased since the last few years. For males, the brand “Nirodhi”, a condom is very popular.
- Use of condom also prevents sexually transmitted diseases such as AIDS besides preventing pregnancy.
- Both male and female condom has to be discarded after use. It can be used by an individual by its own and in this way, it can remain personal.
1.2. The diaphragm, Cervical Cap & Vault:
- The diaphragm, Uterus convex cap, vault, rings etc., are other contraceptives made of rubber and which are put into female reproductive tract to cover Uterus cervix and they stop the entry of sperm into the female tract.
1.3. Spermicidal:
- Spermicidal serum, jelly and foam are also used as contraceptive measures.
2. Intra-Uterine Device (IUD):
- Intra-uterine devices are small devices that are inserted into the uterus by doctors.
- Examples:
- Non-Medicated IUD – Lippes Loop.
- Copper Releasing IUD – Cut, Cu7, Multiload 375 etc.
- Hormone Releasing IUD – LNG 20, Protestant etc.
- These devices promote phagocytosis of sperms to prevent fertilization. They are used to delay pregnancy. Cut, Cu7 are devices containing copper. The release of copper ions inhibits the motility of sperms & fertilisation. These are considered as ideal contraceptives for females. IUD hormones prevent implantation in the uterus two children IUD is an ideal method. It is widely used in India.
3. Contraceptive Pills:
- These Pills are used as oral contraceptives. These pills contain small doses of estrogen or progesterone or a combination of both. These oral contraceptives should be taken for a period of 21 days.
- After a gap of 7 days, that is, at the time of menstruation, these pills should be avoided. After this gap, these pills should be taken again in the same pattern until and unless female desires conception or fertilization.
- Progesterone or combination with estrogen may also be given to females via injections. They work similarly to orally taken pills.
- Saheli is a new oral contraceptive without any steroids hormone. It contains a chemical called centchroman. It is higly effective contraceptive pill.
- Emergency pills Contain a chemical called Levenorgastril. This pill is to be taken after forced sex or unplanned sex within 72 hours. It prevents ovulation. It is also called a pill – 72
4. Surgical methods:
- Surgical methods are also being used to control birth. These methods are also known as Surgical methods. These methods are used to terminate any further pregnancy. These methods block gamete transfer and thus prevent conception.
- They are two types:
1. Vasectomy:
- Vasectomy is one of the methods used in males. In this method, a small incision is made and vas deferens get tied.
It is commonly known as “Male Nasbandi”.
2. Tubectomy:
- Similarly, in females, Tubectomy is done. In tubectomy, a small part of Fallopian tube is removed via an incision or it gets tied.
- This techniques are effective and have reversibility. These techniques are commonly known as “female Nasbandhi”.