Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 19 Central Bank: Functions and Credit Control
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 19 Practice Questions
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 19 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Bank rate means :
(a) The rate at which commercial bank advances loans.
(b) The rate at which central bank rediscounts the bills of commercial banks.
(c) The rate at which moneylenders advance loans to commercial banks.
(d) The rate at which banks advances loans to public.
Answer:
(b)
Question 2.
Which of these is not a qualitative measure of credit control ?
(a) Rationing of credit
(b) Moral persuasion
(c) Open market operation
(d) Direct action
Answer:
(c)
Question 3.
Which of these is the main function of the central bank ?
(a) Issue of currency
(b) Accepting direct deposit from public
(c) Advancing loans to public
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a)
Question 4.
Central bank of India is :
(a) State Bank of India
(b) Reserve Bank of India
(c) Union Bank
(d) Syndicate Bank
Answer:
(b)
Question 5.
Who signs on the one rupee note ?
(a) Governor
(b) Prime Minister
(c) Finance secretary
(d) Finance minister
Answer:
(c)
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 19 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define central bank.
Answer
The central bank is an apex bank. It controls the entire banking system of a country. It is the sole agency of currency issue and controls the supply of money in the economy.
Question 2.
What do you mean by bank rate ?
Answer:
Bank rate is the rate at which central bank makes credit available to the commercial banks.
Question 3.
What do you mean by rationing of credit ?
Answer:
Rationing of credit refers to the fixation of credit quotas for different business activities.
Question 4.
Write the name of Central Bank of India.
Answer:
The name of central bank of India is ‘Reserve Bank of India’.
Question 5.
Write the name of the monthly bulletin published by RBI.
Answer:
The name of monthly bulletin published by RBI is ‘RBI Bulletin’.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 19 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the function of currency issue of central bank.
Answer:
Central bank has a legal right to issue and circulate the currency of the country. Monopoly of note issue rests with the RBI. It brings uniformity in currency. This makes it easier to control and regulate credit in accordance with the requirements in the economy. During the issue of currency, the central bank should keep in mind to issue it according to the needs of the country, neither less nor more. Issuing more money would result in inflation, while less issuing of money can result in deflation.
Question 2.
Write down the quantitative measures adopted by the central bank to control credit.
Answer:
Following are the quantitative measures adopted by the central bank to control credit:
- Bank rate policy
- Open market operations
- Variation of Cash Reserve Ratio
- Variation of Statutory Liquidity Ratio.
Question 3.
Explain the direct action adopted by the central bank.
Answer:
Direct action is adopted by the central bank when commercial banks do not follow the methods and polices suggested by the central bank and issued by it from time to time. In such, an event, it has legal right to take direct action. In direct action, the central bank may refuse rediscounting of bills, or charge a huge rate of interest on it. In this way, commercial banks have to start following the norms suggested by the Central Bank.
Question 4.
Explain through a flow chart the central board of directors of RBI.
Answer:
There are total twenty members in the central board of directors of RBI.

Question 5.
Write down the names of any four publications of RBI.
Answer:
Following are the names of four publications of RBI:
- Manual on currency and banking statistics (annual).
- Monitor policy report of banking (Half yearly).
- Financial stability report (Half yearly).
- Statistics on deposits and credit of scheduled commercial banks (Quarterly report).
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 19 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Define central bank and explain its main functions in detail.
Answer:
The central bank is an apex bank. It controls the entire banking system of a country. It is the sole agency of note issuing and controls the supply of money in the economy. It serves as a banker to the government and manages forex reserves of the country. There is no standard definition of a central bank. The definition depends on the functions it discharges. The common function is that it controls and manages the flow of credit and supply of money in the economy. Important definitions of Central bank are :
- According to S. C. L. Day, “Central bank is that bank which helps in controlling and stabilizing the monetary and Banking system.”
- According to Sameuelson,”Every central bank has one function. It operates to control economy, supply of money and credit.”
- According to Hartrey, “Central bank works as a centre of last resort to the other banks”.
- According to Shaw, “Central bank is the bank which has its control on country’s credit”.
Functions of central bank :
(i) Bank of issuing notes : Central bank of a country has the exclusive right of issuing notes. This is called currency authority function of the central bank. The notes issued by central bank have an unlimited legal tender.
(ii) Banker to the Government: Central bank is a banker, agent and financial advisor to the government. As a banker to the government, it manages accounts of the government. As an agent to the government, it buys and sells securities on behalf of the government. It also manages loans of the government.
(iii) Banker’s bank and supervisory role : As a banker’s bank, it has almost the same relation with other banks in the country as a commercial bank has with its customers. It accepts deposits from the commercial banks and offers them loans.
The rate at which the central bank offers loan to the commercial bank is called ‘Repo rate’.
(iv) Custodian to foreign exchange : Central bank is the custodian of the nation’s foreign exchange reserves. It manages floating to ensure stability of exchange rate in the international money market. It also maintains a stability in the financial rate.
(v) Clearing house function : As a custodian of cash reserves of the commercial banks, the central bank acts as a clearing house for these banks. It means settling the claims of various banks against one another with minimum use of cash.
(vi) Control of credit: Another important function of the central bank is to control the supply of credit in the economy. It implies increase or decrease in the supply of money in the economy by regulating the ‘creation of credit’.
Question 2.
Explain in detail the measures adopted by the central bank to control credit.
Answer:
Following are the measures adopted by the central bank to control credit :
(i) Bank rate : Bank Credit is controlled by the increase or decrease in bank rate. When credit in the country needs to be expanded then RBI credit bank rate is increased. Loan gets cheaper when bank rate is lower, making the demand of loans higher. On the contrary, when bank rate is higher, loan gets costlier, making their demand lesser.
(ii) Repo rate : Repo rate is the rate at which the central bank of a country (Reserve Bank of India, in case of India) lends money to the commercial banks in the event of any short-fall of funds. Repo rate is used by monetary authorities to control inflation.
(iii) Reverse repo rate : It is the rate at which the central bank of a country (Reserve Bank of India, in case of India) borrows money from commercial banks within the country. It is a monetary policy instrument which can be used to control the money supply in the country.
(iv) Cash reserve ratio (CRR) : It is a certain minimum amount of deposits that the commercial banks have to hold as reserves with the central bank. CRR is set according to the guidelines of the central bank of a country.
If credit needs to be expanded, then CRR is decreased, and credit can be contracted when CRR is increased.
(v) Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) : It is an Indian government condition for reserve requirements that the commercial banks in India require to maintain in the form of cash, gold, government approved securities before providing credit to the customers. The SLR is determined by a percentage of total demand and time liablities.
Question 3.
Explain in detail the monetary measures of the Reserve Bank of India.
Answer:
Instruments of monetary policy of the central bank are broadly classified as :
(a) Quantitative methods
(b) Qualitative methods.
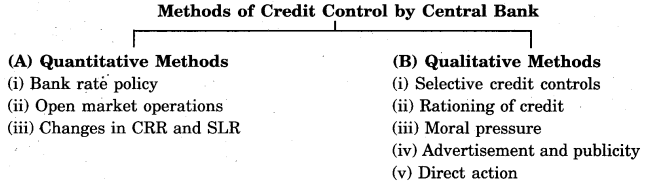
(A) Quantitative methods : Under this method, the central bank tries to control credit by influencing the total quantity of credit in the country. Following are the measures of quantitative methods :
(i) Bank rate policy : Bank rate is the rate charged by the Central bank on its loans that it advances to a commercial bank against the securities. When Central bank needs to expand the credit then Bank rate is decreased and when it is needed to contract the credit, bank rate is increased. It directly affects the loan giving ability of the central bank. It is the easiest way of credit control.
(ii) Open market operations : Open market operations refer to the buying and selling of government securities by the central bank from the public or banks. When government wants to contract credit, the central banks start selling securities to the commercial banks, and when they want to expand credit, the central bank starts buying the securities. Buying the securities results in more money with the banks and they have more capability to advance loans. Similarly, selling the securities to the bank leaves them with less cash reserves, by which they become less capable for advancing loans.
(iii) Change in (CRR) Cash Reserve Ratio : Under CRR, the banks are required to deposit with the central bank a percentage of their net demand and time liablities in the form of liquidity or cash. Banks reduce the percentage of deposits if they want to expand the credit, and they raise the percentage if they want to contract the credit.
(iv) Change in (SLR) Statutory Liquidity Ratio : The SLR requires the banks to maintain a specified percentage of their net total demand and time liablities in the form of designated liquid assets with itself.
(B) Qualitative methods : Under this method, selective methods of credit control are meant to regulate and control supply of credit among its possible users and uses. Following are the qualitative methods adopted by the central bank for credit control :
(i) Selective credit control: Central banks adopts the selective credit control measures for specific sectors and specific requirements.
(ii) Credit rationing: Rationing of credit refers to the fixation of credit quotos for different business activities. Under this method, commercial banks cannot advance loans more than such limits.
Credit Rationing can be done in the following ways:
(i) The comfort of discounting the bill by any bank would be demolished.
(ii) Stating a limit on re-discounting of bills of the bank.
(iii) Applying a quota or stating a limit on the loans provided to the various businesses and industries.
(iii) Moral suasion: It means advising, requesting and persuading the commercial banks to co-operate with the central bank in implementing its general monetary policy. The central bank may request the commercial banks not to grant the loans for their speculative purposes.
(iv) Publicity: Central banks in modem time control the credit by publishing magazines, journals, bulletins, etc. In these publications, the central bank puts forward the type of policies to be adopted.
(v) Direct action: If commercial banks do not follow the methods and policies suggested by central bank issued from time to time, then Central Bank has legal power to take direct action.
Direct Action – Under this, Central bank puts a stop on the loan advancing policy of such banks, and do not re-discount their business bills. Also, it charges a high rate of interest. By applying such measures, commercial banks are forced to follow the rules applied by the central banks.
Question 4.
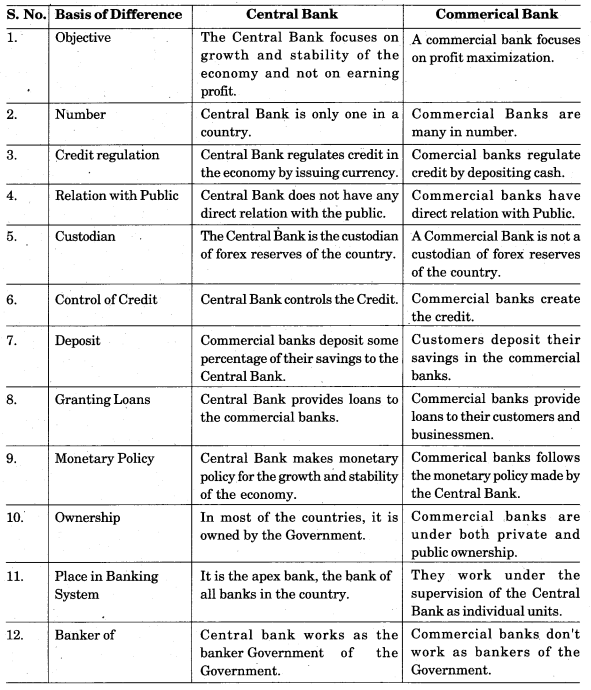
Compare central bank and commercial bank on the basis of their functions.
Answer:
Points of differences between central bank and commercial banks on the basis of their functions are as follows :
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 19 Other Important Questions – Answers
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 19 Multiple-Choice Questions
Question 1.
Main directive principle of the central bank is:
(a) Earning profit
(b) Benefit of the nation
(c) Performing general banking functions
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b)
Question 2.
The function of Central bank is:
(a) Issuing the notes
(b) Banker’s bank
(c) Government’s banker
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d)
Question 3.
By increasing bank rate:
(a) Credit expands
(b) Credit declines
(c) Credit remains unchanged
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b)
Question 4.
Banks keeps cash deposits with:
(a) Central bank
(b) Themself
(c) Government
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b)
Question 5.
Bank rate means:
(a) Interest rate of banks
(b) Exchange rate
(c) Reserve bank rates
(d) Market rates
Answer:
(c)
Question 6.
Selective credit control means:
(a) Applying liberal method of credit control
(b) Applying rigid method of credit control
(c) Applying different methods for different sectors
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c)
Question 7.
Qualitative credit control includes:
(a) Rationing of credit
(b) Publicity
(c) Moral Suasion
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d)
Question 8.
In India, currency and credit is controlled by:
(a) State Bank of India
(b) Punjab National Bank
(c) Reserve Bank of India
(d) Co-operative Bank
Answer:
(c)
Question 9.
Instruments of monetary policy are:
(a) Bank rate
(b) Cash reserve ratio
(c) Statutory liquidity ratio
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d)
Question 10.
Which of the following is not a quantitative method of credit control:
(a) Bank rate
(b) Open market operations
(c) Moral suasion
(d) Cash reserve ratio
Answer:
(c)
Question 11.
Reserve bank was established in:
(a) the year 1935
(b) the year 1947
(c) the year 1951
(d) the year 1971
Answer:
(a)
Question 12.
Reserve bank was nationalised in:
(a) the year 1935
(b) the year 1947
(c) the year 1949
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c)
Question 13.
Ownership of Reserve Bank of that India is of:
(a) Shareholders
(b) Government
(c) Commercial Banks
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b)
Question 14.
Headquarters of Reserve Bank of India is in:
(a) New Delhi
(b) Kolkata
(c) Mumbai
(d) Chennai
Answer:
(c)
Question 15.
Repo rate and reverse repo rate is determined by:
(a) State Bank
(b) Reserve Bank
(c) Commercial Bank
(d) Government
Answer:
(b)
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 19 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is Repo Rate ?
Answer:
Repo rate is the rate at which the central bank of a country lends short-term loans to the commercial banks in the event of any shortfall of funds.
Question 2.
What is Reverse Repo Rate ?
Answer:
It is the rate at which the central bank of a country borrows money from the commercial banks within a country.
Question 3.
What is Statutory Liquidity Ratio ?
Answer:
Statutory liquidity ratio means every commercial banks have to maintain a specified percentage of their net total demand and time liablities in the form of designated liquid asset with them self.
Question 4.
What is cash reserve ratio ?
Answer:
Cash reserve ratio means depositing a percentage of the net demand and time liabilities in the form of liquidity or cash by banks with the central bank.
Question 5.
When is an increase made in cash reserve ratio ?
Answer:
When central bank wants to contract the credit.
Question 6.
What is the effect of increase in statutory liquidity ratio ?
Answer:
It decreases the credit.
Question 7.
In which year was the Reserve Bank of India established ?
Answer:
In the year 1935.
Question 8.
Who is the chief officer of Reserve Bank of India ?
Answer:
Governor is the chief officer of R.B.I.
Question 9.
How many members are there in central board of Reserve Bank of India ?
Answer:
There are twenty members in central board of Reserve Bank of India.
Question 10.
How many deputy governors are there in Reserve Bank of India ?
Answer:
There are four deputy governors in Reserve Bank of India.
Question 11.
What do you mean by monetary policy ?
Answer:
Monetary policy means the policy which regulates and controls money and credit.
Question 12.
Mention the two main functions of central bank.
Answer:
Two main functions of central bank are :
- Note issuing authority
- Banker of Banks
Question 13.
Write two objectives of Central bank.
Answer:
- Maintaining the public confidence in banking system.
- Preserver of depositor’s benefits.
Question 14.
Write two differences between central bank and commercial bank.
Answer:
- Central bank focuses on growth and stability of the economy, whereas commercial banks focus on profit maximisation.
- Central bank accepts deposits and advances loans to the commercial banks, whereas commercial banks accept deposits and advance loans to the general public.
Question 15.
Write one objective of credit control.
Answer:
One objective of credit control is to put a stop on business cycles.
Question 16.
What do you mean by open market operations ?
Answer:
Open market operations refers to the buying and selling of government securities by the central bank from public or banks.
Question 17.
What is meant by rationing of credit ?
Answer:
Rationing of credit refers to the fixation of credit quotas for different business activities.
Question 18.
Which method is adopted by the central bank for issuing notes ?
Answer:
The method used for issuing notes by central bank is Minimum Reserve System.
Question 19.
How many regional offices of Reserve Bank of India are there in India ?
Answer:
There are four regional offices of Reserve Bank of India, situated in Mumbai, New Delhi, Chennai and Kolkata.
Question 20.
Who regulates monetary policy in India ?
Answer:
In India, monetary policy is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
Question 21.
How many non-government directors are there in RBI board of directors ?
Answer:
There are twelve non-government directors in RBI board of directors.
Question 22.
What is the function of reserve bank as a banker of banks ?
Answer:
Reserve bank accepts deposits from the commercial banks and offers them loans. The central bank regulates and controls all the activities of commercial banks. It works as the lender of last resort to the banks.
Question 23.
How much fund is kept by the Reserve Bank for issuing notes through minimum reserve system?
Answer:
₹ 200 crore fund is kept by the Reserve Bank in which 115 crore gold and 85 crore foreign securities are kept.
Question 24.
What is the name of central bank of America ?
Answer:
Name of central bank of America is ‘Federal Reserve Bank’.
Question 25.
The establishment of RBI has been done under which act ?
Answer:
The establishment of RBI has been done under the provisions of Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
Question 26.
“There have been three great inventions in the world – fire, wheel and central banking”. Who said this ?
Answer:
It has been said by Bill Rogers.
Question 27.
Who is the present governor of Reserve Bank of India ?
Ans.
The Governor of India is Uijit Patel.
Question 28.
Does Reserve Bank have a direct connection with the public ?
Answer:
No, Reserve Bank does not have any direct connection with the public.
Question 29.
Who issues notes in India ?
Answer:
In India, one rupee note is issued by the authority and signature of finance secretary of goverment of India and other notes are issued by the Reserve Bank of India.
Question 30.
When was minimum cash ratio system adopted in India ?
Answer:
Minimum cash ratio system was adopted on 6th October 1956 in India.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 19 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-I)
Question 1.
Give historical reference of establishment of central bank.
Answer:
Central bank was established in the seventeenth century, when the first central bank was established in the year 1656 in Sweden. After that, in the year 1664, Bank of England was established. Bank of England is known as the mother of Other central banks because other banks follows the policies of this bank. In the year 1800 in France, in the year 1856 in Netherlands, in 1869 in Russia and in 1875 in Germany, central banks were established. In India, it was established as the Reserve Bank in the year 1935.
Question 2.
Define central bank.
Answer:
Central bank is the apex bank of a country. It controls and regulates the monetary and financial system of the country. Following are a few definitions of the central bank given by different writers :
According to A.C.L. Day, “A central bank is that bank which helps to control and stabilize the monetary and banking system.”
According to Hartrey, “Central bank is the banker’s bank, because it works as a lender of last resort to the various other banks”.
According to Shaw, “Central bank controls the credit of the country”.
Question 3.
Why is establishment of central bank needed ?
Answer:
Establishment of central bank is needed because of the following reasons :
- Bank of issuing notes
- Banker to the government
- Banker’s bank and performing supervisory role
- Lender of the last resort
- Custodian of foreign exchange
- Clearing house function
- Control of credit.
Question 4.
Mention four points of difference between centered bank and commercial bank.
Answer:
Four points of difference between central bank and commercial bank are as follows:
- Central bank is the apex bank-the banker of all banks in the country, whereas commercial banks function under the control of the central bank.
- Every country has only one central bank, but many commercial banks.
- Central bank is a note-issuing authority, whereas commercial bank is not a note issuing authority.
- Central bank focuses on growth and stability of the economy, whereas commercial bank focuses on profit maximisation.
Question 5.
How is central bank a banker’s bank ?
Answer:
The central bank regulates and controls all activities of commercial banks. It performs the function of a banker for all other banks in the country. The central bank essentially keeps a part of the cash reserves of all commercial banks as deposits with a view to meeting liabilities of these banks in the time of crises.
Question 6.
What is the function of central bank as a government’s banker ?
Answer:
The Central bank works as a government’s banker and accepts receipts and makes payments on behalf of the government and carries out exchange remittance and other banking operations. It advises the government on banking and financial matters. It arranges public loan and sells/buys government securities.
Question 7.
Explain the credit control function of the central bank.
Answer:
One of the most important functions of the central bank is to control the credit. The Central bank controls ‘credit creation’, so that the business cycles can be stopped, because business cycle can negatively affect the market system.
Question 8.
What is minimum reserve system ?
Answer:
Under the system, the Reserve Bank of India does not keep cent percent metal (bullion) reserve, but it keeps a reserve of 115 crores in the form of gold and foreign securities worth of 85 crore as a minimum reserve fund with itself. With this reserve fund of minimum 200 crore, the Reserve Bank can issue currency upto unlimited quantity. In our country, it is on this basis that the Reserve Bank can issue 115 crore worth of gold and 85 crore worth of foreign securities.
Question 9.
Why is. central bank to be the said custodian of foreign exchange reserves ?
Answer:
The central bank is the custodian of a country’s stock of gold and international currencies. The central bank maintains the stability of exchange rate fixed by the government, the Central bank also maintains the stability of exchange rate of domestic currency.
Question 10.
How does the central bank influence credit control through bank rates ?
Answer:
The central bank controls credit by making variations in the bank rate. If the need of economy is to expand the credit, the central bank lowers the bank rate, and thus the loans by central bank to commercial banks become cheaper, which makes their credit giving ability more. When the central bank wants to contract credit, it will raise the bank rate which reduces the credit-providing ability of commercial banks.
Question 11.
What are open market operations ?
Answer:
Open market operation refers to the buying and selling of government securities by the central bank from public or banks. Government uses this to control the credit. When the government wants to contract the credit, then the central bank starts selling securities to the commercial banks. When the government wants to expand credit, then the central bank starts purchasing securities from the open market, so that cash reserves of commercial banks become less and their loan-giving ability is reduced.
Question 12.
Differentiate between cash reserve ratio (CRR) and statutory liquidity ratio (SLR).
Answer:
Under cash reserve ratio (CRR), the commercial banks deposit with the central bank a percentage of their net demand and time liabilities in the form of liquidity or cash; whereas, under statutory liquidity ratio (SLR), commercial banks maintain a specified percentage of their net total demand and time liabilities in the form of designated liquid assets with themselves, so that they can easily clear the loans of the public.
Question 13.
How is credit controlled by cash reserve ratio and statutory liquidity ratio by RBI ?
Answer:
If the central bank wants to expand the credit, then it reduces the percentage of both the deposits, and if the central bank wants to contract the credit, then raises the percentage of both the deposits by which the banks have more money to offer loans by which the funds become lesser, and the ability of providing loan of the banks become less too.
Question 14.
What are the qualitative methods of credit control ?
Answer:
Following are the qualitative methods of credit control :
- Selective credit control
- Rationing of credit
- Moral suasion
- Publicity
- Direct action.
Question 15.
How is credit controlled by publicity ?
Answer:
Central bank publishes magzines, journals, bulletins, etc. to influence the activities of commercial banks and also puts forward various policies to meet the challenges associated with the economy. By following the policies and strategies provided by the central bank through publication, the commercial banks control the credit.
Question 16.
What is the credit rationing method of credit control ?
Answer:
Rationing of credit refers to the fixation of credit quotes for different business activities. Under this method, the commercial banks cannot advance loans more than such limits. Credit can be controlled by the central bank by changing such limits.
Question 17.
What do you mean by Direct Action used for credit control by the central bank ?
Answer:
If the commercial banks do not follow the methods suggested and policies of the central bank issued from time to time, than the central bank has legal right to take direct action against them. Under direct action, the central bank may refuse rediscounting of bills, stop providing loans to such banks or charge higher rates of interest from those banks. This creates problems for such commercial banks and then they start following the central bank’s policies and suggestions.
Question 18.
Write two functions of the Reserve Bank.
Answer:
Two functions of the Reserve Bank are :
- Issuer of Currency : RBI issues and exchanges currency and coins not fit for circulation. Its main objective is to give the public, adequate quantity and supply of currency notes and coins of good quality.
- Monetary Authority : It formulates, implements and monitors the monetary policy for the economy of the country. Its main objective is to maintain price stability and ensure adequate flow of credit to all the productive sectors.
Question 19.
What is the task of the Reserve Bank as a government banker ?
Answer:
The Central bank is a banker, agent and financial advisor to the government. As a banker to the government, it manages the accounts of the government. As an agent to the government, it buys and sells securities on behalf of the government. The Central bank offers loans to the government against government securities or treasury bills.
Question 20.
Explain the term Repo Rate.
Answer:
Repo Rate is that rate at which the central bank of a country lends money to the commercial banks in the event of any shortfall of funds. Repo rate allows repurchase of the securities. The holders of securities can repurchase them at a later date. Therefore, repo rate is also called repurchase rate. Repo rates relates to short-term borrowings by the commercial banks. At present, this rate is 6.25%.
Question 21.
What do you mean by reverse repo rate ?
Answer:
It is the rate at which the central bank of a country (Reserve Bank of India, in case of India) borrows money from the commercial banks within the country. It is the monetary policy instrument which can be used to control the money supply in the country. When this rate is increased, banks increase their savings in the central bank, which makes their loan-giving ability weaker. And if this rate is decreased, than banks decrease their savings from the central bank which increases their ability of giving loans. At present, this rate is 5.75%.
Question 22.
What is bank rate ? Explain.
Answer:
The bank rate is a rate at which the central bank lends long-term funds as a lender of last resort to the commercial banks, against approved securities or eligible bills of exchange. The central bank controls credit by making variations in the bank rate. Bank rate does not allow any facility of repurchase of securities. The bank rate is simply the rate of discount.
Question 23.
What are the functions of the Reserve Bank of India as a custodian of foreign exchange ?
Ans.
The central bank is a custodian of the country’s stock of gold and foreign currencies. The central bank maintains the stability of exchange rate fixed by the government. The central bank performs two major functions in the field of foreign exchange : One, it is the custodian of the country’s reserves of international currencies, and second, it maintains stability of exchange rate of domestic currency. In this way, the loans can be fulfilled at the time of need, and the people going to foreign countries are also provided with the required currency.
Question 24.
How is the Reserve Bank of India administered and controlled ?
Answer:
Management and operation of the Reserve Bank of India is in the hands of the central board of directors. There are twenty members in this board. There is one governor and four deputy-governors along with the ten directors nominated by the government and four directors from each regional office and one government officer. Together, they make the structure of the board of Reserve Bank of India.
Question 25.
Explain the structure of regional boards of the Reserve Bank of India in brief.
Ans.
There are four regional boards of the Reserve Bank of India. These are situated in Mumbai, New Delhi, Chennai and Kolkata. There are five members in each board. These members are experts in their fields. There is one head in each board who is elected by every member of the board. The tenure of every member is of five years. Their task is to give timely information and suggestions on important things to the central government.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 19 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-II)
Question 1.
Define Central Bank.
Answer:
A central bank is an apex institution of a country that controls and regulates the monetary and financial system of the country. Following are a few definitions of central bank:
According to M.H. De Kock, “A bank which constitutes the apex of the monetary and banking structure of the country is called a central bank.”
According to A.C.L. De, “A central bank is that which helps to control and stabilize the monetary and banking system.”
According to Samuelson, “A central bank is a banker’s bank and its responsibility is to control monetary base and high power money.”
According to Hawtrey, “Central bank is the Banker’s bank, since it is the lender of last resort to the banks”.
Question 2.
What are the functions of the central bank ?
Answer:
Following are the functions of the central bank:
- Issuing of currency.
- Banker’s bank and controller.
- Banker and adviser to government.
- Custodian of foreign exchange reserves.
- Lender of last resort.
- Clearing house function.
- Regulator and controller of credit.
Question 3.
Differentiate between Central bank and commercial bank.
Answer:
Following are the points of difference between central bank and commercial bank:
- The Central bank is an apex bank which means the banker all the banks in the country.
A Commercial bank functions under the control of the central bank. - The Central bank accepts deposits and advances loans to the commercial banks.
A Commercial bank accepts deposits and advances loans to the general public. - The Central bank regulates the supply of money.
A Commercial bank only contributes to the supply of money. - The Central bank is a custodian of forex reserve of the country.
A Commercial bank is not a custodian of forex reserve of the country. - The Central bank is a note-issuing authority
A Commercial bank is not a note-issuing authority. - The Central bank focuses on growth and stability of the economy.
A commercial bank focuses on profit maximisation.
Question 4.
Which functions of central bank are performed by the Reserve Bank of India ?
Answer:
Following are the functions of central bank performed by the Reserve Bank of India:
(i) Bank of issuing notes : The Reserve Bank of India has the exclusive right of issuing notes, so that a proper maintenance of currency can be done.
(ii) Banker to the government : The Reserve Bank of India is the banker to the government as it manages the accounts of the goverment and buys and sells securities on behalf of the government.
(iii) Banker’s bank : As a banker’s bank, it accepts deposits from the commercial banks and offers them loans. It is their lender of the last resort as it offers loans to the banks to cope with the crises with confidence.
(iv) Custodian of foreign exchange : The Reserve Bank is a custodian of nation’s foreign exchange reserves. The Reserve bank maintains stability of exchange rate fixed by the government.
(v) Clearing house function : It means that the Reserve Bank settles the claims of various banks against one another with minimum use of cash.
(vi) Credit control: The central function of the Reserve Bank of the India is to control the supply of credit in the economy.
Question 5.
What functions of general banks are performed by the Reserve Bank of India.
Answer:
(i) Accepting deposits : The Reserve bank accepts deposits from central government, state government and commercial banks but does not pay any interest.
(ii) Advances loans : The Reserve bank offers loans to the central government and commercial banks.
(iii) Borrows loans : The Reserve bank also borrows loans from commercial and foreign banks.
(iv) Sale and purchase of foreign securities : The Reserve bank also sells and purchases foreign securities. But the date of clearance of these securities should not exceed more than 10 years from the date of purchase.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 19 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the functions of the Reserve bank of India ?
Or
What are the activities performed by the central bank? Explain.
Answer:
Functions of the Reserve Bank of India are divided into two categories:
(a) Central bank functions
(b) General bank functions
(a) Central bank functions of the Reserve Bank of India:
(i) Bank of issuing note : The Reserve bank has a legal right to issue and circulate the currency of the country. Monopoly of note issue rests with the Reserve Bank of India. It brings uniformity in the currency. To make currency notes available in adequate quantity, Reserve bank uses the minimum reserve system. Under this system, RBI keeps a reserve of? 115 crore in the form of gold and foreign securities worth of ? 85 crore as a maximum reserve fund with itself.
(ii) Banker’s bank and controller : The Reserve bank regulates and controls all activities of the scheduled commercial banks. It performs the functions of a banker for all other banks in the country. The Reserve Bank essentially keeps a part of the cash reserves of all commercial banks as financial deposits, with a point of view to meet liabilities of these banks in the time of crises. It also re discounts their bills and keeps an eye on their activities.
(iii) Government’s banker, agent and advisor: The Reserve Bank acts as an associate in achieving higher growth rate of the country. The Reserve Bank accepts receipts and makes payments on behalf of government. It advises the government on banking and financial matters.
(iv) Custodian of foreign exchange reserve : The Reserve Bank is the custodian of a country’s stock of gold and foreign currencies. The Reserve Bank maintains the stability of exchange rate fixed by the government. It buys and sells foreign currency according to the requirement, to maintain the stability.
(v) Clearing house function : The Reserve Bank settles the claims of various banks against one another with the minimum of cash with use of cheque, draft, etc. The Reserve Bank acts as a mediator in payments and funds transfer.
(vi) Regulation and control of credit : The Reserve Bank acts as a controller and regulator of quantity of currency and credit. The total money in circulation and its dynamism directly affects inflation and deflation in a country’s economy. The Reserve Bank uses monetary policy measures for expansion and contraction of credit.
(vii) Publication of Journals : The Reserve Bank publishes magazines, journals, bulletins, etc: In these publications, the Reserve Bank puts forward the type of policies to be adopted to meet the challenges associated with the economy.
(b) General banking functions of the reserve Bank :
- Accepting deposits from central government, state government and commercial banks.
- Borrowing loans from commercial and foreign banks if needed.
- Advancing loans to central government, state governments and commercial banks.
- Sale and purchase of foreign securities.
- Re discounting of commercial bills.
- Sale and purchase, and discounting of foreign bills.
- Opening accounts in foreign banks.
- Providing locker facility.
Question 2.
Explain different methods of credit control adopted by the Reserve Bank of India.
Answer:
There are two methods of credit control adopted by the Reserve Bank of India:
(a) Quantitative method
(b) Qualitative Method
(a) Quantitative method : Under this method, the Reserve Bank tries to control the credit by influencing the total quantity of credit in the country. Following are the quantitative methods :
(i) Bank rate policy: The bank rate is the rate at which the central bank lends funds as a lender of last resort to the commercial banks, against the approved securities or eligible bills of exchange. The Reserve Bank controls credit by making variations in the bank rate upon, increase in bank rate, the loans get costlier, which makes their demand lesser, and credit creation also becomes lesser. On the contrary, while decreasing the bank rate, loans get less expensive and their demand increases, making credit creation more.
RBI has made various changes in the rate after its establishment, but this policy has not been up to the mark. Since 4th October, 2016, the bank rate is 6.75%.
(ii) Open market operations: Open market operations refers to the buying and selling of government securities by the Reserve Bank from the public or commercial banks. To control credit reserve, the bank uses this instrument. To contract the credit in the economy, these securities are sold out which leaves the economy with lesser cash and credit is contracted. To expand the credit, these securities are purchased from the market which makes the flow of cash in the market making greater, which, in turn, expands credit.
(iii) Variation of Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) : Under CRR, the commercial banks are required to deposit with the central bank a percentage of their net demand and time liabilities in the form of liquidity or cash. Thus, a higher CRR reduces credit creation and vice versa.
(iv) Variation of Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR): Under this, the commercial banks are required to maintain a specified percentage of their net total demand and time libilities in the form of designated liquid assets with them self. A higher SLR means less credit-giving ability.
(v) Change in Repo Rate and Reverse repo Rate : The Reserve Bank of the country lends money to commercial banks at Repo Rate in the event of any shortfall of funds. Repo rate is used by the Reserve Bank to control inflation.
Reverse Repo Rate: It is the rate at which the central bank of the country borrows money from the commercial banks within the country. When credit is to be reduced then government decreases these rates, and to make the credit more, these rates are increased. At present, repo Rate is 6.25% and Reverse Repo Rate is 5.75%.
(b) Qualitative method: Under this method the Reserve Bank tries to control the flow of credit from unproductive to productive uses. Following are the qualitative credit control methods:
(i) Margin requirements: The margin requirement Refers to the difference between the current value of the security offered for loan and the value of loan granted. Like, if on the goods of ₹ 200, the loan rate is changed from ₹ 60 to ₹ 50, meaning, margin money is increased from 40% to 50%, then it will lessen the loan-providing ability.
(ii) Rationing of credit: Rationing of credit refers to fixation of credit quotas for different business activities. Under this method, the commercial banks cannot advance loans more than such limits. Credit can be controlled by the Reserve Bank by changing such limits.
(iii) Moral Suasion: It means advising, requesting and persuading the commercial banks to cooperate with the central bank in implementing its general monetary policy.
(iv) Publicity: The Reserve Bank publishes magazines, journals, bulletins, etc. In these publications the central bank puts forward the type of policies to be adopted to meet the challenges associated with the economy.
(v) Direct action : If the commercial banks do not follow the methods suggested above and do not follow the policies of the central bank issued from time to time, then the Reserve Bank has legal right to take direct action, such as to put a stop on the branch expansion of such banks, or nullifying their licence. In this way, the commercial banks forcefully have to follow the rules of the RBI.
The RBI can use any method against them.