Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 16 Measurement of National Income
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 16 Practice Questions
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 16 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Methods of calculation of national income are :
(a) Production method
(b) Income method
(c) Expenditure method
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d)
Question 2.
Which goods and services are included in calculation of national income in India ?
(a) Intermediary goods and services
(b) Semi-finished goods and services
(c) Finally consumed goods and services
(d) Raw material
Answer:
(c)
Question 3.
In which method of calculation of National income, possibilities of double counting is more ?
(a) Expenditure method
(b) Production method
(c) Income method
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b)
Question 4.
Which are not the components of calculation of National income by income method ?
(a) Wages and interest
(b) Rent
(c) Mixed income and profit
(d) Goods and services of final consumption
Answer:
(d)
Question 5.
What is included in Green Accounting ?
(a) Irrational industrialization
(b) Higher growth of employment
(c) Loss of environment
(d) Higher growth in personal consumption
Answer:
(c)
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 16 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the methods of calculation of National income ?
Answer:
There are three methods of calculation of national income :
(a) Production or value-added method
(b) Income method
(c) Expenditure method.
Question 2.
Which types of goods and services are included in the calculation of national income ?
Answer:
Finally consumable goods and services.
Question 3.
Which method is used to avoid double counting?
Answer:
Value-added method.
Question 4.
What are the components of Income method for calculating National income ?
Answer:
Following are the components of income method of calculating national income –
- Compensation of employees (wages, salaries)
- Operating surplus (rent, interest, profit)
- Mixed income
- Net factor income from abroad.
Question 5.
What is green accounting ?
Answer:
Green accounting is a type of accounting that attempts to factor environmental costs in the financial result of operations.
Question 6.
What type of distribution of national income increases economic welfare ?
Answer:
Equitable distribution of national income increases economic welfare.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 16 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain in brief the methods of calculation of national income.
Answer:
There are three methods of calculation of national income:
(a) Product method or value added method – It is that method, which measures national income in terms of value addition by each producing enterprise in the economy during an accounting year.
(b) Income method – In this method, national income is measured in terms of factor payments (wages, rent, interest and profit) to the Owners of factors of production (labour, capital and enterprise) during an accounting year.
(c) Expenditure method – According to this method, national income is measured in terms of expenditure on the purchase of final goods and services produced in the economy during an accounting year.
Question 2.
How is value added method useful in avoiding double counting? Explain with an example.
Answer:
To avoid double counting in value added method, only the value of final consumable goods is added to find the correct value at every step. The expenditure made on factors of production is reduced from value of product.
Example : Production of bread includes three parties-baker, flourseller, and farmer. The value of product is calculated as follows :
Market value of bread = ₹ 30
Value of flour = ₹ 25
Value of wheat = ₹ 20
The production value of bread = Value of wheat + (value of flour – value of wheat) + (value of bread – value of flour)
= ₹ 20 + (₹ 25 – ₹ 20) + (₹ 30 – ₹ 25)
= ₹ 20 + ₹ 5 + ₹ 5
= ₹ 30 (This will be added to national income)
If we add the value of products of all the three parties (i.e. ₹ 30 + ₹ 25 + ₹ 20 = ₹ 75), then the value of production which we get is faulty.
Question 3.
Explain in brief the calculation of national income by income method.
Answer:
In order to calculate national income by income method, the income of resources used in production process is added up. There are five factors of production – Land, labour, capital, organisation and enterpreneurship (courage). The returns of these five factors are received in the .form of rent, wages, interest, salary and profit respectively. Thus, all these five returns are added up to calculate gross national income.
Question 4.
What are the problems in calculation of National income ? Explain in brief.
Answer:
Many problems occur in the calculation of national income. On account of illiterate people of under-developed nations and due to the popularity of barter system, many transactions happen outside the market system and the government has no information about them. Thus, we cannot get accurate information about national income in these countries. Moreover, we face the problem of double counting in national income.
Question 5.
Explain the relationship between economic welfare and distribution of national income.
Answer:
There is a close relationship between national income and economic welfare. Generally, both are directly related which means, when national income increases, economic welfare also increases, and vise versa. Distribution of national income also affects economic welfare. An equitable distribution of national income increases economic welfare, whereas an inequitable distribution lowers economic welfare.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 16 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain in detail the methods of calculation of National income.
Answer:
National income means the monetary value of all the goods and services produced in a country in a year. Net factor income from abroad is called national income. National income (NNPFC) is calculated by adding net factor income from abroad to net domestic income (NDPFC). There are three
methods of calculation of national income :
(a) Production method or value-added method
(b) Income method
(c) Expenditure method
(a) Production method or value added method – In this method, we measure national income in terms of value addition by each producing enterprise in the economy during a year plus net factor income from abroad. In this method, value addition plays an important role, which means the difference between value of final goods of an enterprise and the value of its intermediate goods.
Value addition = Value of output – value of Intermediate consumption (goods)
Following table illustrates the concept of value addition:
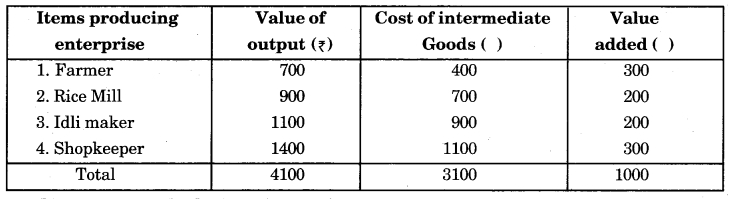
(b) Income method – According to this method, national income is measured in terms of factor payments to the owners of factors of production during an accounting year. In this method, factor income plays an important role, which means income earned by a person or resource as a reward for rendering his/its factor service.
Components of factor income and their returns (incomes) are :
- Land – rent
- Labour – wages
- Capital – interest
- Organisation – salaries
- Entrepreneurship – profit
Thus : Gross National income = Rent + wages + interest + salary + profit
(c) Expenditure method – In this method, national income is measured in terms of expenditure on the purchase of final goods and services produced in the economy during an accounting year. In this method, final expenditure plays an important role in measuring of national income. Final expenditure comprises of Investment expenditure (I) and Consumption expenditure (C).
For computation of national income, the main components of expenditure done in a country are :
(a) Private consumption expenditure
(b) Investment
(c) Government expenditure
(d) Net export (Total Exports – Total Imports)
(e) Depreciation
By Formulae :
Gross National Expenditure (GNE) = C + I + G + NE + D
C = private consumption expenditure;
I = investment; G = government expenditure;
NE = net export; D = depreciation
Question 2
Explain in detail the calculation of national income by production method.
Answer:
This method is used to measure national income in different phases of production in the circular flow. It shows the contribution (value added) of each producing unit in the production process.
Every individual enterprise adds certain value to the products, which it purchases from some other firm as intermediate goods. When value added by each and every individual firm is summed up, we get the value of national income.
Concept of value added – Value added refers to the addition of value to the raw material (intermediate goods) by a firm by virtue of its productive activities. It is the contribution of an enterprise to the current flow of goods and services. It is calculated as the difference between value of output and value of intermediate consumption.
Value added = Value of output – Intermediate consumption
Example of concept of value addition :
Suppose a baker needs only flour to produce bread. He purchases flour as input worth ₹ 500 from the miller and then by virtue of its productive activities converts the flour into bread and sells the bread for ₹ 700. In this, flour is an input (intermediate good) and its value of ₹ 500 is termed as value of ‘intermediate consumption’. Bread is the output and its value of ₹ 700 is termed as ‘value of output’. Difference between the value of output and intermediate consumption is termed as ‘value added’. It means, that the baker has added a value of ₹ 200 to the total flow of final goods and services in the economy.
Question 3.
Explain in detail the calculation of national income by expenditure method.
Answer:
Factor income earned by factors of production is spent in the form of expenditure on purchase of goods and services produced by firms. This method measures national income as the sum total of final expenditures incurred by households, business firms, government and foreigners. This total final expenditure is equal to gross domestic product at market price, i.e. ∑ Final expenditure = GDPMP. This method is also known as ‘Income Disposal Method.
Components of Final expenditure : Expenditure is done by all the sectors of an economy, households, government, firms and foreign sector. The various components of final expenditure are :
1. Private final Consumption expenditure (PFCE) – It refers to expenditure incurred by households and private non-profit institutions providing all types of consumer goods, i.e. durable, semidurable goods and consumer services to the households.
2. Government Final Consumption Expenditure (GFCE) – It refers to the expenditure incurred by the government on various administrative services like defense, law and order, education, etc.
3. Gross domestic capital formation (GDCF) or Gross investment – It refers to the addition to capital stock of the economy. It represents the expenditure incurred on acquiring goods for investment by the production units located within the domestic territory.
4. Net Exports (X – M) – It refers to the difference between export and imports of a country during a period of one year.
The steps included in calculating national income by expenditure method are :
STEP I : Identify the economic units incurring final expenditure. All the economic units, which incur final expenditure within the domestic territory are classified under four groups :
- Household sector
- Government Sector
- Producing Sector
- Rest of the world.
STEP II : Classification of final expenditure : Final expenditures incurred by the above mentioned economic units are estimated and classified under the following heads :
(a) Private final consumption expenditure (PFCE)
(b) Government final consumption expenditure (GFCE)
(c) Gross domestic capital formation (GDCF)
(d) Net exports (X – M)
The sum total of four components of final expenditure gives gross domestic product at market price. (GDPMP).
i. e. GDPMP = PFCE + GFCE + GDCF + (X – M)
STEP III : Calculate domestic income (NDPFC)
By subtracting the amount of depreciation and net indirect taxes from GDPMP, we get domestic income, i.e.
NDPFC = GDPMP – Dep – NIT
STEP IV : Estimate net factor income from abroad (NFIA) to arrive at national income: In the final step, NFIA is added to domestic income to arrive at national income.
National Income NNPFC = NDPFC + NFIA
Question 4.
Increase in national income increases economic welfare. Do you agree ?
Answer:
National income and economic welfare have direct relation, which means economic welfare increases with the increase in national income and vice-versa. Economic welfare refers to that welfare which can be measured in terms of money. Increase in economic welfare by rise in national income can be clarified from the following points :
(i) Employment and development : Opportunities of employment increase due to rise in national income which increases effective demand. It increases the income of citizens which makes them capable to fulfil their needs. It increases economic welfare.
(ii) Effect of distribution of income : If the distribution of income is equitable in the country, the economic welfare increases, and unequal distribution of income reduces economic welfare.
(iii) Indicator of national prospertiy : Rise in national income is an indicator of national prosperity because it increases the purchasing power of citizens so that they can buy more goods which raises thier living standard.
(iv) Ways to spend the income : Economic welfare depends upon the way of spending income. If people spend most of their income on luxurious goods, then economic welfare reduces.
(v) Effects on environment: If the increased national income is spent on new goods, it has adverse affects on environment because pollution increases and it also adversely affects public health. Thus, economic welfare starts declining.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 16 Other Important Questions – Answers
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 16 Multiple-Choice Questions
Question 1.
Income earned in foreign countries is ……………………….. in counting national income.
(a) added
(b) not added
(c) deducted
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a)
Question 2.
Duration of calculating national income is :
(a) Every day
(b) Every month
(c) Every year
(d) Every ten years
Answer:
(c)
Question 3.
There is no practical, problem in the calculation of national income :
(a) True
(b) False
(c) Not sure
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b)
Question 4.
National income can be expressed as :
(a) Private income
(b) per capita income
(c) Real disposable income
(d) Private real income
Answer:
(b)
Question 5.
Environment modified national income is calculated by :
(a) Adding environmental loss in national income
(b) Deducting environmental loss from national income
(c) Over looking environmental loss
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b)
Question 6.
In calculating national income from income method :
(a) Factor income is considered
(b) Factor income is not considered
(c) Value of production is considered
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a)
Question 7.
Equal distribution of national income :
(a) Reduces economic welfare
(b) Increases economic welfare
(c) No change in economic welfare
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b)
Question 8.
Green accounting is associated with :
(a) Sustainable development
(b) Adding environmental loss in national income
(c) Environment modified national income
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c)
Question 9.
Circular flow indudes :
(a) Monetary flow
(b) Real flow
(c) Both (a) & (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c)
Question 10.
Net export means :
(a) Summation of import and export
(b) Value of export
(c) Difference of import and export
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c)
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 16 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by final consumable goods ?
Answer:
Those goods which are used to fulfil the needs of a consumer are called final consumable goods.
Question 2.
What do intermediary goods mean ?
Answer:
Goods which are used in production process.
Question 3.
What is Depreciation ?
Answer:
Loss in value of machines, tools, etc. because of their continuous use or wear and tear is called depreciation.
Question 4.
What is the remuneration/return of labour ?
Answer:
Wages.
Question 5.
What are factor inputs ?
Answer:
Land, labour, capital, organisation and entrepreneurship are factor inputs.
Question 6.
What is meant by investment ?
Answer:
Expenditure made for production is called investment.
Question 7.
What are non-durable goods ?
Answer:
Those goods which can be used only once.
Question 8.
What are durable goods ?
Answer:
Goods which can be used many times.
Question 9.
What are savings ?
Answer:
Part of income which is not Spent on consumption and kept aside for future use.
Question 10.
What is private income ?
Answer:
Income earned from various sources by individuals and households.
Question 11.
Explain government expenditure.
Answer:
Money spent by government on different activities.
Question 12.
What do you mean by import ?
Answer:
Goods purchased from other countries.
Question 13.
What is export ?
Answer:
Goods sold to other countries.
Question 14.
What is national income ?
Answer:
Monetary value of all the final goods and services produced in a country in a year is called national income.
Question 15.
What is per capita income ?
Answer:
National income divided by total population of a country is called per capita income.
Question 16.
Why only final value of goods and services is taken in counting of national income ?
Answer:
To avoid double counting.
Question 17.
What is transfer income ?
Answer:
Income recieved without the exchange of goods and services-for example- scholarship.
Question 18.
Is transfer income countable for national income ?
Answer:
No, it is not included.
Question 19.
Why is national income calculated ?
Answer:
It is calculated for economic analysis, future prediction and policy making.
Question 20.
Write two problems in counting national income.
Answer:
Illiteracy and barter system.
Question 21.
Which method is adopted to avoid dual counting of national income ?
Answer:
Value-added method.
Question 22.
Final goods can be divided in how many parts ?
Answer:
It can be divided in two parts :
- Consumption goods
- Capital goods.
Question 23.
What does rise in national income indicate ?
Answer:
It indicates increase in economic welfare.
Question 24.
What do you mean by production ?
Answer:
Creation of utility in goods is called production.
Question 25.
What is meant by Net National Income ?
Answer:
Deduction of depreciation from Gross national product generates Net National Income.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 16 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-I)
Question 1.
Why is national income calculated ?
Answer:
Calculation of national income helps in economic analysis. On the basis of it, government can predict future uncertainties and can make policies which can be applied effectively.
Question 2.
What is gross national product ?
Answer:
Market value of all the final goods and services produced in an economy plus net factor income from abroad in an accounting year is called gross national product.
Question 3.
What is meant by depreciation ?
Answer:
Due to continous use or wear and tear of machinery, tools and other capital goods, the reduction in thier value is called depreciation.
Question 4.
What is the production method of calculating national income ?
Answer:
In the production method of calculating national income, the market value of final goods and services produced by agriculture, minerals, industries and various services is calculated out and added to find the national income.
Question 5.
What is value added method ?
Answer:
To avoid double counting, exact value of production is calculated at every step. The expenditure on factor inputs is deducted from production value to find its exact value. This method is called value-added method.
Question 6.
What are durable goods ?
Answer:
The goods which can be used many times during their lifetime are called durable goods. For example – furniture, machines, etc.
Question 7.
What are non-durable goods ?
Answer:
The goods which perish only after a single use are called non-durable goods. For example- milk, fruits, bread, etc.
Question 8.
What are final goods ?
Ans.
The goods which are ready do be consumed and are not to be passed through any other process of production. For example – Furniture, bread, etc.
Question 9.
What is meant by intermediary goods ?
Answer:
The goods which are to be passed through the process of production before reaching a consumer are called intermediary goods.
For example -Wool used for knitting sweater.
Question 10.
What precautions should be taken while counting national income from income method ?
Answer:
For correct computation of national income by income method, following precautions should be taken :
- Only factor incomes which are earned by rendering productive services are included. All types of transfer income like old age pension, etc. are excluded.
- Sale and purchase of second-hand goods are excluded, but commission paid on sale of second-hand goods is included.
- Imputed rent of owner-occupied dwellings and value of production for self consumption is included, but value of self consumed services like those of housewife is not included.
- Incomes from illegal activities like smuggling, black marketing, etc. as well as windfall gains (eg from lotteries) Eire excluded.
- Direct taxes such as income tax and corporate tEix are included. Similarly, indirect taxes like GST, excise duties are excluded.
Question 11.
Write the major components of expenditure method to calculate national income.
Answer:
Following are the four major components of expenditure to calculate national income:
- Private consumption expenditure
- Investment expenditure
- Government expenditure
- Net export.
Question 12.
What is included in private consumption expenditure ?
Answer:
The following are to be included- in private consumption expenditure :
- Expenditure on non-durable goods
- Expenditure on durable goods
- Expenditure on consumer services.
Question 13.
Explain the concept of investment.
Answer:
Investment is Em expenditure made for production. It increases the stock of capital. It has four types :
- Fixed business investment
- Investment on inventories
- Investment on building construction
- Government investment
Question 14.
Describe net export expenditure.
Answer:
It is calculated from the difference of export and import in a certain period of time. Net export expenditure is added while calculating national income by income method.
Question 15.
Which factors are necessary for sustainable development ?
Answer:
Two factors are necessary for sustainable development of an economy :
- Equitable distribution of national income
- Favourable environmental condition.
Question 16.
Write two features of national income.
Answer:
Two features of national income are :
- It is calculated for a certsun time, mainly for one year.
- It is related with the annual income of a specific country.
Question 17.
Write two points of difference between final goods and intermediary goods.
Answer:
Following are two points of difference between final goods and intermediary goods :
- Final goods are demanded by consumers, whereas intermediary goods are demanded by producers.
- Market value of final goods is included in national income, whereas market value of intermediary goods is not included in national income.
Question 18.
Describe the concept of private income.
Answer:
It is the sum total of the income of households from all the sources. It includes factor income from abroad and transfer income also.
Question 19.
What is government expenditure ?
Answer:
Expenditure on welfare activities like-education, medical aid, defence, law and order, etc. made by government is called government expenditure. It also includes government consumption expenditure, fixed capital consumption and employee remuneration payment.
Question 20
Which expenses are not included in government expenditure for calculating national income ?
Answer:
Many transfer payments made by government which are non-productive are excluded from national income, e.g. : old-age pension, widow pension, scholarship, etc.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 16 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-II)
Question 1.
Describe the production method of calculating national income.
Answer:
In most countires, national income is calculated by the production method. It is also the simplest way of calculating national income. A list of produced consumable goods and services is prepared, in which names of goods or services, produced quantity and market price is written. The quantity of final produced goods and services is multiplied by their respective price to calculate the total value of production. The stun total of values thus obtained is called national income.
Question 2.
Describe the components of factors of production included in the income method of calculating national income.
Answer:
In the income method of calculating national income, various components of income of production factors are:
- wages
- interest
- rent
- salary commission, etc.
- profit.
The returns obtained upon complete distribution of production is the income of production factors. The income of owners of factors of production is gross income. The sum total of this gross income is called gross national income.
Question 3.
Explain briefly the expenditure method of national income.
Answer:
In this method, national income is calculated in terms of expenditure on the purchase of final goods and services produced in the economy during an accounting year.
Measurement of national income using expenditure method:
The sum total of capital consumption expenditure, private capital investment to increase production, government expenditures, net foreign expenditures and depreciation is found. Transfer expenditures are not included in calculation of national income, since these are not economic transactions.
Question 4.
Describe the hindrances in the calculation of national income.
Answer:
The following hindrances appear in the calculation of national income :
- Widely used barter system in some countries.
- Lack of accurate data due to illiteracy.
- Biased or altered information/data.
- Difficulty in getting information.
- Double counting of income.
Question 5.
Write a short note on Green Accounting.
Answer:
Nowadays, economic welfare is associated with environment. A new terminology “Green Accounting” is being used. Under green accounting, loss in environment is studied. Loss of environemnt is deducted from national income and environment modified national income is determined.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 16 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain in detail the problems in calculating the National Income.
Answer:
There may be many difficulties in calculation of national income, which are stated as follows : .
(a) Theoretical difficulties
(b) Practical difficulties
(a) Theoretical difficulties – Various theoretical or conceptual difficulties are faced in calculating the national income. There is no particular policy regarding the concept of national income. It is difficult to determine which services are to be included in national income and which are not. Only those services are added which can be measured in monetary terms.
(b) Practical difficulties –
(i) Barter System : Barter system eliminates the true value of transactions because there is no integrity in barter transactions. In some parts of country, it is still in practice.
(ii) Unreliable and insufficient data : Most of the data available is either faulty, false, incomplete or insufficient. Data of unorganised sector is either unavailable or not reliable. Thus, national income cannot be measured correctly.
(iii) Double counting : Many times, it becomes difficult to understand the difference between interihediary and final goods and it leads to double counting of the value of one product. Therefore, we cannot compute the national income accurately.
(iv) Illiteracy and Superstition : Because of illiteracy and superstition, people do not provide correct information about their business or income and it becomes difficult to accumulate data.
(v) Black money : It is the money which is kept unspent, like unpaid tax. Information about this money is either not visible or is incomplete, which prevents the exact calculation of national income.
(vi) Depreciation : Depreciation cannot be ascertained accurately, and thus, capital goods are also not valued properly.
(vii) No proper accounting : Farmers and small businessmen do not maintain proper accounts due to illiteracy. So, the information remains incomplete.
(viii) Lack of public cooperation : People do not co-operate in the collection of data, so the information either is faulty or remains incomplete.
Question 2.
Explain in detail the income method for calculating national income.
Answer:
Income method calculates national income from the perspective of factor income. Under this method, income received by all the residents of a country for their productive services during a year are added up to obtain the national income. According to this method, all the incomes that accrue to the factors of production by way of wages, profits, rent, interest, etc. Eire summed up to obtain the national income. Income method is also known as “Distributive Share Method’ or ‘Factor Payment Method’ :
Components of Factor Income :
1. Compensation of employees (COE) : COE refers to amount paid to employees by employer for rendering productive services. It includes all the payments and benefits, which the employees receive directly or indirectly from the employer.
2. Rent and Royalty: Rent is that part of national income which arises from ownership of land and building. Rental income includes both actual rents as well as imputed rent.
Royalty refers .to income received by the owners for granting rights of use of assets. For example, owners of mineral deposits can earn income by giving rights of mining to the contractors.
3. Interest : Interest refers to the amount received for lending funds to a production unit. It includes both actual interest as well as imputed interest of funds provided by the enterpreneur.
4. Profit: Profit is the reward to the enterepreneur for his contribution to the prouction of goods and services. It is the residual income, which an entrepreneur earns after paying all the other factors of production.
5. Mixed income : It is the income generated by self-employed workers (like farmers, barbers, etc) and unincorporated enterprises (like retail traders, small shopkeepers, etc.). It is the term used for any income that has elements of more than one type of factor income.
Steps Of Income Method :
The various steps involved in estimating national income by income method are :
STEP 1 : Identification and classification of the production units :
All the producing enterprises employing various factors of production are identified and classified into primary, secondary and tertiary sectors.
STEP 2 : Estimating the factor income paid by each sector :
The factor incomes paid by each sector are classified under the following heads :
- Compensation of employees
- Rent and Royalty
- Interest
- Profit
- Mixed income
STEP 3 : Calculating domestic income (NDPFC) :
When factor incomes of all the sectors are summed up, we obtain domestic income (NDPFC).
In Short, NDPFC
= Compensation of employees
+ Rent and Royalty
+ Interest
+ Profit
+ Mixed income
STEP 4 : Estimating net factor income from abroad (NFIA) to arrive at national income :
In final step, NFIA is added to domestic income to arrive at national income (NNPFC). In short, NNPFC
= NDPFC
+ NFIA