Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 9 Concept of Revenue
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 9 Practice Questions
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 9 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
By multiplying the amount of quantity sold with its price, we get:
(a) Average Revenue
(b) Total Revenue
(c) Marginal Revenue
(d) Average Output
Answer:
(b)
Question 2.
If total quantity sold in a month is 200 at ₹ 10 per unit, then AR will be :
(a) 50
(b) 20
(c) 25
(d) 10
Answer:
(d)
Question 3.
In which market, AR = MR?
(a) Perfect competition
(b) Imperfect competition
(c) Monopoly
(d) In all markets
Answer:
(a)
Question 4.
In perfect competition, which curve represents price line?
(a) AR = MR
(b) AR > MR
(c) TR
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a)
Question 5.
In monopoly market, relationship between AR and MR is :
(a) AR = MR
(b) AR > MR
(c) AR < MR
(d) AR × MR
Answer:
(b)
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 9 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write the formula for AR.
Answer:
AR = TR/Q = Total Revenue/Quantity sold.
Question 2.
Define Marginal Revenue.
Answer:
Marginal Revenue: Marginal Revenue is the amount of money obtained by selling an additional unit of a firm’s product, or it can be said that marginal revenue (MR) is the addition made to the total revenue by selling one more unit.
Question 3.
Explain revenue.
Answer:
By selling a commodity, whatever money a firm receives is called its revenue or the amount of money which the firm receives by the sale of its output is known as revenue.
Question 4.
What is the shape of AR and MR curve in perfect competition?
Answer:
In a perfect competition market, both the AR and MR curves are the same, and they are parallel to the X-axis.
Question 5.
Which curve represents price in perfect competition market?
Answer:
AR curve represents price in perfect competition market. In such condition, AR = MR = P.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 9 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain AR and MR with the help of an imaginary table.
Answer:
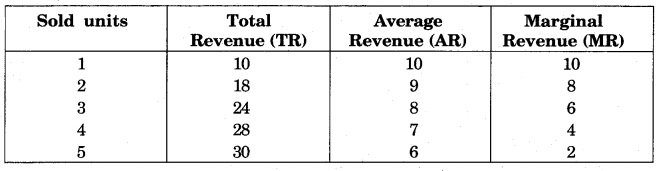
It is clear from the above table, that the increase in total revenue happens at a diminishing rate, and average revenue is falling continuously. The marginal revenue is also falling continuously, but the fall in MR is steeper than in AR.
Question 2.
Complete the following table :
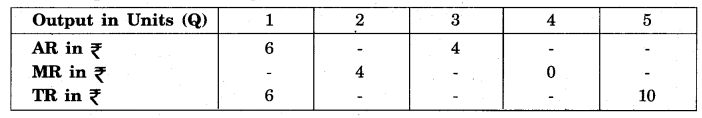
Answer:
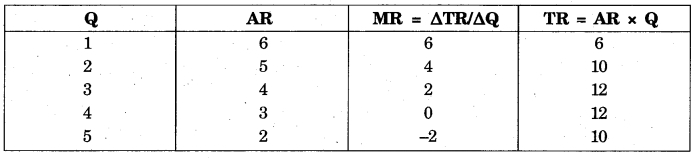
According to the question, in second line, given MR = 4
And we know MR = ∆TR/∆Q,
So MR = x – 6/1 = 4
X = 10 = TR of second line
TR = AR × Q
Or 10 = AR × 2
Or AR = 10/2 = 5
According to the questions in third line given AR = 4
We know that TR = AR × Q = 4 × 3 =12
So MR = ∆TR/∆Q
= 12 – 10/1 = 2
According to the question in fourth line given MR = 0 = 12 – 12/1 = 0
So TR = 12 and AR = TR/Q = 12/4 = 3
According to the question in fifth line given TR = 10
So, MR = 10 – 12/1 = -2
And AR = 10/5 = 2
Question 3.
Calculate AR and MR from the following table:
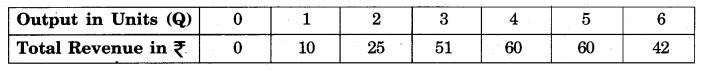
Answer:
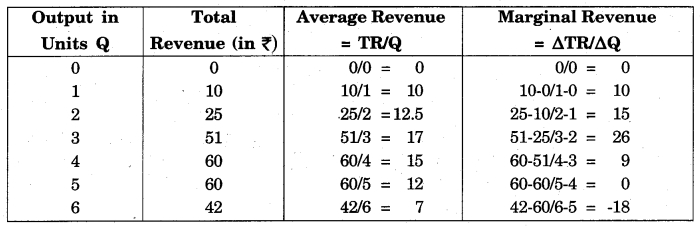
Question 4.
Calculate TR and MR from the following table:
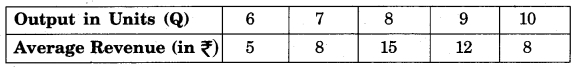
Answer:
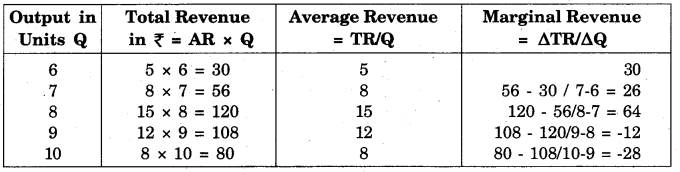
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 9 Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the relationship between Total Revenue, Average Revenue and Marginal Revenue with the help of an imaginary table and diagrams.
Answer:
The behaviour of the revenue curves in different market conditions is different. For example, the average and marginal revenue curve in the perfect competition market are the same, which is a straight line parallel to the X axis, whereas in monopoly and imperfect competition market, both these curves are different and sloping downward from top to bottom. Table related to the imperfect competition market is given below :
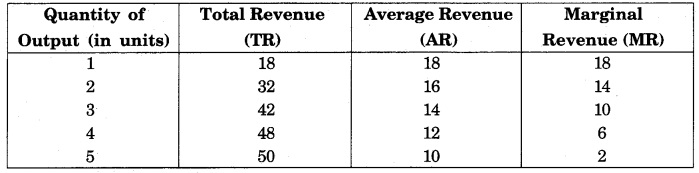
The following things are clear from the table –
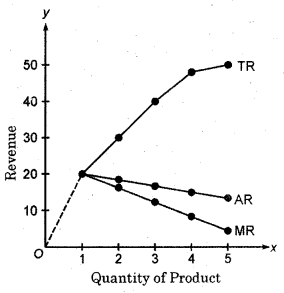
- The average revenue which is the price of the item is constantly decreasing. This means that the price has to be reduced to sell more commodities.
- Marginal Revenue is also continuously decreasing, but its rate of reduction is higher than the average revenue.
- There is a steady increase in total revenue but it is increasing at a decreasing rate.
- The average revenue is never zero, whereas marginal revenue can be zero also, and can also be negative.
The revenues of these three can also be displayed by the adjacent figure, and total revenue, average revenue and marginal revenue curves can be obtained.
From the picture, it is clear that the AR curve is above the MR curve, because the rate of decline of AR is less than that of the MR. TR curve is showing the increasing state of TR.
Question 2.
What is perfect competition market? Why is demand curve for a firm perfectly elastic in perfect competition? Explain.
Answer:
Perfect Competition It is a market situation in which a large number of producers offer a homogeneous product to a very large number of buyers of the product. The number of sellers is so large that each seller offers a very small fraction of the total supply, and therefore, has no control over the market price. Likewise, the number of buyers is so large that each buyer buys an insignificant part of the total supply and has no control over the market price.
Both buyers and sellers are “price takers” and not” price makers”. The price of a commodity is determined in this kind of markets by the market demand and market supply. Each seller faces a horizontal demand curve ( with e = ∞), which implies that a seller can sell any quantity at the market determined price. This kind of market is, however, more of a hypothetical nature rather than being a common or realistic one. Some examples of a perfectly competitive market include share markets, and vegetable markets and wheat and rice mandis where goods sure sold by auction.
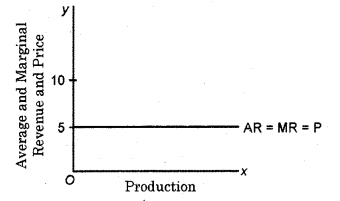
Figure shows the Revenue Curves under Perfect Competition
Under the perfect competition, no firm can take more than the prevailing market price. Nor can it charge at a lower price than the prevailing market value. To do this, will not be beneficial. This is because the production of a firm under perfect competition is a very small fraction of the total production of the industry.
As such, a firm could sell its entire production at the current market price, but if it charges a higher price than the prevailing market price, it won’t be able to sell a single unit, and if it reduces price below the prevailing market price, all consumers will flock to it, and he won’t be able to supply such volumes. Both curves are straight lines parallel to X-axis. In the given figure, the horizontal line DD represents both marginal as well as average revenue or price. It signifies that at a price of ₹ 5, a firm under perfect competition can sell any number of units of output.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 9 Other Impotant Questions and Answers
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 9 Multiple-Choice Questions
Question 1.
Formula of calculating Marginal
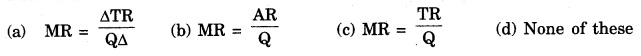
Answer:
(a)
Question 2.
Perfect Competition Market is:
(a) Real Position of Market
(b) Imaginary Position of Market
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b)
Question 3.
Firm in Perfect Competition Market:
(a) is price determiner
(b) accepts the price
(c) can influence the price
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b)
Question 4.
Speciality of Monopoly competition:
(a) There are many sellers in market.
(b) There are two-four sellers in the market.
(c) There is only one seller in the market.
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c)
Question 5.
A firm in the imperfect competition is:
(a) Price determiner
(b) May affect the price
(c) The value is acceptable
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a)
Question 6.
Monopoly Market:
(a) It is the imaginary position of the market
(b) It is the real position of the market
(c) Can be both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a)
Question 7.
Meaning of Revenue :
(a) The firm’s profit
(b) The firm’s sales
(c) The cost of the goods sold by the firm
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b)
Question 8.
Meaning of Marginal Revenue :
(a) The price of goods
(b) The cost of goods
(c) Additional proceeds from the sale of an additional unit
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c)
Question 9.
If a firm sells 10 units of commodity it gets ₹ 50 and when it sells 11 units, it gets ₹ 54 then the marginal revenue of 11 units is :
(a) ₹ 54
(b) ₹ 50
(c) ₹ 4
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c)
Question 10.
If the cost of commodity is ₹ 5 in perfect competition market and the firm sells 50 commodities then what will be the marginal revenue and average revenue?
(a) ₹ 5
(b) ₹ 250
(c) ₹ 10
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a)
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 9 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write down the definition of revenue.
Answer:
According to Dooley, ” The revenue of a firm is its sales receipts or money receipts from the sale of a product.”
Question 2.
Define average revenue.
Answer:
Average revenue can be obtained by dividing the total revenue by the number of units produced and sold.
Question 3.
What are the two characteristics of perfect competition?
Answer:
Two characteristics of perfect competition are the following
- The firm is acceptor of price and not the determiner.
- Products are homogenous in market.
Question 4.
What is ment by total revenue ? Write its formula.
Answer:
Total revenue means the total sales value of a firm. It can be calculated by multiplying the total sales quantity with the charged price.
TR = Q × P, Where Q = quantity of sale and P = price
Question 5
State the two characteristics of imperfect competition market.
Answer:
The two characteristics of imperfect competition are the following:
- It is the actual position of the market.
- Product differentiation can be seen in this market, which can be done on basis of colour, packing, brand, etc.
Question 6.
Mention two features of monopoly market?
Answer:
Following are the two features of monopoly market:
- There is a single producer or seller of the commodity.
- This is an imaginary situation, absolute monopoly is not found in reality.
Question 7.
Can the average revenue be negative?
Answer:
Average revenue can never be negative.
Question 8.
Which concept of revenue is called price?
Answer:
Average revenue refers to the rate at which the output is sold. AR is the price of the product.
Question 9.
What is marginal revenue? Write its formula.
Answer:
Marginal revenue is the addition made to the total revenue by selling one more unit of a commodity. It is the change in total revenue which results from the sale of one (or one less) unit of a commodity. MR = TR/AQ (Here A denotes change).
Question 10.
What do you mean by oligopoly?
Answer:
Oligopoly is an important form of imperfect competition where there are few firms in the market producing either homogeneous products or close substitutes.
Question 11.
State the two characteristics of oligopoly.
Answer:
The two characteristics of oligopoly are:
- Number of sellers is less.
- Mutual dependence is clearly seen among sellers.
Question 12.
What is monopoly ?
Answer:
Monopoly is a market structure characterized by a single seller, selling a unique in the market. In a monopoly market, the seller faces no competition, as he is the sole seller of goods with no close substitute. He enjoys the power of setting the price for his goods.
Question 13.
What do you understand by market of imperfect competition?
Answer:
Imperfect competition is that market situation which lies in the intermediate position of monopoly and perfect competition. Here, the number of buyers and sellers are less, and they don’t have complete knowledge about the market.
Question 14.
What do you mean by market of perfect competition?
Answer:
Perfect Competition refers to a market situation in which there are large number of buyers and sellers of homogeneous products, and firms have to accept the price determined by the market.
Question 15.
What is the relation between marginal revenue and average revenue under perfect competition?
Answer:
If price or average revenue remains the same when more units of a product are sold, marginal revenue will be equal to average revenue.
Question 16.
What is the shape of marginal revenue curve and average revenue curve under perfect competition?
Answer:
The shape of marginal revenue curve and average revenue curve under perfect competition is a straight line parrallel to the X axis.
Question 17.
What is the real and practical concept of market?
Answer:
Monopolistic market or imperfect competition is a real and practical concept of the market. It is found in every economy.
Question 18.
On what basis is the financial position of any firm evaluated?
Answer:
The financial condition of any firm is evaluated on the basis of average revenue and average cost. When both of these are equal, the firm is in the normal profit position.
Question 19.
What is the shape of demand curve in oligopolistic market?
Answer:
In the case of an oligopoly market, the seller’s demand curve is uncertain. In this market, the demand curve is distorted, which reflects the price persistence in the market.
Question 20.
In which market AR and MR are equal?
Answer:
Average Revenue and Marginal Revenue are equal in perfect competition market.
Question 21.
What do we get if the value of the item is multiplied with the quantity of sold item?
Answer:
We get total revenue by multiplying the value of the item with the quantity of sold items.
Question 22.
What is the shape of average income curve in the position of perfect competition?
Answer:
In the position of perfect competition, the shape of average curve is parallel to X axis and it is a straight line.
Question 23.
What will be the average revenue, when the total revenue of firm ‘A’ is ₹ 50,000 and the quantity of sold commodity is 1,000 units.
Answer:
Average Revenue = Total Revenue / Quantity [TR/Q = AR]
= ₹ 50,000/1,000 = ₹ 50
Question 24.
What will be the marginal revenue of the firm, if the total sales increases from 500 to 501 units and the total revenue of the firm increases from ₹ 2,500 to ₹ 2,504.
Answer:
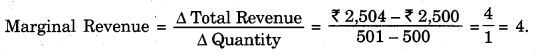
Question 25.
How do marginal revenue and average revenue curves look like under monopoly and monopolistic competition?
Answer:
The average revenue curve and marginal revenue curve slope downwards from left to right and it is similar in monopolistic competition.
Question 26.
When average revenue is constant, what is the state of marginal revenue?
Answer:
When average revenue is constant, marginal revenue is also constant.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 9 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the meaning of revenue.
Answer:
Revenue is the the value obtained by producer or firm by selling its product. Thus, total revenue received includes the cost of the item as well as the profit. A product or seller of a commodity is also very much concerned with the demand for it, mainly because revenue obtained by him from selling the good depends largely upon the demand for the good. He is, therefore interested in knowing what sort of demand curve faces him. The demand curve of the consumers for a product is the average revenue curve from the standpoint of the sellers, since the price paid by the consumers is the revenue of the sellers.
Question 2.
What is the meaning of Total Revenue? How is it calculated? Explain with example.
Answer:
The total sales value received in terms of rupees from the quantity of a product produced sold. The total sales value received by the seller from selling a given amount of the product is called total revenue.
The total revenue is equal to the total quantity of the commodity sold multiplied by the price (or average revenue) TR = Q × P. For example, if a firm sells 1,000 units of a product at a rate of ₹ 5, its total revenue will be 1,000 × 5 = ₹ 5000.
Question 3.
What do you mean by Average Revenue? How is it calculated? Explain with example.
Answer:
Average revenue is the per unit revenue received from the sale of a commodity. Price paid by the consumer for a product forms the revenue or income of the seller. It can be obtained by dividing the total revenue by the number of units produced and sold. Thus,
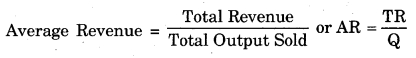
For example, if a firm’s total revenue for one year is ₹ 20 Lac and total quantity sold is 20,000 units, its average revenue will be 20,000,00 ÷ 20,000 = ₹ 100 .
Question 4.
What is marginal revenue ? How is marginal revenue calculated ? Explain with an example.
Answer:
The additional revenue obtained by a firm by selling one additional unit of a commodity, is called marginal revenue. It is calculated by the following formula :

For example – If ₹ 500 are obtained by selling 100 units, and ₹ 504 are received by selling 101 units, the marginal revenue will be –
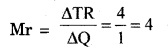
Question 5.
How do changes in total revenue affect marginal revenue?
Answer:
- When TR is increasing at constant rate, MR should be constant.
- When TR is increasing at diminishing rate, MR should be diminishing.
- When TR is maximum, MR is zero.
- When TR is diminishing, MR is negative.
Question 6.
What change in total revenue will result in
(a) A decrease in marginal revenue, and
(b) An increase in marginal revenue.
Answer:
(a) A decrease in marginal revenue – When MR is declining, less is added to TR for every additional unit sold. Accordingly, TR increases only at a diminishing rate. TR stops increasing when MR = 0 so that TR is maximum when MR = 0.
(b) An increase in marginal revenue – In case AR is constant (as under perfect competition), MR is also constant, implying that TR increases at a constant rate. Accordingly, TR forms a straight line sloping upward and starting from the origin.
Question 7.
What do you understand by Monopoly Market? What is the shape of Revenue Curve in Monopoly Market?
Answer:
The word monopoly is composed of two letters ‘mono’ and ‘poly’, where mono means single, whereas ‘poly’ means to sell. Actually, the term in economics is associated with the degree of competition prevailing in the monopoly market. The absence of any form of competition and the existence of pure or complete control of a firm on the production and sale of a commodity is the fundamental property of monopoly.
According to John D. Sumur, “Pure monopoly implies zero elasticity of demand in contrast to the infinite elasticity of demand which is the characteristic of pure competition.”
In the case of monopoly, one firm constitutes the whole industry. Therefore, the entire demand of the consumers for a product faces the monopolist. Since the demand curve of the consumers for a product slopes downward, the monopolist faces a downward sloping demand curve.
Quiestion 8.
What is imperfect competition market? What is the type of Marginal Revenue Curve and Average Revenue Curve of firm in this market?
Answer:
Imperfect competition is a market frame in which there are many vendors of an item, but the products of such vendors are different from other vendors. Products of different producers are close choices.
According to Lim Clong Yah, “Imperfect Competition is a market situation where there are many producers but each offers a slightly differentiated product.”
At this stage of the market, the firm’s average and marginal revenue is declining, and thus their curves slope downwards (have a negative slope), but the slopes are lesser (less sleep) than those in a monopolistic market.
Question 9.
What is Oligopoly? What is the shape of Demand Curve in this market?
Answer:
The term oligopoly is coined from two Greek words ‘oligol’ meaning a few and ‘pollein’ meaning to sell. Oligopoly is an important form of imperfect competition where there are few firms in the market producing either homogeneous products or close substitutes.
According to Prof. George J.Stigler, “That situation in which a firm bases its market policy in part on the expected behaviour of a few close rivals.”
Due to this uncertainty of the price, the demand curve of the seller is also uncertain and the market demand curve is also somewhat distorted, which reflects the price persistence in the market.
Question 10.
What do you understand by perfect competition market? What are the shape of Average and Marginal Revenue Curves of firm in this market?
Answer:
Perfect competition refers to the position of a market in which there are large number of buyers and sellers of a large homogeneous product. The price of the product is determined by the demand and supply forces of the market. The maximum output that a personal firm can produce, is relatively small for the total demand of the industry’s product so that it can not influence the price by changing the supply of the output. With this, many companies are in a position to influence the price of the product.
The average and marginal curves in such market are the same, which is a straight line parallel to the X axis.
Question 11.
If the monthly total sales of a firm is ₹ 20,000 and the quantity of sales is 800 units, then what will be the average revenue?
Answer:
Average Revenue = Total Revenue/Total quantity sold = 20,000/ 800 = ₹ 25.
Question 12.
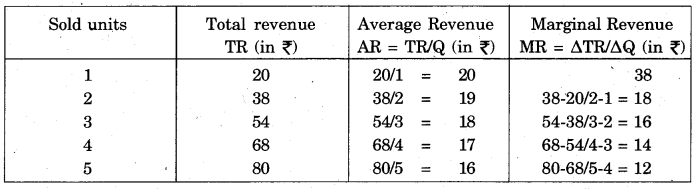
Calculate the average and marginal revenue with the help of the following:
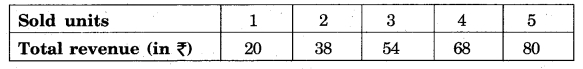
Answer:
Question 13.
What is the difference between the revenue curves of perfect and imperfect competition markets?
Answer:
- In a perfect competition market, the average and marginal curves are not different but the same curve. In imperfect market, both these curves are different.
- The revenue curves in a perfect market are perfectly elastic, while in imperfect competition market, the revenue curves are moderately elastic.
Question 14.
Why does the revenue curve form a negative slope in imperfect competition market and monopoly market?
Answer:
The revenue curve forms a negative slope in imperfect competition market and monopoly market because in these conditions when a firm increases its level of putput, the price of its product falls. In monopoly and other various forms of imperfect competition, average revenue (AR) curve slopes downward and marginal revenue curve (MR) lies below it. An important fact about the position of MR curve corresponding to the downward sloping straight-line AR’curve should be remembered. When a straight-line average revenue curve slopes downward, marginal revenue curve (MR) which lies below it will pass through the middle of the distance between the AR curve and Y-axis.
Question 15.
What is the relation between total revenue and marginal revenue?
Answer:
Following points show the relation between total revenue and marginal revenue :
- When TR is increasing at constant rate, MR should be constant.
- When TR is increasing at diminishing rate, MR should be constant.
- When TR is maximum, MR is zero.
- When TR is diminishing, MR is negative.
Question 16.
What is the relation between average revenue and marginal revenue?
Answer:
- Average revenue expresses the per unit price of a commodity. It can never be negative, while marginal revenue can be negative.
- When average revenue is constant, both average and marginal revenue are equal.
- When average revenue is decreasing, it is greater than marginal revenue.
Question 17.
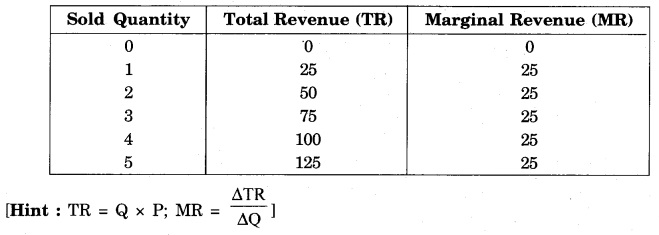
The price of a commodity is ? 25 per unit in a perfectly competitive market. Complete the table given below :
Answer:
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 9 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain revenue, total revenue, marginal revenue and average revenue with the help of examples.
Answer:
(A) Revenue – The amount of money earned by a company through the sale of goods or services, rent and other sources. Revenue includes cost of production and profit of the company.
(B) Total Revenue – The total sales value received in terms of rupees from the quantity of a product produced and sold. The total sales value received by the seller from selling a given amount of the product is called total revenue.
The total revenue is equal to the total quantity of the commodity sold multiplied by the price or average revenue [TR = AR × Q] or [TR = Q × P]
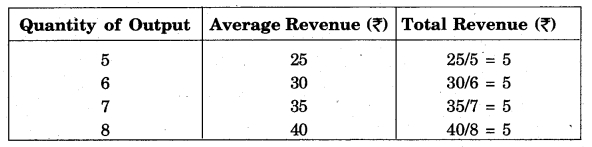
For Example – Find out TR with the help of given AR and Quantity of output:
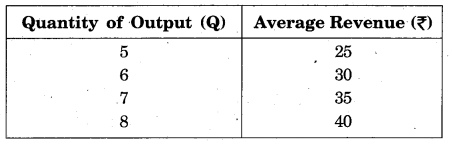
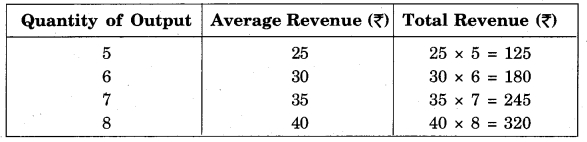
Solution:
According to the formula :
Total Revenue = Average Revenue × Quantity of Output
(C) Marginal Revenue – Marginal revenue is the addition made to the total revenue by selling one more unit of a commodity. When the price remains the same, and an additional unit is sold, the marginal revenue will be equal to the average revenue, due to the fall in the price, there is no damage to the previous units. When the average revenue falls, the marginal revenue is less than the average revenue and when the average revenue remains constant the marginal revenue is equal to the average revenue.
It is expressed like this –
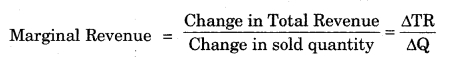
For Example – If we get ₹ 500 from the sales of 100 units and ₹ 504 from the sales of 101 units, then the Marginal Revenue will be ₹ 4.
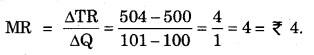
(D) Average Revenue – Average revenue is the per unit revenue received from the sale of a commodity. Price paid by the consumer for a product forms the revenue or income of the seller. It can be obtained by dividing the total revenue by the number of units produced and sold. Thus,
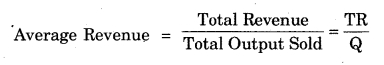
For Example
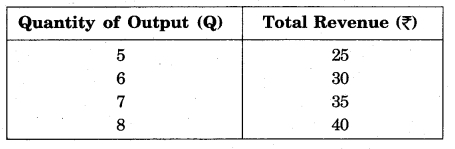
Solution:
According to the formula :
Average Revenue = Total Revenue/Quantity of output
Question 2.
What do you understand by imperfect competition market? What are the types of revenue curves in this market? Explain it with the help of a table and diagram.
Answer:
Imperfect Competition Market – Imperfect competition is an important market category wherein individual firms exercise control over the price to a smaller or larger degree depending upon the degree of imperfection present in case. Control over price of a product by a firm and therefore the existence of imperfect competition can be caused either by the ‘fewness’ of the firms or by the product differentiation. It exists in which a large number of firms produce and sell products which are differentiated but close substitute of each other.
According to Leftwich, “Imperfect competition is a market situation in which there are many sellers of a particular product, but the product of each seller is in some way differentiated in the minds of consumer from the product of every other seller.”
According to Lim Clong Yah, “Imperfect competition is a market situation where there are many producers but each offers a slightly differentiated product.”
The demand curve of an Imperfect competitive market slopes downward. This means that as price decreases, the quantity demanded for that good increases. The revenue concept in an imperfect competition market can be explained by the following table :
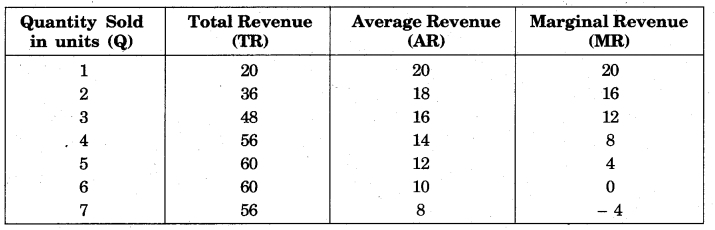
From the above table, the curves of total revenue, average revenue and marginal revenue can be drawn for comparative study.
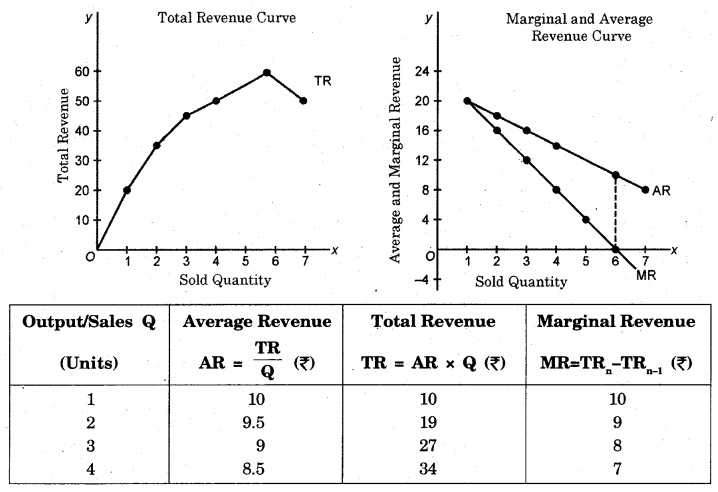
Under imperfect competition, AR and MR curves are more elastic. It means that when a firm under imperfect competition raises the price, the proportionate fall in its demand will be more. It is so because in a imperfect competitive market, goods have their substitutes and buyers are equally attracted towards them. Thus, if a firm raises price, demand for its product will fall and if it lowers the price, demand for its product will rise.
Question 3.
What are the features of monopoly market? What is the type of revenue curve in this market? Explain it with the help of table and diagram.
Answer:
Following are the features of Monopoly Market –
(a) Single Seller – Under monopoly, there should be a single producer of the commodity.
(b) Monopoly is also an Industry – There being only one firm, the distinction between firm and industry no longer exists. Monopoly firm is also an industry.
(c) Substitute of the Commodity – All the units of a commodity are identical and there are no close substitutes of that commodity.
(d) No entry of new firms – There is restriction on other firms to enter the market.
(e) Price Control – Another distinct feature of monopoly firm is that it enjoys freedom and independence in fixing the price of the commodity or the ouptput, it can fix either the price or output, but not both.
(f) Different Average and Marginal Revenue Curves – Under monopoly, average revenue or demand curve and marginal revenue curve are separate and downward sloping.
(g) Selling Costs are very Small or Marginal – This is so because if a buyer has to buy that product, he has to buy it from the monopoly firm only. Therefore, there is no competition, and hence, no need of incurring selling costs, i.e., costs on advertisement, etc.
(h) The demand curve – The demand curve in a monopolist market slopes downward. This means if he sets a lower price of his product, he can sell more. On the other hand, if he sets a higher price of his product, he will be able to sell less quantity of his product.
Under monopoly, the average revenue curve and marginal revenue curve slopes downwards from left to right. It means that if a monopolist desires to sell more units of the output, he will have to reduce the price. On the other hand, if the monopolist desires to charge high price, he will be able to sell less units of output. In other words, there is negative relationship between the demand for the product of monopolist and its price. Such average and marginal revenue curves are shown in given table and diagram-
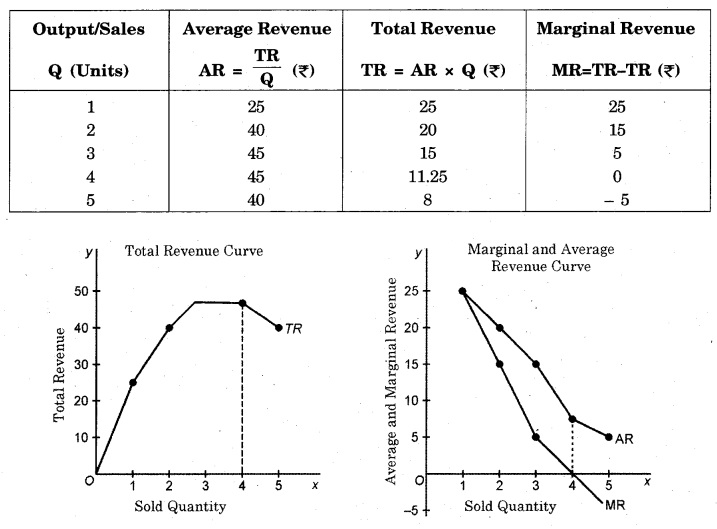
It is clear from the figure, that after the fourth unit, the total revenue starts decreasing, because after this, marginal revenue becomes negative. The slope of marginal revenue curve is steeper in comparison to the slope of average revenue curve. This impolies that marginal revenue is falling at a higher rate than the average revenue. The average revenue curve is the demand curve of the firm.