Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 11 World: International Trade
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 11 Text Book Questions
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 11 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
An important aspect of International Trading is:
(a) Population Factor
(b) Foreign Investment
(c) Trade volume
(d) Transportation
Answer:
(c) Trade volume
Question 2.
GATT – Trading agreement was implemented in:
(a) 1948
(b) 1995
(c) 1950
(d) 1945
Answer:
(a) 1948
Question 3.
World Trade Organisation has its headquarters at:
(a) Japan
(b) France
(c) United States of America
(d) Geneva
Answer:
(d) Geneva
Question 4.
World Trade Organisation was formed in:
(a) 1948
(b) 1947
(c) 1994
(d) 1996
Answer:
(c) 1994
Question 5.
Which is the group of International oil – producing countries?
(a) ASEAN
(b) OPEC
(c) SAFTA
(d) E.U.
Answer:
(b) OPEC
Question 6.
Where is the headquarter of ASEAN located?
(a) Jakarta
(b) Singapore
(c) Malaysia
(d) Vietnam
Answer:
(d) Vietnam
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 11 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 7.
Define International Trade.
Answer:
International trade is the exchange of goods and services that takes place between two or more countries through national boundaries.
Question 8.
What is GATT?
Answer:
GATT is the world’s first and most extensive trade agreement which gave various member countries of the world a platfrom to discuss their trade problems and find their solutions.
Question 9.
When was WTO established?
Answer:
WTO was established in 15th April, 1994.
Question 10.
Where is the headquarter of WTO located?
Answer:
WTO’s headquarter is located in Geneva in Switzerland.
Question 11.
Name any two member countries of ASEAN.
Answer:
Malaysia and Thailand are two member countries of ASEAN.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 11 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 12.
Write a note on the history of International Trading.
Answer:
In ancient time, due to lack of transport system, trading was limited within the boundaries of the nation. Only a few rich people used to buy ornaments and expensive garments, this instigated international trade. The merchants then started trading of expensive goods like silk, precious metals, spices, etc through a 6000 km long route also known as the “silk route” which connected Rome to China.
After division of the Roman Empire, there was an increase in European trade during 12th and 13th century. With the development of seafaring warships, trade between Europe and Asia increased.
Trading of foreign commodities began in 15th century with the rise of European colonialism. In the first half of the 19th century, most of the international trade in the world began amongst industrialised nations of the world.
But after Second World War, the nations imposed trade tax. and quantities restriction which adversely affected international trade. To overcome this situation, GATT was signed to promote trade by reducing or eliminating trade tariffs on January 1, 1948.
Question 13.
Write a note on either GATT or WTO.
Answer:
General Agreement on Tariff and Trade was an agreement signed by 96 countries with an objective to promote international trade by reducing or eliminating trade’barriers. This agreement was signed on 30th October 1947, and was implemented on 1st January 1948. It was a multilateral international treaty that covered almost 80% of the world trade. The GATT was dissolved on 1st January 1985 and it was merged into World Trade Organisation (WTO). GATT was a permanent international organisation which had its headquarters at Geneva (Switzerland).
OR
World Trade Organisation:
GATT was dissolved on January 1, 1985, and in its place, an international organisation named World Trade Organisation began to work. WTO is an international work plan to promote liberalisation, globalisation and privitisation, whose all members follow the trade-related laws directed to countries. By December 19, 2015, about 164 countries became members of WTO, in which India is also included. Both developed and developing countries of the. world are included in it The major part of global trade is carried out between these countries.
Question 14.
State some advantages of International Trading.
Answer:
Many economic and socio – cultural benefits are obtained from international trade. The main benefits among these are the following:
1. Increased Production:
Every country of the world exports those commodities to foreign countries, which it produces at lesser cost as to other countries. The exporting country increases its exports and attains specialisation in production of that product, and thus increases its production.
2. Increased National Income:
Through the income from export, the national income of the concerned country increases.
3. Export of Surplus:
By exporting excess amount of produced commodity than its domestic needs, a country earns foreign exchange.
4. Efficient Management of Resources:
Through international trade, from the point of view of comparative profits, resources are more efficiently managed.
Other Benefits:
- Benefits of division of labour and specialisation.
- expansion of international markets.
- large – scale production.
- availability of commodities and services.
- uniformity/rationalisation in costs of commodities.
- familiarity with culture, language, religion, customs and traditions of different countries.
Question 15.
What is International Trade? Explain.
Answer:
International Trade is the exchange of goods and services between two or more than two nations. In other words, international trade is the exchange of commodities and services among various countries through their national boundaries. Any country needs to trade in order to obtain those commodities which they either cannot produce themselves or which they can obtain form other countries at lesser costs.
Question 16.
Describe Regional Trading Groups and provide explanation of any one group.
Answer:
Regional Trade Groups came into existence to remove restrictions of trade from developing countries and to maintain equality among local countries. The development of these trade groups has finally occurred in response to the failure of the World Trade Organization to accelerate regional trade. Although these regional groups removed trading interest from member countries and promoted free trading, but it is very difficult among trading organisations to do free trading.
European Union:
This organisation is called EU in short. The European Union was originally formed in March 1957 in Europe as EEC which included six European countries – Italy, France, Germany, Belgium, Netherlands and Luxemberg. Later, Austria. Denmark, Finland, Ireland, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, and Britain joined it in 1992, and it was renamed E.U.
The headquarters of this group is located in Brussels, Belgium. The major trading commodities of this group are – agricultural produce, minerals, chemicals, timber, paper, transport modes, optical articles, watches, art pieces and antique articles. In addition to this, single currency and single market is available among countries of the European Union.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 11 Essay Type Questions
Question 17.
Explaining International Trade describe its advantages and disadvantages.
Answer:
International trade:
International trade is such trade which is carried out between two or more than two countries. Countries need to trade in order to obtain those ’commodities which they either cannot produce in the country or which they can obtain at lesser costs from other countries.
Advantages of International Trade:
International (foreign) trade receives many types of economic and socio – cultural benefits. Some of these are static types and some are variable or dynamic types. Major advantages of international business are the following:
1. Increases in production:
Countries engaged in international trade get specialisation in the production of those items, those which can be manufactured at a relatively low cost. Every country exports such items. Thus, the production of such a product increases by increasing export.
2. Increase in national income:
After getting increased export in the production of an item, more income is obtained from many manufactures. It increases national income of the country The increase in the level of production increases the growth rate of the economy.
3. Export of Surplus:
The resources which were lying unutilised (i.e., land labour etc.) before engaging in international trade add no benefit to the economy of the country. Benefits can be obtained only by exporting more produced items than internal requirements.
4. Efficient use of resources:
Countries that are engaged in international trade often receive specialisation in the production of those items whose production is even more efficient. So, the efficient use of resources is done in terms of comparative advantages.
5. Benefits of division of labour of the country and specialisation:
Expansion of business outside the borders of division of labour provides a country benefits. It separates the area of specialisation in the production of goods and the benefits it generates. Countries participating in international trade receive all the benefits of regional labor division and specialisation.
6. Market expansion:
International trade extends the boundaries of the market for goods and services of a country, by which goods and services begin to be supplied in a very wide area.
7. Mass production:
Due to foreign trade, the country enjoys the convenience of optimally utilising its natural resources by expanding market area. Considering increase in demand, the production of goods is done on a large scale in order to increase export.
8. Availability of goods and services:
Citizens of any country engaged in international trade can also use those goods and services, which are not produced in their country. Such goods and services are imported from other countries. Any country can buy goods from countries where their prices are minimal.
9. Parity in values:
Equality is established in the costs of commodities by international trade. As a result, the goods are sent for a place with lower values than the actual value. Thus, due to market actions, there is a tendency for value to come into equity.
10. Cultural benefits:
People from different countries come in contact through international trade and become familiar with one another culture and languages, religion, tradition and customs. International trade brings people close to one another and they interact with one another’s traditional culture. International Trade, sometimes blocks the growth of developing nations. Developed nations do not provide opportunities to developing nations to grow in economic sphere. Business delegations often visit other countries. This makes mutual reconciliation between people of different countries possible.
Disadvantages:
International trade is generally considered to be profitable but there are some disadvantages also.
1. Excessive use of natural resources:
Generally, developing nations for the purpose of earning more and more by exporting abroad exhaust their mineral resources and power resources, etc. very soon. Due to excess demand of coal, iron, manganese, petrol or mineral oil etc. in developed industrial areas, excessive export of these substances ends their accumulated stock at very fast speed.
2. Singular development of a Country:
Each country produces only those items for foreign trade that is based on specialisation and division of labour. Only a few industries are developed. Due to one dimensional development, many resources of the country remain unutilised. The country sometimes falls into a grave economic crisis.
3. Foreign Dependence:
The dependence of different countries in international trade increases on one another and the sense of self reliance and economic status weaken. When import – export is interrupted during emergent wartime, then appears a huge financial crisis in the country.
4. Adverse effect of foreign competition:
Import of relatively cheap foreign goods poses a threat to many industries in the country. Due to this, the factories are closed in developing countries and new industries are not established. Thus, the economy of a country becomes dependent on other countries and its self reliance begins to end. In the 19th century, due to British business competition, many small and cottage industries in India were destroyed.
5. Political Slavery:
The resourceful foreign capital sources try to dominate the country through international trade. Independence of weaker countries gets threatened. New colonialism is expanding even by the present globalization. One can understand this fact, when impact of China is growing over Pakistan, Bangladesh and Nepal. China can change its policy and can interfere in their internal politics.
Question 18.
What is World Trade Organisation’s role in India’s International Trade? Explain.
Answer:
World Trade Organisation was established on 1st January 1994. WTO benefited the Indian international trade in numerous ways. Such as:
The ministry of commerce and trade has illustrated the following facts on 18 January 2016:
- Indian international trade was very low due to grave recession.
- During April to December 2015 there was a negative trade balance recorded due to fall in the global demand. (Both exports and imports dropped)
- The growth of dollar and rupee both registered a negative trend.
- There was fall in the import of oil, petroleum and other products. With the decrease in the price of the crude oil in international markets, there was a fall of 41.6% in crude oil import bill in just 9 months
- In this 9 – month period in 2015 – 16 (April – December) the trade deficit of the country also decreased.
- Non – petroleum imports dropped from 235 billion dollars to 227 billion dollars in this period.
The Data of foreign trade is given in the below table:
Table: India’s foreign Trade statistics – At a glance (in billion dollars)
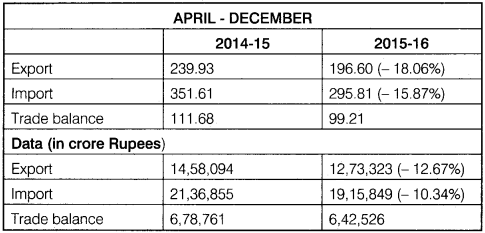
Note:
The figures given in brackets show decrease in percentage terms from previous year.
Question 19.
What is the importance of International Trade? Describe important aspects of it.
Answer:
Importance of International Trade:
International trade is the result of specialisation in production. When various countries use division of labour and specialisation in providing availability of services and production of commodities, then international trade brings benefits to entire world’s economy. This kind of specialisation creates trade opportunities. In this way, international trade is based on the principle of comparative profits of commodities and services, sufficiency and transferability.
In principle, this trade partnership should be mutually and equally profitable. In present times, trade has become the basis of economic organisations of the world, and it has become related to foreign policies of nations. Today, no country, which has a well – developed transport and communication system is prepared to forgo the benefits derived from being a partner in international trade.
Important aspects of International Trade:
1. Trade Volume:
The actual weight of commodities traded is known as trade volume. However, the value of trading merchandise and services cannot be measured by their weight. Therefore, the total value of goods and services traded is known as the volume of trade.
2. Trade combination:
In the last century, there have been changes in the types of goods imported and exported by the countries. In the beginning of the last century, the primary products were trading heads. Later, the manufactured goods gained prominence, and at the present time, though most of the world trade is dominated by manufacturing sector, service sector, which includes travel, transportation and other commercial services has also entered foreign trade in a big way.
3. Trade direction:
It is historically known that from developing countries like India, value items and crafts are exported to European countries. During the 19th century, there was a reversal in the direction of trade. European countries started exporting goods from their colonies’ in exchange for food and raw materials. Europe and the United States emerged as major trading partners in the world because of leading trade in manufacturing commodities.
At that time, Japan was also the third important trading country. In the second half of the 20th century there was a rapid change in the practice of world trade. The colonisation ended in Europe, while India, China and other developing countries started counter-revolution with developed countries. At present, the nature of merchandise has also changed.
4. Trade balance:
Trade balance documents the quantity of goods and services imported by one country and similarly exported by other country. If the value of import is higher than the country’s export value, the trade balance of the country is uninspirational or unfavorable. If there is more export then import then the trade balance of the country is positive or friendly. There is a serious importance of balance of trade and payment for the economy of the country. A negative balance will mean that the country cannot purchase more than it earns from the sale of its goods.
Question 20.
Describe Regional Trade Groups.
Answer:
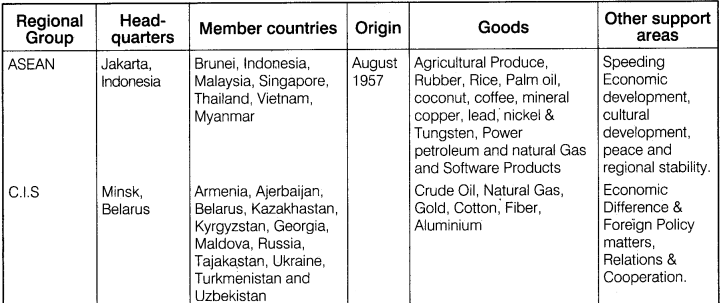
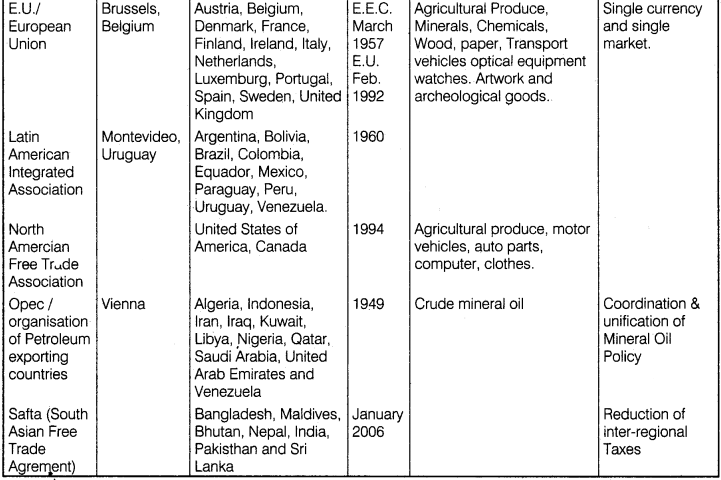
Regional Trade Groups came into existence to remove the restrictions of trade from developing countries and to maintain equality among local countries. The development of these trade groups has finally happened in response to the failure of the World Trade Organisation to accelerate regional trade. Although these regional groups removed trading barriers from member countries and promoted free trading, but it is very difficult among trading organisations to do free trading. Some of the important regional trading Organisations are given below:
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 11 Additional Questions with Answers
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 11 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
In ancient time the Silk Route connected:
(a) Rome and China
(b) Tehran and India
(c) Berlin and India
(d) Kabul and China
Answer:
(a) Rome and China
Question 2.
Who started “Slave Trade” in the 17th and 18th century?
(a) Portuguese
(b) Dutch and Spanish
(c) British
(d) All these
Answer:
(d) All these
Question 3.
In which year was GATT transformed into WTO?
(a) 1995
(b) 1997
(c) 1999
(d) 2001
Answer:
(a) 1995
Question 4.
Which of the following countries are not a part of ASEAN trade group?
(a) Indonesia
(b) Russia
(c) Singapore
(d) Malaysia
Answer:
(b) Russia
Question 5.
The headquarters of C.I.S. is in:
(a) Minsk
(b) Vienna
(c) Brussels
(d) Jakarta
Answer:
(a) Minsk
Question 6.
When was European Union formed?
(a) 1990
(b) 1992
(c) 1994
(d) 1996
Answer:
(b) 1992
Question 7.
In which of the continents does the highest flow of international trade occur?
(a) Asia
(b) Europe
(c) North America
(d) Africa
Answer:
(b) Europe
Question 8.
Which one of the following South American countries is a member of OPEC?
(a) Brazil
(b) Venezuela
(c) Chili
(d) Peru
Answer:
(b) Venezuela
Question 9.
India is a member of which of these regional groups?
(a) SAFTA
(b) ASEAN
(c) OECD
(d) OPEC
Answer:
(a) SAFTA
Question 10.
The headquarters of OPEC is located in:
(a) Riyadh
(b) Tehran
(c) Vienna
(d) Jakarta
Answer:
(c) Vienna
Question 11.
Which of the following countries is not a member of OPEC?
(a) Iraq
(b) Iran
(c) Saudi Arabia
(d) Oman
Answer:
(d) Oman
Question 12.
“Single currency and single market” is the objective of which of these Organisations?
(a) ASEAN
(b) SAFTA
(c) EU
(d) NAFTA
Answer:
(c) EU
Match the Following
Question 1.
Match the options given in column A with correct options given in column B:
| column A (Trade Organisation) | Column B (Headquarters) |
| (i) WTO | (a) Brussels |
| (ii) ASEAN | (b) Vienna |
| (iii) C.I.S. | (c) Geneva |
| (iv) E.U. | (d) Jakarta |
| (v) OPEC | (e) Minsk |
Answer:
(i) c, (ii) d, (iii) e, (iv) a, (v) b.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 11 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Trade comes under which economic activity?
Answer:
Trade is a tertiary economic activity.
Question 2.
What are the different levels of trade?
Answer:
Trade can be divided into two levels, International and National Trade.
Question 3.
What is National Trade?
Answer:
National Trade is exchange of goods and services within the boundaries of a particular nation.
Question 4.
What is “Silk Route”?
Answer:
Silk route is the name given to the trade route transporting silk, wool and other commodities which connected Rome to China. This route was 6000 km long and it passed through India, Iran and Central Asia.
Question 5.
How has trade between Asia and Europe increased?
Answer:
With the development of seafaring warships, trade between Europe and Asia increased.
Question 6.
Which countries were mainly involved in “Slave Trade” between 15th to 18th century?
Answer:
Holland, Denmark, Spain, Great Britain and United States of America were the countries mainly involved in “Slave Trade”.
Question 7.
What resulted in International Trade?
Answer:
Specialisation in goods and services resulted in International Trade.
Question 8.
What is the basis of International Trade?
Answer:
Basis of International Trade are:
- Difference in natural resources.
- Population Factor.
- Phase of economic development.
- Foreign investment limit.
- Transport.
Question 9.
What are the important aspects of International Trade?
Answer:
The important aspects of International Trade are:
- Trade Business volume.
- Trade combination.
- Trade direction.
- Trade balance.
Question 10.
What is trade volume?
Answer:
The actual weight of commodities traded is known as trade volume. The total value of goods and services traded is known as the volume of trade.
Question 11.
What is trade balance?
Answer:
Trade balance is the difference between a country’s imports and its exports for a given time period.
Question 12.
What does trade balance document ?
Answer:
Trade balance documents the quantity of goods and services imported by a country and similarly the quanity of commodities and services exported to other countries.
Question 13.
When does the trade balance of any nation become negative?
Or
What is meant by unfavourable trade balance?
Answer:
If the import value of a nation is more than the export value then it is known as negative or unfavourable trade balance.
Question 14.
Why is a negative trade balance harmful for any country?
Answer:
If the value of imports of a country is more than the value of its exports, the country is in a state of negative trade balance which accelerates the exhaustion of foreign exchange reserves as a final consequence.
Question 15.
What is meant by positive trade balance?
Or
When does a country have a favourable trade balance?
Answer:
If the value of exports of a country exceeds the value of its imports, it is called positive trade balance.
Question 16.
Into how many categories is international trade categoried ?
Answer:
International trade is categorised into two types – bilateral trade and multilateral trade.
Question 17.
What is bilateral trade ?
Answer:
When two countries carry out trade between them, it is called bilateral trade.
Question 18.
What is multilateral trade?
Answer:
When commodities and servies are traded among many countries, it is called multilateral trade.
Question 19.
Mention the benefits of international trade.
Answer:
Among the major benefits of international trade are – increased production, increased national income, disposal of surplus, efficient use of resources, division of labour, expansion of market, mass production, availability of commodities and services, equality of prices and cultural benefits.
Question 20.
Mention the disadvantages of international trade.
Answer:
Among disadvantages of international trade are – excessive exploitation of natural resources, singular development of country, foreign dependence, adverse effects of foreign competition and political slavery.
Question 21.
What is free trade ?
Or
What is meant by trade liberalisation?
Answer:
The opening of economics for trade is called free trade or trade liberalisation. This process reduces trade barriers (i.c.,toll tax/customs duty).
Question 22.
Write the full form of GATT.
Answer:
General Agreement on Tariff and Trade.
Question 23.
When and why was GATT established?
Answer:
In order to free the world from high rate of customs duty and various other obstacles, some countries formed GATT, in 1948.
Question 24.
What is World Trade Organisation?
Answer:
World Trade Organisation is the international body which lays down the laws of global trade among various countries.
Question 25.
When and where was World Trade Organisation established?
Answer:
World Trade Organisation was established in January 1995 in Geneva, Switzerland.
Question 26.
What is the objective behind the formation of World Trade Organisation?
Answer:
The objective of World Trade Organisation is to develop smooth international trade among various member countries.
Question 27.
What are the basic functions of World Trade Organisation?
Answer:
- WTO lays down rules for the global trading system.
- It resolves trade-related issues among member countries.
- It also includes functions such as telecommunications, banking services and intellectual property right trading.
Question 28.
Mention the names of any one founding country of WTO.
Answer:
India.
Question 29.
Write the names of any four regional trade groups.
Answer:
1. ASEAN.
2. C.I.S.
3. OPEC
4. SAFTA.
Question 30.
Write the names of any two member countries of ASEAN.
Answer:
1. Thailand.
2. Singapore.
Question 31.
When was OPEC established ?
Answer:
OPEC was established in 1949.
Question 32.
What benefits are obtained from trade groups by countries ?
Answer:
Geographical proximity, parity and sufficiency in trade heads are achieved from the regional groups. This enables removal of trade barriers and development of trade among various countries.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 11 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-I)
Question 1.
Explain how difference in natural resources increases International Trade?
Or
Difference in natural resources affects international trade. Explain this statement.
Answer:
Difference in natural resources increases international trade. This is because:
1. Geographical structure:
Geographical structure determines the mineral resource base. The surface variations ensure variety of crops and animals. The agricultural potential is high in the plains. Mountains attract tourists and this promotes tourism.
2. Mineral resources:
Mineral resources are distributed unequally around the world. Availability of mineral resources provide basis of industrial development and encourge international trade.
3. Climate:
The climatic conditions of a country determine diversity of products made in it, which promotes international trade.
Question 2.
Explain how population as a factor affects International Trade.
Answer:
The distribution and the rise of population in different countries affects the type and quantity of commodities traded.
1. Cultural factors:
Various forms of art and handicrafts have evolved in specific cultures, which are supported throughout the world. For example, best selling Porcelain and China clay pottery are produced by China. The carpet of Iran is famous, while leather work in North Africa and Indonesian Batik clothing is a valuable handicraft.
2. Population size:
Internal trade is more in countries with high population densities while external trade is less. Countries with high living standard have more demand of imported products, while it is not so in countries with low living standard.
Question 3.
How cultural factor is a basis of International Trade?
Answer:
Art and culture is the basis of any nation’s identity. Each nation has its own specialised forms of art and handicrafts. For example : China clay crockery of China, carpets of Iran etc. These handicraft products are in high demand throughout the world. This increases the demand for such products which ultimately increases international trade.
Question 4.
Why business volume is an important aspect of International Trade?
Answer:
The actual weight of commodities traded is known, as trade volume. However, merchandise services cannot be measured in terms of weight. Therefore, the total value of goods and services traded is known as the. volume of trade.
Question 5.
Explain International trade combination.
Answer:
International Trade Combination:
In the last century, there have been changes in the types of goods imported and exported by the countries. In the beginning of the last century, the primary products were trade heads. Later, the manufactured goods gained prominence, and at the present time, though most of the world trade is dominated by manufacturing, the services sector has made rapid, progress in international trade.
Question 6.
What is trade balance? Explain its different types.
Answer:
Trade balance or balance of trade is the difference between the value of imports and exports of a country for a given time period.
Types of Trade:
- Positive trade balance: If the exports of a nation are more than its imports
- Negative trade balance: If the exports of a nation are less than its imports.
Question 7.
How is foreign investment limit and transportation a basis of International Trade?
Answer:
Foreign investment can promote trade in developing countries. Those countries which have deficient capital resources for development extraction, oil mining, heavy engineering and horticulture or agriculture can develop through foreign investment. By developing such capital – intensive industries in developing countries, industrial nations ensure import of foodgrains, minerals and manufactured products. This entire cycle advances the volume of trade among countries.
Similarly, in the olden times, lack of adequate and proper means of transportation restricted trade in local areas. Only high value items such as gemstones, silk and spices were used for long distance trade. Trade has experienced spatial expansion, along with better means of expansion, preservation and maintenance of road, marine and air transport.
Question 8.
Differentiate between bilateral and multilateral trade.
Or
Explain the types of International Trade.
Answer:
| Bilateral Trade | Multilateral Trade |
| 1. Trade done between two countries. | 1. Trade done between more than two countries. |
| 2. A country ‘A’ can agree to purchase/trade some raw goods on the basis that the country ‘B’ will purchase some specific goods or the other way round. | 2. Any country of the world can provide the most favoured Nation (MFN) status to any trading , partner. |
Question 9.
“Usually, International trade is beneficial to the related countries but it can be very harmful too.” Explain the statement.
Answer:
As stated above, international trade is beneficial to the related countries because it helps in gaining foreign currency which helps to improve the standard of living of a country But this also increases the dependence of a nation on another nation, uneven development, exploitation and rivalry, which may lead to world wars.
Global trade affects many of aspects of life, from world environment to health and welfare of the people etc. With the increase in trade, the production increases, which means more utilisation of natural resources like forests, minerals, water, etc. This will also increase the level of pollution, ultimately leading to various problems in the future.
Question 10.
What is the objective of regional trade groups?
Answer:
The objective of regional trade groups is to reduce or eliminate trade tariff among the member nations and to promote uninterrupted trade. These trade groups classify goods trades according to their geographical proximity, they encourage free trade, parity and sufficiency among trade in member countries.
Question 11.
Write a short note on ASEAN.
Answer:
ASEAN (Association of South – East Asian Nations) is regional trading group which was established in August 1967 with the objective of Speeding Economic development, cultural development, peace and regional stability. Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar are the member countries of ASEAN. ASEAN has its headquarters in Jakarta, Indonesia. Goods that are traded under this group are agricultural produce, rubber, rice, palm oil, coconut, coffee, minerals like copper, lead, nickel and tungsten, power, petroleum and natural gas and software products.
Question 12.
Write a short note on C.I.S.
Answer:
C.I.S stands for Commonwealth of Independent States. C.I.S was formed with an objective to economic, defence and foreign policy matters, mutual relations and cooperation. Armenia, Ajerbaijan, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyztan, Maldova, Russia, Tajakistan, Ukraine, Turkmenistan, Georgia and Uzbekistan are the member nations of C.I.S. It has its headquarters in Minsk, Belarus. Crude oil, natural gas, gold, cotton, fibre, are major commercial goods of trade of this organisation.
Question 13.
Describe the European Union briefly.
Answer:
European Union was established in February 1957 in Europe with six countries Italy, France, Germany, Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxemburg in the name of E.E.C. Later on, Austria, Denmark, Finland, Ireland, Portugal, Spain, Sweden and Britain joined the group in the year 1992. And then it was named as European Union.
E.U. has its headquarters in Brussels, Belgium. Goods that are traded under it include agricultural produce, minerals, chemicals, wood, paper, transport vehicles, optical equipment, watches, artwork and archaeological goods. The main objective of E.U. is to promote single currency and single market.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 11 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-II)
Question 1.
Why does international trade exist? Explain briefly.
Answer:
International trade is an outcome of specialisation in production. If different countries employ division of labour and specialisation in production of commodities or services, then international trade will provide benefit to global economy. This kind of specialisation can encourage trade, and also bring comparatively higher profits, sufficiency and movement – principles on which it is based. In principle, this partnership should be profitable to all equally.
In present time, trade has become the basis of economic organisations and it also directs and regulates foreign policy of nations. Today, no country which has developed communication and transport facility wants to be deprived of the benefits obtained from partnership in international trade.
Question 2.
Describe the direction of international trade in brief.
Answer:
Till the 18th century, manufactured and precious goods were exported by presently developing countries to Europe. In the 19th century, European countries imported food grains and raw materials from their colonies, and in return, European countries exported manufactured goods to their colonies. Europe, United States of America and Japan emerged as major trade partners. In the twentieth century, European colonies existed no longer and the share of developing countries like India, China and others increased, and competition arose among these countries and developed countries.
Question 3.
What is the difference between import and export? How is it related to trade balance?
Answer:
Import:
Commodities brought in one country from another country is called import.
Export:
Commodities sent from one country to another is called export.
Relation of Import export with balance of trade:
The relative values of import and export of a country is called its trade balance. There are two types of trade balance:
- Favourable trade balance – when exports exceed imports.
- Unfavourable trade balance – when imports exceed exports.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 11 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain main bases of International Trade.
Answer:
1. Bases of International Business:
(i) Differences in National Resources:
Mention of three national resources is notable in this context:
(a) Geographical structure:
Determines the differences in surface, agricultural and livestock resources. The surface variations ensure the variety of crops and animals. Thus, the agricultural potential is high in the plains. Mountains attract tourists and promote tourism.
(b) Mineral resources:
These are distributed unequally around the world. This encourages international trade. Availability of mineral resources provide basis to industrial development.
(c) Climate:
Climate of a country determines the diversity of products produced in a country. This encourages international trade.
2. Population as a Factor:
The distribution, size and diversity of population in different countries of world affect the type and quantity of commodities traded internationally.
(a) Cultural factors:
Various forms of art and handicrafts have evolved in specific cultures, which are in demand throughout the world. Handicrafts of high quality of various countries are highly traded items.
(b) Population size:
Internal business is more in countries with high population density. External trading is in less quantity because most of the agricultural and industrial products are consumed in local markets only. The living standard of the population determines the demand for imported products of superior quality because only a few people with high living standard are able to buy expensive imported items.
3. Phase of economic development:
The nature of commodities traded is influenced by the phase of economic development of a country. Various stages of economic development of countries have changed, in agriculture dominated countries, agricultural products are regulated for manufacturing goods. Industrial countries export machinery, manufactured products, and import food grains and other raw materials.
4. Foreign investment limit:
Foreign investment can promote trade in developing countries, which have less, capital to develop mining, oil mining, heavy engineering and horticulture, agriculture. There is lack of necessary capital for the development of such capital intensive industries in developing countries. By developing such capital-intensive industries in developing countries, industrial nations ensure the import of minerals and food grains. This entire cycle advances the volume of trade among countries.
5. Transportation:
In olden times, lack of adequate and proper means of transportation restricted trade to the local areas. Only high value items such as gemstone, silk and spices were used for long distance trade. Trade has experienced spatial expansion, along with better means of expansion, maintenance and preservation of road, marine and air transport.