Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 24 Concept of International Trade
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 24 Practice Questions
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 24 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Foriegn exchange market is defined as a place where :
(a) Goods and services are transacted
(b) Transactions of exchange of foreign currencies are effected
(c) Transactions of resources are done
(d) Transactions of services are done
Answer:
(b)
Question 2.
Which of the following exhibits trade deficit ?
(a) Imports > Exports
(b) Imports = Exports
(c) Imports < Exports
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a)
Question 3.
Lowering down the external value of a country’s own currency is called
(a) Depreciation
(b) Devaluation
(c) Revaluation
(d) Inflation
Answer:
(b)
Question 4.
Balance of trade includes :
(a) Import of Services
(b) Export of Services
(c) Import of assets
(d) Import and export of goods
Answer:
(d)
Question 5.
If value of one dollar changes from ₹ 65 to ₹ 60, it is called :
(a) Revaluation
(b) Devaluation
(c) Depreciation
(d) Inflation
Answer:
(a)
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 24 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define International trade.
Answer:
Trade beyond the geographical boundaries of a country is called International trade.
Question 2.
What is foreign exchange market ?
Answer:
It is the market where currencies of two or more countries are exchanged.
Question 3.
What is the meaning of trade ?
Answer:
Trade means sale and purchase of goods and services. Trade is of two types- internal trade and international trade.
Question 4.
When does trade deficit take place ?
Answer:
When import is more than the export, trade deficit takes place.
Question 5.
State one importance of foreign trade.
Answer:
It provides more chances of selection of goods to the consumers, producers and investors.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 24 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define Devaluation.
Answer:
Devaluation is a process of lowering the country’s currency in terms of foreign currency. It simply means lowering the external value of country’s currency. Government adopts this measure to reduce the trade deficit. This makes imports costlier and exports cheaper. In this way, government, though devaluation, tries to correct disequilibrium in balance of payment.
Question 2.
What are invisible items ?
Answer:
Invisible items are those items which cannot be seen and which cannot be measured in terms of quantity. Invisible items simply means those items which are not physical in nature. Invisible items include services like banking, insurance and technological knowledge, etc.
Question 3.
What do you mean by Exchange Rate ?
Answer:
Exchange rate refers to the price of one currency in relation to other currencies in the international money market (or international exchange market).
Question 4.
What do you mean by visible items ?
Answer:
Visible items means those commodities which are physical in nature and can be seen and measured. The value of import and export of visible items is included in the Balance of Trade. In this way, only visible items are included in the Balance of Trade.
Question 5.
What is closed economy ?
Answer:
It is the economy of that country which does not have business and monetary transaction relations with the .other countries. In these countries, population of the country uses only those products and services which are produced within the country.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 24 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain in detail the process of determination of foreign exchange rate ?
Answer:
Exchange rate refers to the price of one currency in relation to other currencies in the International money market. It means, exchange rate is the price of one currency expressed in terms of another currency. Foreign exchange rate is determined in Foreign exchange market where exchange of curencies between two or more than two countries takes place. There are many types of exchange rates. For example- forward, spot, favourable, adverse, fixed and flexible exchange rate.
Determination of exchange rate : Economists have developed various theories to determine the exchange rate. Major ones among them are Demand Supply Theory, Purchasing Power Theory (PPT), Balance of Payment theory and Mint Par theory.
Demand and supply theory : As prices in the market are determined through the forces of demand and supply, so is the case for determination of exchange rate in foreign exchange market. It can be explained with the help of a simple example :
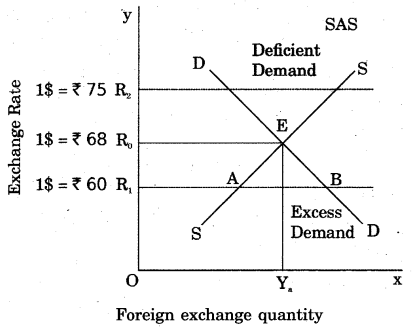
In the above figure, equilibrium point is E. Here, demand for foreign exchange is equal to the supply of foreign exchange. Demand and supply of foriegn exchange is OYa and exchange rate is OR0, i.e. 1$ = ₹ 68. If exchange rate is OR2 it means that the supply of foreign exchange is greater than the demand for it. As a consequence, exchange rate will come down and equilibrium will be again at E. On the other hand, if exchange rate is OR1; it means that demand for foreign exchange is greater than its supply. It will push the exchange rate upward and equilibrium will again be’established at point E.
In this way, change in exchange rate bring change in demand and supply. For this, so many other economic factors are also responsible. For example, quantity of imports and exports, flow of countries’ capital, bank rate, uncertainty of international money market and political environment, etc.
Question 2.
Define International trade. Why is it essential ?
Answer:
International trade : In International trade, goods and services are exchanged among the countries. Trade beyond the goegraphical boundaries of a country is called International trade. For example- trade between India and USA is an example of International trade. In simple language, we call it foreign trade.
Need for International trade
We may understand the importance of international trade from the following points :
(i) All countries are not equally competent to produce all types of goods. Therefore, they have to depend on other countries for obtaining the goods of their need.
(ii) Natural resources of the world are unequally distributed. For example, fertile land, minerals, forests resources and climatic conditions, etc. are unequally distributed. Therefore, each country tries to specialize in the production of that commodity in which it has natural endowment. It exports these goods to earn profit. On the other hand, it imports those commodities for which it does not have a natural endowment. In this way, every country tries to minimize the cost of production and to gain from International trade.
(iii) Due to the International trade, advanced technology is obtained. This transforms developing and backward countries into advanced countries.
(iv) Domestic, competition also increases due to International trade. They adopt two measures:
(a) Improving the quality of goods.
(b) Increasing sales volume.
(v) Presently, income from international trade is a large part of Gross National Product. In all the developing countries, International trade is an important component of their development.
Question 3.
Differentiate between Devaluation and Revaluation.
Answer:
Both Revaluation and Devaluation are used to adjust a country’s Balance of Payment. Devaluation is a process of lowering country’s currency in terms of foriegn currency. It simply means lowering the external value of country’s currency. Government adopts this measure to reduce the Trade Deficit. This makes imports costlier and exports cheaper. In this way, government, through devaluation, tries to correct disequilibrium in Balance of Payment.
Revaluation is a policy instrument to adjust Balance of Payment. Through revaluation, value of country’s currency is increased in terms of foriegn currency. This makes exports of the country relatively costlier and imports cheaper and this reduces the surplus foreign trade.
Devaluation and revaluation both are adopted under fixed monetary exchange rate system. If revaluation is done under flexible or floating exchange rate system, then it is called appreciation money.
Question 4.
Balance of Payment is a more wider term than Balance of Trade. Explain.
Answer:
Every country imports and exports goods and services. Out of these, certain items are visible and certain items are invisible. The value of visible items is included in balance of trade, whereas balance of payment is a wider concept. In this, visible and invisible both items are included. Invisible items include services like banking, insurance and technological knowledge, etc. The payment of these services is made between the coutries, but not recorded at ports. Along with it, capital account is also included.
According to Sodersten : “Balance of payment is a method to record the payments for international transactions for any country”.
Therefore, Balance of Payment is a more wider term than Balance of Trade, because in this, both visible and invisible items are included.
Question 5.
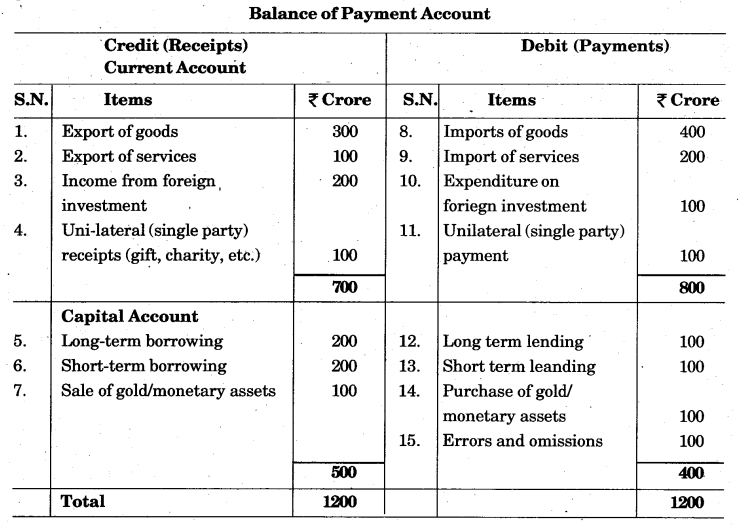
Explain different items of Balance of Payment through a hypothetical example.
Answer:
Different items of Balance of Payment may be understood through an imaginary table given below :
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 24 Other Important Questions – Answers
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 24 Multiple-Choice Questions
Question 1.
There is no change in the exchange rate between different currencies. This is called –
(a) Backward exchange rate
(b) Forward exchange rate
(c) Fixed exchange rate
(d) Flexible exchange rate
Answer:
(c)
Question 2.
By what system different countries sought out their economic or business issues ?
(a) Self Exchange System
(b) Domestic Exchange System
(c) Foreign Exchange System
(d) Monetory fund System
Answer:
(c)
Question 3.
When total debit is equal to the total credit of any country then Balance of Payment is:
(a) Balanced
(b) Unbalanced
(c) Not equal
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a)
Question 4.
Which principle is adopted in case of non-convertible paper money?
(a) Payment Equilibrium/Parity
(b) Coin parity
(c) Purchasing power parity
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c)
Question 5.
If government does not interfere, then exchange rate is determined:
(a) By importers
(b) By exporters
(c) By businessmen
(d) By forces of demand and supply
Answer:
(d)
Question 6.
Lowering country’s currency in terms of foreign currency by the government of any country is known as:
(a) Revaluation
(b) Devaluation
(c) Demonetization
(d) Monetization
Answer:
(b)
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 24 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is a closed economy ?
Answer:
It is the economy of that country which does not have business and monetary transaction relations with other countries.
Question 2.
Explain Balance of Payment.
Answer:
Balance of Payment is a method to record the payments for an international trade transaction for any country.
Question 3.
Cost of one American dollar in context to Indian Rupee declines from ₹ 50 to ₹ 48. Then it is said …… of Indian Rupee.
Answer:
Revaluation.
Question 4.
What is surplus foreign trade ?
Answer:
When export is more than the import in international trade.
Question 5.
Explain foreign exchange market.
Answer:
It is a market where currencies of two or more countries are exchanged.
Question 6.
What will be the effect on foreign market demand if Indian rupee undergoes revaluation in context to American dollar ?
Answer:
There will be a decline in demand for Indian goods and services.
Question 7.
What do you mean by fixed exchange rate.
Ans.
Fixed rate of exchange refers to rate of exchange as fixed by the government.
Question 8.
How is foreign currency demand fulfilled ?
Answer:
Foreign currency demand is fulfilled through exports and by foreign investments.
Question 9.
What do you mean by Trade Balance ?
Answer:
Trade Balance is a record of import and export between two countries for one year.
Question 10.
Write three reasons for imbalance in Balance of Payment.
Answer:
- Huge Expenditure on development.
- Increase in consumption of imported goods.
- High cost of production.
Question 11.
What do you mean by devaluation ?
Answer:
Devaluation is a process of lowering a country’s currency in terms of foreign currency.
Question 12.
Mention two objectives of devaluation.
Answer:
- Increasing the export.
- Decreasing the import.
Question 13.
Which items are included in Balance of Trade ?
Answer:
Only visible items are included in balance of trade.
Question 14.
Which items are included in balance of payment ?
Answer:
Visible and invisible, both items, are included in balance of payment.
Question 15.
What is meant by the monetary (money) value ?
Answer:
The value or worth that product or service would bring to someone if sold.
Question 16.
What is the relation between demand of foriegn currency and exchange rate?
Answer:
There is an inverse relation between demand of foriegn currency and exchange rate.
Question 17.
How is loss covered in current account ?
Answer:
Loss is covered in current account by the flow of net capital.
Question 18.
What is the main objective of foreign currency market ?
Answer:
Main objective of foreign exchange market is expanding the foreign market and increasing foreign investment.
Question 19.
What do you mean by Actual Exchange Rate ?
Answer:
It refers to the ratio of international and domestically demanded price in one currency.
Question 20.
What do you mean by Devaluation ?
Answer:
Devaluation means decrease in value of the country’s currency in terms of foreign currency.
Question 21.
In which conditions will international trade not occur ?
Answer:
If cost of production is similar, there will be no international trade.
Question 22.
What do you mean by trade rate?
Answer:
The rate at which the goods are exchanged with other country’s goods.
Question 23.
What is tariff ?
Answer:
Tax imposed on goods and services while crossing the border of any country.
Question 24.
How does export duty influence demand?
Answer:
Due to export duty cost of product increases which leads to a decrease in demand.
Question 25.
What is venture capital ?
Answer:
It refers to an investment in the purchase of forex (foreign exchange) in the international money market with a view to earn profits.
Question 26.
What is hedging ?
Answer:
Hedging means protection against the risk related to the variations in foreign exchange rate. Exchange rate is locked for future supplies of foreign exchange.
Question 27.
What is the necessary requirement for the success of devaluation ?
Answer:
Foreign demand of the goods to be exported should be very flexible.
Question 28.
Write two ways to increase export.
Answer:
- Minimising the cost of production.
- Maintaining the quality of product.
Question 29.
What is the nature of foreign exchange demand curve ?
Answer:
Foreign exchange demand curve slopes downward.
Question 30.
What is the nature of foreign exchange supply curve ?
Answer:
Foreign exchange supply curve moves upward.
Question 31.
If one dollar costs ₹ 40, What is the exchange rate of dollar and rupee ?
Answer:
Exchange rate : $1 = ₹ 40.
Question 32.
Write two sources of foreign exchange supply.
Answer:
- Getting subsidies from foreign countries.
- Getting loans from foreign countries.
Question 33.
What do you mean by Balance of Payment ?
Answer:
Difference between the value of goods imported and exported.
Question 34.
What is predicted by deficit Balance of Payments ?
Answer:
Deficit balance of payments shows increase of exports over imports.
Question 35.
Write two items of Current Account.
Answer:
- Export of goods.
- Income from foreign investments.
Question 36.
Write two barriers of foreign trade.
Answer:
- Tarariff (commercial rate)
- Quota.
Question 37.
What do you mean by exchange rate ?
Answer:
Exchange rate is the price of one currency expressed in terms of another currency.
Question 38.
Write two reasons of development of foreign trade market.
Ans:
- Increase in international trade.
- Increase in foreign capital investment.
Question 39.
What do you mean by visible trade ?
Answer:
Import and export of goods between two countries.
Question 40.
Open economy helps in the development of which factors ?
Answer:
- Selection of goods.
- Selection of Properties.
- Selection of employment and production.
Question 41.
In foreign exchange market if ₹ 50 is paid for one dollar. What is the exchange rate ?
Answer:
1 $ = ₹ 50.
Question 42.
If one country’s import is ₹ 280 crore and export is ₹ 320 crore, what will be the Balance of Trade?
Answer:
Balance of trade = Export – import
= 320 – 280
= ₹ 40 crore. (surplus)
Question 43.
Write two items of capital account.
Answer:
- Foreign borrowings
- Foreign investments.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 24 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-I)
Question 1.
Differentiate between Foreign Trade Surplus and Trade Deficit.
Answer:
When a country’s export is more than its import, it is called foreign trade surplus, and when a country’s export is less than its import, it is called trade deficit.
Question 2.
What do you mean by foreign trade exchange ? Mention two competitors of foreign trade exchange.
Answer:
It is the market where currencies of two or more countries are exchanged.
Two main competitors of foreign exchange market are –
- commercial banks, and
- International Monetary Fund.
Question 3.
What do you mean by flexible exchange rate ?
Answer:
It is a floating rate of exchange, determined by the supply and demand for the different currencies.
Question 4.
What records are kept by Balance of Payment ?
Answer:
Balance of Payment is a method to record the payments for international transactions for any country.
Question 5.
When does Balance of Trade shows loss ?
Answer:
Whenever the cost of imported goods is more than the cost of exported goods, Balance of Trade shows loss.
Question 6.
When does Balance of Trade shows surplus ?
Answer:
Whenever the cost of exported goods is more than the cost of imported goods, Balance of Trade shows surplus.
Question 7.
Write down the basic principle of ascertaing the exchange rate.
Answer:
The basic principle of ascertaining the exchange rate is determination of point at which the currency of one country’s demand and supply is equal.
Question 8.
Who are the individuals due to whom foreign currency demand takes place ?
Answer:
Demand of foreign currencies are made by those individuals who want to import or want to pay for foreign service or want to invest in other countries.
Question 9.
What does unfavourable trade condition mean ?
Answer:
If, in any country’s trade, cost of import remains more than the cost of export for a specific time, it is an unfavourable trade condition for that country.
Question 10.
What do you mean by Balance of Payment?
Answer:
Balance of payment is a wide concept. In this, both visible and invisible items are included.
Question 11.
Which records are kept in the Capital Accounts?
Answer:
Capital Accounts keep the records of financial transactions. All the international transaction records of assets are kept in this account.
Question 12.
What do you mean by loss in current account ?
Answer:
When foreign payments are more than the foreign receipts, it is termed as loss in current account.
Question 13.
What is spot exchange rate ?
Answer:
Spot exchange rate is that exchange rate which happens to prevail in the market when transactions occur.
Question 14.
What do you mean by import and export ?
Answer:
Purchasing of goods and services from other countries by one country is called import and selling of goods and services to other countries by one country is called export.
Question 15.
What do you mean by internal trade ?
Answer:
Sale and purchase of goods and services within the geographical boundaries of a nation is called internal trade.
Question 16.
What do you mean by protectionism ?
Answer:
To put a stop on the international trade and banning the import and export of goods [. and services is known as protectionism.
Question 17.
What is the effect on exchange rate by a change in banking rate ?
Answer:
If the bank rates get high, then exchange rates are favourable, and if the bank rates are lower, then exchange rates become unfavourable.
Question 18.
What do you mean by exchange control ?
Answer:
All the restrictions by RBI and government which affect the exchange rate or the ; concerned markets are termed as exchange control.
Question 19.
What do mean by Dumping ?
Answer:
It is that form of discrimination in which a manufacturer sells his products at a cheaper rate in foreign market in comparison to the domestic market.
Question 20.
What is shown by the third element, “error and omission”, of Balance of Payment?
Answer:
The third element “error and omission”of Balance of Payment shows our incapability of accounting all the transactions.
Question 21.
Explain the relation between demand of foreign currency and exchange rate.
Answer:
There is an inverse relation between demand of foreign currency and exchange rate. Slope of demand curve of dollar is negative, i.e., downward sloping. It means lower the exchange rate higher the demand of dollar in India. In other words, prices of American goods and services will become cheaper in India.
Question 22.
What is shown by the downward slope of foreign exchange demand ?
Answer:
It means that if exchange rates are high, then foreign exchange demand will be less, and if the exchange rates are lower, then foreign exchange demand will be higher.
Question 23.
When is Balance of Trade account favourable?
Answer:
Whenever a country’s value of export is more than the value of import then the Balance of Trade account of that country is favourable.
Question 24.
Differentiate between Balance of Trade and Balance of Payment.
Answer:
In Balance of Trade, the value of imports and exports are included, and in Balance of Payment, all the foreign financial transactions are included.
Question 25.
Write two points of importance of Fixed Exchange Rate System.
Answer:
- In Fixed Exchange Rate System, there will be no speculation in foreign exchange market.
- In fixed exchange rate system, international trade increases.
Question 26.
Write down one benefit of open economy.
Answer:
Open economy provides the investors choice of selection between domestic and foreign properties which increases competition in the market.
Question 27.
Write down the features of Balance of Payment.
Answer:
- Both visible and invisible itmes are included in this payment.
- Receipts and payments are recorded through double entry system.
Question 28.
Comment in favour of Fixed Exchange Rate.
Answer:
- Fixed exchange rate increases the international trade.
- In helps in providing subsidy for food and investment for the remaining world.
- It helps in increasing the foreign exchange reserve.
Question 29.
Comment in favour of fluctuating exchange rate.
Answer:
- It helps in balancing the exchange rate on international level.
- Due to this rate system, the trend of speculation is discouraged.
Question 30.
Write two reasons of obtaining foreign currency.
Answer:
- For making payments of imports.
- For making international payments.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 24 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-II)
Question 1.
What do you*mean by open economy ? Mention any two types in which open economy extends your choice of selection.
Answer:
Open economy is an economy in which one country trades goods and services with other countries. Following are the two ways to extend our choice :
- Choice of selection between domestic goods and foreign goods.
- Investors can choose between domestic and foreign assets.
Question 2.
What do you mean by flexible exchange rate ?
Answer:
Flexible exchange rate means those rates which are controlled independently in the foreign exchange market by the forces of demand and supply. In this rate system, there is no interference of banks and government authority.
Question 3.
What do you mean by foreign exchange market ?
Answer:
Foreign exchange market is a marketplace, where sale and purchase of foreign currencies take place. Therefore, it is a place where organised management of sale and purchase of foreign currencies occur. Exporters sell foreign currencies and importers purchase foreign currencies.
Question 4.
Mention the main functions of foreign exchange market.
Answer:
- Transfering the purchasing power : The main function of foreign exchange market is to transfer the purchasing power between the different countries.
- Arranging goodwill: Foreign exchange market arranges the goodwill for international trade.
- Risk management: Foreign exchange market provides the facility of current or post sale and purchase to minimise risk.
Question 5.
Define foreign exchange rate.
Answer:
Foreign exchange rate refers to the rate at which domestic currency can be exchanged for a foreign currency. It is the price paid in domestic currency for buying one unit of foreign currency.
Question 6.
Differentiate between Balance of Trade and Balance of Payment.
Answer:
- Balance of payment is a wider concept, whereas Balance of Trade is a narrow concept.
- Balance of Trade is included in Balance of Payment.
- Both visible and invisible items are included in Balance of Payment, whereas only visible items are included in Balance of Trade.
Question 7.
What do you mean by open economy ? How does our choice expand through open economy ? State two ways.
Answer:
Open economy is an economy in which goods and services of one country are traded with the other countries. In other words, it is Em economy in which mutual exchange of goods and services and financial monetary assets takes place with other countries.
Following are the ways by which our choice expands :
- Consumers and firms can choose between domestic goods and foreign goods,
- Investors can choose between domestic assets and foreign assets.
Question 8.
What do you mean by Balance of Payment of any country ?
Answer:
Balance of Payment is a method to record the payments for international transactions for any country within a specific time period. It can be divided into two parts :
- Current Account
- Capital Account.
Question 9.
Differentiate between open economy and closed economy.
Answer:
Following are the differences between open economy and closed econmy :
Open Economy
- Open economy has trade relations with the remaining world.
- Development opportunities are more in an open economy.
- There can be a difference between domestic income and national income in this economy.
Closed Economy
- Closed economy does not have any trade relation with the remaining world.
- Development opportunities are less in a closed economy.
- Domestic income and national income are same in this economy.
Question 10.
What do you mean by current account ?
Answer:
Current Account is a part of Balance of Payment in which all the payments within the specific time limit are included. The biggest part of current account comprises of import and export. Other items of current accounts are services and gifts.
Question 11.
What do you mean by capital account ?
Answer:
All those receipts and payments are included in capital account which help in formation of new capital or ends the current liabilities. Capital Account can be divided into two parts :
- Long term Capital Account, and
- Short term capital account.
Question 12.
Explain fixed exchange rate system. State two benefits of fixed exchange rate system.
Answer:
When the central bank of any country fixes the exchange rate at certain point, it is said to be the Fixed Exchange Rate System. ,
Following are the two benefits of fixed exchange rate system :
- Due to fixed exchange rate, international trade increases.
- Due to this system, foreign investment also increases.
Question 13.
What is flexible exchange rate system ?
Answer:
Flexible rate of exchange is that rate which is determined by the supply-demand forces in the foreign exchange market. It is also called “Free exchange rate”, as it is determined by the free play of supply and demand forces in the international money market.
Question 14.
Mention the benefits of flexible exchange rate.
Answer:
Following are the benefits of flexible exchange rate :
- In flexible exchange rate system, this is.no compulsion of incurring expenditure by Reserve Bank for keeping foreign exchange reserve.
- Due to flexible exchange rate system, the obstacles that might emerge between the international trade and capital traffic are removed.
- It helps in getting rid of problems like devaluation and revaluation.
Question 15.
What do you mean by Managed Floating ?
Answer:
It is a system of floating exchange rate, but occasionally, the float is managed by the central bank of the country by the way of sale and purchase of foreign exchange in the international money market. Managed floating, which is also known as ‘dirty floating’, is an attempt to keep the exchange rate within the desired limits.
Question 16.
Mention two factors of foreign exchange demand.
Answer:
- Purchasing foreign assets: If the Indians want to purchase land, house, shares, bonds, etc. in foreign countries, they demand foreign exchange.
- Imports from abroad : If the Indians want to import goods and services from other countries, they demand foreign exchange.
Question 17.
Mention the main sources of foreign exchange supply.
Answer:
Following are the main sources of foreign exchange supply :
- Foreign exchange through export of goods and services.
- Foreign currencies through Foreign Direct Investment in a domestic economy.
- Income through purchase of land and other assets by the foreigners in the country.
- Income through subsidies and gifts from rest of the world.
Question 18.
Explain the meaning of Balance of Payment.
Answer:
Financial transactions of one’s country occur with rest of the world in international trade. Record of these transactions is kept in Balance of Payment account. Therefore, Balance of Payment means a method to record the payments for international transactions for a country in one financal year.
Question 19.
Mention the main elements of Current Account.
Answer:
Main elements of Current Account are divided into three parts :
- Visible trade : All items that are physical in nature are included in this trade.
- Invisible trade : In this, only trade of services is included, like-banking, insurance, etc.
- Current transfer payments : In this, foreign gifts, donations, military help, technological help, etc. one-sided transactions are included. Therefore, it is also known as one-sided transaction.
Question 20.
Mention the main elements of Capital Accounts.
Answer:
Following are the main elements of Capital Accounts of Balance of Payment in India:
(i) Foreign investment: In this, foreign investors purchase domestic companies and also establish the units of business in the domestic economy.
There are two types of foreign investments :
(a) Direct Foreign Investment. (b) Portfolio investment.
(ii) Loans : In this, borrowings are included. These are of two types : Foreign aid and Commercial loans.
(iii) Banking Capital: In this, mainly those banks and financial institutions are included, which officially work under foreign exchange market.
Question 21.
What do you mean by Balance of Trade?
Answer:
Balance of Trade means transactions of all the of visible items traded, within one financial year. In other words, it means keeping a systematic record of visible items of one country. Invisible items are not included in Balance of Trade.
Question 22.
What is Current Account balance ?
Answer:
In Current Account, all the current transactions of goods and services and one-sided transfers are included.
Balance of Current Account = (Visible Exports + Invisible Exports) – (Visible Imports + Invisible Imports)
Question 23.
Explain Capital Account balance.
Answer:
In Capital Account, sale and purchase of monetary assets at international level are recorded. When we subtract the income from the sale of domestic assets from expenses from the purchase of foreign assets, we get Capital Account balance.
Capital Account balance = (Income from sale of domestic assets) – (Expense from purchase of foreign assets)
Question 24.
What is meant by Currency Appreciation ?
Answer:
Currency appreciation means rise in the value of domestic currency in relation to the foreign currency. Example- ₹ 50 are required to buy one US dollar, instead of ₹ 60 as required earlier.
Question 25.
What is meant by currency depreciation ?
Answer:
Currency depreciation refers to a fall in the value of domestic currency in relation to the foreign currency. Example- ₹ 60 are required to buy one US dollar instead of ₹ 50 as required earlier.
Question 26.
What is the effect of Balance of Payment on foreign exchange reserve ?
Answer:
If Balance of Payment is unfavourable then foreign exchange reserve will be less. If Balance of Payment is favourable then foreign exchange reserve will be more.
Question 27.
Why does supply of foreign currency increase due to the increase in foreign exchange rate ?
Answer:
Due to the increase in foreign exchange rate, domestic goods become cheaper. This increases the export of domestic goods and services. Due to this, foreign currency supply increases.
Question 28.
When foreign currencies rate declines its demand increases. Comment.
Answer:
Let us understand this by an example. Suppose, Euro rate declines; it means Euro can be exchanged in Indian currency for less amount. Now, Indian people will import goods in exchange of Euro. This will raise the demand of European currency, Euro, in the foreign exchange market. People in India will start exchanging Euro for Rupees for exporting European goods.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 24 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the factors which influence the foreign exchange rate.
Answer:
Following are the factors which are responsible for affecting the foreign exchange rate:
(i) Import & Export : If domestic import is more than the export, it increases the demand of foreign currency. Due to this, foreign exchange rate comes in favour of the foreign currency. Hence, it increases the rate of foreign currency. In opposite situation, rate of foreign currency declines.
(ii) Capital investment: When domestic investors invest capital in foreign countries then the demand of foreign currency increases and exchange rate also increases and when foreign investors invest in the domestic economy then they demand for domestic currency. This helps in increasing the rate of exchange of domestic currency.
(iii) Sale and purchase of shares, and bonds : If the people of one country purchase the shares and bonds of foreign countries, it increases the demand of foreign currencies and decreases the value of domestic currencies. In a converse case, if people of one country sell the shares and bonds of foreign countries, it increases the rate of domestic currencyin comparison to foreign currency.
(iv) Bank rates: Due to the increase in bank rates, foreign investment comes into domestic country for more interest rates. It increases the supply of foreign currency. As a result, exchange rate of foreign currency goes down and value of domestic currency goes up.
(v) Speculation: If a speculator thinks that the rate of exchange of particular country’s currency will go high in the future, he starts to purchase such currency. If he speculates that the rate of particular country’s currency will go down in the future, he starts to sell that currency. This speculation affects the exchange rates in the market.
(vi) Inflation and Deflation: In case of inflation, value of domestic currency goes down. In this situation, foreign currency flows outwards. This increases the demand of foreign currency and value of foreign currency goes up in comparision to domestic currency. In the converse situation of deflation, the value of the domestic currency goes up and for earning financial profit foreign currency flows in.
Question 2.
Define Balance of Payment. Explain the main items of balance of payment.
Answer:
Balance of Payment is a statement of accounts showing all the monetary transactions of a country with the rest of the world during a period of time, generally one year.
In the words of Kindlegerger, “The balance of payment of a country is a systematic record of all economic transactions between its residents and also the residents of foreign countries.”
Following are the items included in accounts of Balance of Payment:
(i) Export and import of commodities : Those commodities which are exported and imported form a very important part of a Balance of Payment. Gold and silver is also included in these commodities.
(ii) Export and import of services : Just like export and import of goods, import and export of services also affects the Balance of Payment. The country which provides services is called an exporter and the country which gets the service is called an importer. Mainly, there are three types of services :
(a) Services provided by business organisations: Services under this category include banking, shipping, insurance, etc.
(b) Specialist services: Services under this category include service provided by doctors, professors, engineers, technical specialists and by financial experts.
(c) Tourism services: Services included under this category include transportation, hotels, tour and travel agencies, etc.
(iii) Loan, interest and profit transactions : Some countries pay interest to other countries for loams. Countries also invest in other countries for earning profits. All these transactions are included in Balance of Payments .
(iv) Migration of population: When people migrate from one country to another country, they also take away cash with them. This affects the Balance of Payment.
(v) Expenses by the government: Many countries spend on building their embassies in foreign countries and also spend by giving donations and subsidies. This also affects Balance of Payment.
(vi) Transfer of Gold : If, by the above items, balance of payment does not take place, then balance of payment is done by transferring the gold.
Question 3.
Define exchange rate. Explain favourable and unfavourable exchange rate.
Answer:
Exchange rate is the price of one currency expressed in terms of another currency. Exchange rate is determined by equality of demand and supply of foreign exchange.
In the words of Crowther, “The rate of exchange measures number of units of one currency which are exchanged for one unit of another.”
Favourable and unfavourable exchange rates: To find out whether the exchange rate is favourable or unfavourable, we should find out whether the exchange rate is in our domestic currency or in foreign currency. Any exchange rate which is favourable for our country will be unfavourable for another country. Therefore, there are two conditions :
(i) Exchange rate applicable in domestic currency : In this situation, decreasing, exchange rate is in the country’s favour and increasing exchange rate is unfavourable. For example, if one dollar costed ₹ 25 earlier and after change it becomes one dollar = ₹ 15, then this exchange rate will be favourable for us because now we have to pay ₹ 15 instead of ₹ 25 for purchasing one dollar worth goods. If, against this, one dollar’s value becomes ₹ 30, then this will be unfavourable exchange rate for us because we will have to pay ₹ 30 in place of ₹ 25 now.
(ii) Exchange rate is applicable in foreign currency : In this situation, increasing exchange rate will be in our favour and decreasing exchange will be an unfavourable situation. For example: If present exchange rate is ₹ 1 = 70 Euro and its changed rate is ₹ 1 = 90 Euro, it will be in favour of our country and ₹ 1 = 50 Euro will be unfavourable situation for the country.
Question 4.
Define foriegn exchange rate. How foreign exchange rate is determined in an independent market ?
Answer:
The mutual price of currencies in terms of each other is called foreign exchange rate. Foreign exchange rate is the price of one currency expressed in terms another currency. Example : If 50 rupees are to be paid to buy one US dollar, then the exchange rate may be specified as:
$ 1 = ₹ 50 or 1 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 50 } \) Dollar = 2 cents. Thus, exchange rate expresses the ratio of exchange between the currencies of two countries. Some economists refer to it as the external value of the domestic currency.
In the words of Crowther, “The rate of exchange measures the number of units of one currency which are exchanged in the foreign market for one unit of another”.
Exchange rate in independent market is determined by the forces of demand and supply. This can be understood by following graphical examples :
Demand of foreign currency : Foreign currencies are demanded by the following individuals:
- Those who want to purchase goods from other countries.
- Those who want to pay for foreign services.
- Those who want to invest in foreign countries.
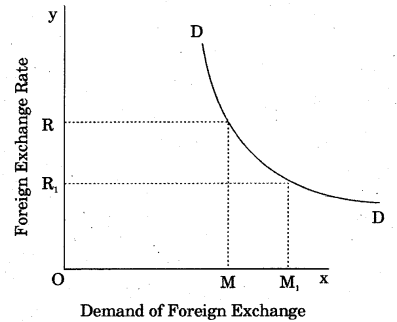
In this figure, DD is a demand curve whose slope is negative. It is clear from this figure that as exchange rate decreases from OR to OR1 the demand increases from OM to OM1.
Supply of foreign Currency : In supply of foreign currency there are exports behind it. For the payments of export of goods and services, foreigners purchase our currency by paying their currencies which increases our foreign exchange reserve.
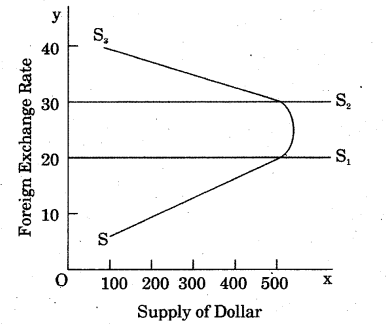
According to the figure, if elasticity of foreign demand of country’s export is more than one, then foreign exchange supply curve will be positive from left to right S to S1
If country’s export foreign demand elasticity is one, then foreign exchange supply curve will be vertical S1 to S2. If country’s export foreign demand elasticity is less than one, foreign exchange supply curve will be negative from S2 to S3
Equilibrium rate of exchange: Equilibrium rate of exchange determines the point where foreign currency demand curve cuts the foreign currency supply curve. In this figure, demand for foreign currency is shown by DD curve and supply of foreign currency is shown by SS curve. Both of these curves cut each other at point P, where OM is the demand and supply of currency and OR is the exchange rate. Determination of rate at this point is called equilibrium rate.
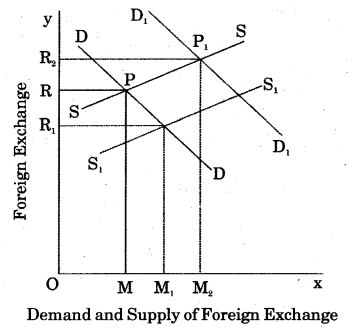
If demand of foreign currency does not change and supply increases from OM to OM1 then the exchange rate will decline to OR1 In contrast, if supply is constant and demand increases to M2 then exchange rate wll increase to OR2.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 24 Numerical Questions
Question 1.
Prove using the following information, that open economy multiplier is less than closed economy multiplier.
Consumption (C) = 0.75
Marginal propensity to import (M) = 0.25
Answer:
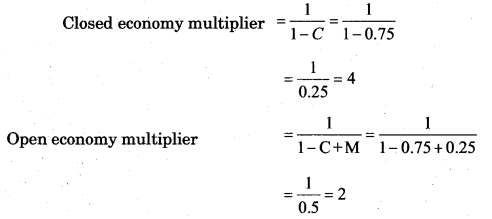
In this case, closed economy multiplier is 4 and open economy multiplier is 2. Therefore, it is proved that open economy multiplier is less them the closed economy multiplier.
Question 2.
One country’s export is ₹ 7,500 crore and import is ₹ 6000 crore. What will be the balance of trade ?
Answer:
Balance of trade = Export – Import
= ₹ 7,500 – 6,000
= ₹ 1,500 crore.
Hence, balance of trade is showing ₹ 1,500 crore surplus.
Question 3.
One country’s export is ₹ 7,000 crore and import is ₹ 9,000 crore. Calculate its balance of trade and mention its nature.
Answer:
Balance of trade = Export – Import
= ₹ 7,000 – 9,000
= ₹ – 2,000 crore.
In this, balance of trade is – ₹ 2,000 crore. Nature of balance of trade is negative (deficit).
Question 4.
Balance of trade deficit of one country is ₹ 5,000 crore. If the value of imports is ₹ 9,000 crore, calculate the value of export.
Answer:
Balance of trade = Export – Import
– ₹ 5,000 = Export – ₹ 9,000
Export = ₹ 9000 – ₹ 5000
Export = ₹ 4,000 crore.
Therefore, the values of export is ₹ 4,000 crore.
Question 5.
Balance of trade deficit of one country is ₹ 4,000 crore. If the value of export is ₹ 13,000 crore, calculate the value of imports.
Answer:
Balance of trade = Export – Import
– ₹ 4,000 = ₹ 13,000
– Import Import = ₹ 13,000 + ₹ 4,000
Value of import = ₹ 17,000 crore.
Question 6.
Surplus of balance of trade of one country is ₹ 3,000 crore. If the value of export is ₹ 8,000 crore, calculate the value of import.
Answer:
Balance of trade = Export – Import
₹ 3,000 = ₹ 8,000 – Import
Import = ₹ 8,000 – ₹ 3,000
Value of import = ₹ 5,000 crore.
Question 7.
Surplus of balance of trade of one country is ₹ 800 crore. If the value of imports is ₹ 9,000 crore, calculate the value of export.
Answer:
Balance of trade = Export – Import
₹ 800 = Export – ₹ 9,000
Export = ₹ 800 + ₹ 9,000
Value of Export = ₹ 9,800 crore.
Question 8.
Calculate the value of imports when the balance of trade is (-) ₹ 800 crore and the value of exports is ₹ 500 crore.
Answer:
Balance of trade = Value of export – Value of import
(-) ₹ 800 crore = ₹ 500 crore – Value of import
Value of import = ₹ 500 crore + ₹ 800 crore
= ₹ 1300 crore
Value of import = ₹ 1,300 crore.
Question 9.
Calculate the balance of Current Account from the following:

Answer:
Balance of Current Account = Balance of visible trade + Export of services + Transfer of money from one country to another
= 40 crore + 25 crore + 5 crore
= ₹ 70 crore.
Therefore, the balance of Current account is ₹ 70 crore.
Question 10.
Calculate the balance of Balance of Payment account. Is the total balance of payment balanced ?

Answer:
Balance of balance of payment account = Value of exports – Value of imports + One-sided transfers + Balance of capital account
= 450 crore – 150 crore + 100 crore + (- 400 crore)
= 450 crore + 100 crore – 150 – 400 Crore = 0
Yes, Balance of Payment is balanced Because balance of Payment account is zero.