Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 12 Environmental Problems and Solution
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 12 Text Book Questions
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 12 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
pH value of acid rain water is:
(a) between 5 to 2.5
(b) between 5 and 7.5
(c) more than 7.5
(d) less than 2.5
Answer:
(a) between 5 to 2.5
Question 2.
Formula of acid rain is:
(a) SO2 + NO2
(b) H2SO4
(C) NO2 + SO4
(d) HNO3 + SO
Answer:
(b) H2SO4
Question 3.
Which sphere does the work of preventing ultraviolet rays?
(a) Troposphere
(b) Ozonsphere
(c) Ionosphere
(d) Exosphere
Answer:
(b) Ozonsphere
Question 4.
What is emphasised in Montreal Protocol 1987?
(a) Ozone Layer
(b) Bio – diversity
(c) Green House Effect
(d) Industrial Pollution
Answer:
(a) Ozone Layer
Question 5.
First World Climate Conference was organised in:
(a) Japan
(b) Vienna
(c) Geneva
(d) Canada
Answer:
(c) Geneva
Question 6.
Earth Summit Conference 1992 was organised in:
(a) Rio de Janeiro
(b) Geneva
(c) Switzerland
(d) Copenhagen
Answer:
(a) Rio de Janeiro
Question 7.
World Bio – diversity Day is celebrated on:
(a) 5th June
(b) 11th July
(c) 22nd May
(d) 16th September
Answer:
(c) 22nd May
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 12 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 8.
In which country is the Kyoto city located?
Answer:
Kyoto city is located in Japan.
Question 9.
Which decade has been declared as the hottest decade?
Answer:
The decade 2001 – 10 has beeen declared as the hottest decade.
Question 10.
Who was elected as IPCC Chairman in Nusa Dua?
Answer:
In 2007, an Indian, Rajendra Kumar Pachauri, was elected as the chairman of IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) in Nusa Dua city located in Bali Island of Indonesia.
Question 11.
Where was the Second World Summit Conference organised?
Answer:
The Second World Summit Conference was organised in New York.
Question 12.
In which conference was the Green Climate Fund (GCF) established?
Answer:
The Green Climate Fund (GCF) was established in Cancun (Mexico) Conference.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 12 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 13.
Mention any two causes of acid rain.
Answer:
The main reason for acid rain is the emission of gases like nitrogen oxide (NO2) and sulphur dioxide (SO2), which are primarily responsible for acid rain. The following two causes are important for acid rain due to sulphur – dioxide:
- Sulphur dioxide emitted in large amount from automated vehicles and coal power plants.
- Sulphur dioxide emitted from the exploitation of fossil fuels.
Question 14.
Describe the harmful consequences of Green House Effect.
Answer:
- Due to greenhouse effect, the average temperature of the entire world is increasing steadily.
- There will be more rainfall in some countries of the world, while in other countries there will be lesser rainfall than average.
- With 0.5 degree centigrade to 1.5 degree centigrade increase in the average temperature of the earth, the ice of snowy areas will melt rapidly and flood will occur in coastal areas.
- Changes will occur in the borders of grasslands and forest areas, and the possibility of famine in desert areas of Africa will increase.
- Increasing temperature will result in the rapid growth of malaria and other diseases.
Question 15.
Write measures to prevent water pollution.
Answer:
The effective measures to prevent water pollution are as follows:
- For effective disposal of waste in water, sewage treatment plants should be established in all the cities.
- After treating water having industrial waste, it should be reused in the industries.
- In place of chemical farming, organic farming should be highly encouraged.
- Dumping of dead bodies of animals in rivers should be strictly prohibited. Electric crematoriums can be established at appropriate places along the riverside.
Question 16.
What is China Red Alert?
Answer:
On November 30, 2015, about 5.3 lakh square km area of 32 cities of China turned into escalated situation in heavy mist. Smog level reached historic level. To prevent this, China released Red Alert, under which, production of industrial plants was reduced or completely stopped. Traffic of transporting vehicles on roads was stopped. Schools in Beijing were closed. Traffic on more than 200 express – highways of China was also banned.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 12 Essay Type Questions
Question 17.
Comment on the Greenhouse Effect.
Answer:
Greenhouse Effect is a natural process, through which, the increased presence of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxide and methane in the atmosphere of the earth increases the temperature of the earth. Greenhouse effect is a process in which the rays comes from the sun stay on the earth, but that heat cannot be expelled out of the atmosphere. Due to this process, there is a steady increase in the temperature of the earth.
Causes of Greenhouse Effect:
The following factors are primarily responsible for Greenhouse Effect:
-
- The increasing use of coal and petroleum in industries.
- Due to deforestation, the increasing amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- Due to excessive exploitation of fossil fuels like wood, coal, etc., the increasing amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- Due to excessive use of refrigerators and air – conditioners, the increasing amount of chloro – fluoro – carbon (C.EC.) in the atmosphere is increasing.
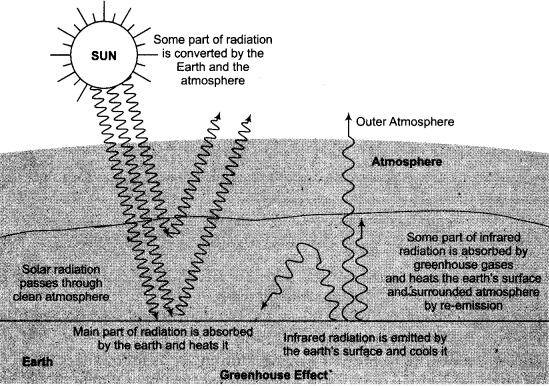
Harmful Consequences of Greenhouse Effect:
In the previous 100 years, there has been a remarkable increase in the amount of gases named carbon dioxide, methane and nitric oxide in the atmosphere, due to which, the greenhouse effect has increased on the earth. Due to the influence of greenhouse effect, the earth is steadily getting warmer. The following are the harmful consequences of greenhouse effect:
- An increase in the average temperature of the entire world is being seen. The strong sunlight and the lack of oxygen are adversely affecting the growth of trees.
- As an impact of greenhouse effect, there will be floods in some areas, while droughts will occur in some countries.
- As a consequence of greenhouse effect, with 0.5 degree centigrade to 1.5 degree centigrade increase in the average temperature of the earth, the world’s huge glaciers will melt rapidly, due to which, on the one hand, floods will occur in some coastal areas, while on the other hand, with an increase in the water level of the ocean, innumerable islands will submerge in the ocean.
- Changes will occur in the border of the world’s important grasslands and forest areas, and the possibility of famine in desert areas of Africa will increase.
- All this is likely to increase insect – borne diseases, especially malaria.
- Increasing global temperature wall have adverse effect on 8% of the bio – diversity of the world.
- Due to the impact on weather cycle, severe food – crisis may have to be faced.
Measures to Reduce Greenhouse Effect:
- Less use of fossil fuels.
- Afforestation and plantation to the maximum to maintain the balance of carbon dioxide level in the atmosphere.
- Restricting the use of chlorofluorocarbons.
Question 18.
Explain in detail the causes, consequences of acide rain and potential measures to prevent it.
Answer:
Causes of Acid Rain:
Sulphur dioxide is the main cause of Acid Rain. Sulphur dioxide gas and nitrogen oxide gas (NCR), which are released in excess amount in the atmosphere, react with water (H2O), of the atmosphere, and produce sulphuric acid (H2SO4) and nitric acid (HNO3) respectively. The main sources of the release of sulphur dioxide in the atmosphere are:
- Automobiles and automated vehicles.
- Coal – based thermal power plants.
- Mineral refineries.
- Exploitation of fossil fuels (coal, petroleum and wood).
Consequences of Acid Rain:
In the acid rain affected areas, following effects are seen:
- Acidity increases in soil with the effect of acidic – water. Also, soil minerals and nutrients are destroyed due to which soil productivity decreases.
- Factors responsible for acid rain are carried thousands of kilometers away along with the wind and on getting sufficient humidity they fall in the form of acid – rain.
- Drinking – water reserves become contaminated.
- In humans, respiratory and skin – related diseases and the problem of burning sensation in the eyes occur.
- Stomata of tree-leaves get closed, by which many biological actions of these trees slow down. Thus, acid rain has adverse effects on forests.
- Water of lakes and rivers gets polluted by acid rain, which has adverse effect on the aquatic creatures. In many lakes of Norway and Sweden, most of aquatic creatures died due to acid rain.
- Erosion begins in stone and marble due to acid rain. The Taj Mahal of Agra is getting damaged by the influence of acid rain.
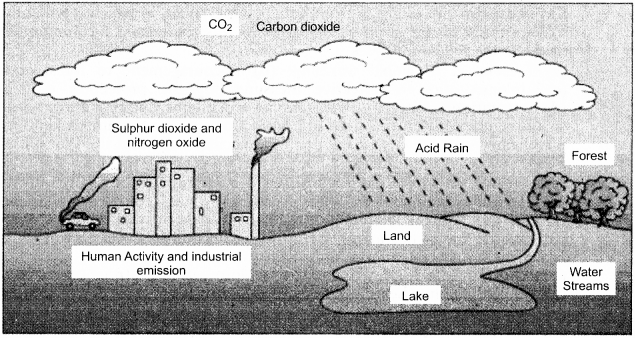
Potential Measures:
- Emissions of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide, which are responsible for acidic rainfall, should be effectively controlled. Scrubbers should be used in industries. Bag filters and colloidal tanks should be employed.
- Use of non – conventional sources of energy like solar energy and wind power should be highly encouraged.
- Automated vehicles should be tested and verified for pollution from time-to-time and use of personal vehicles should be reduced.
- To eliminate the acidity of acidity – affected water and soil, lime should be used in water and soil.
Question 19.
Describe famous Conferences to protect the world environment.
Answer:
famous International Conferences organised by the United Nations Organisation (UNO) for the protection of world environment are as follows:
1. Stockholm Conference:
To overcome the global environmental crisis, a Declaration containing 25 principles was formulated at Stockholm city of Sweden on June 5, 1972. Since this conference, the World Environment Day is being celebrated every year on June 5.
2. World Climate Conference (1979):
The first World Climate Conference was held in Geneva city of Switzerland.
3. Vienna Conference (1985):
This conference was held in Vienna city of Austria for the protection of ozone layer.
4. Montreal Protocol:
Under the auspices of United Nations Environment Programme, in 1987, at Montreal city of Canada, 33 countries of the world signed an agreement, under which, a huge reduction in the emission of harmful gases including chlorofluorocarbons, was agreed upon to prevent degradation of ozone layer.
5. Toronto World Conference:
In June, 1988, at Toronto city of Canada, with the objective of reducing greenhouse effect, the developing nations of the world were expected to voluntarily reduce the emission of chloro – fluoro – carbons by 20% by the year 2005.
6. Earth Summit Conference:
The First Earth Summit Conference was organised at Rio-de-Janeiro city of Brazil from 3 to 14 June, 1992, in which representatives from 178 countries of the world participated. At this conference, a common consent was made on the following issues:
- Prevention of global warming.
- Encouragement to forest conservation.
- Implementation of effective measures for the protection of bio – diversity.
- Restoration of integrity and quality of ecosystems, and providing mutual support to different countries for safety and protection.
- For the above – mentioned works, establishment of the Global Environment Facility Fund and the World Environment Fund.
7. Kyoto Conference:
World Environment Conference was held at Kyoto city of Japan from 1 to 11 December, 1997, which is also known as Kyoto Protocol or Green House Conference. In this conference, 159 countries of the world including India participated and signed an agreement for protection of the earth from Green House Effect, under which, on the emission of responsible gases for green house effect named carbon dioxide, methane, hydrochloro carbon, nitrous oxide, chloro – fluoro – carbon, and sulphur hexachloride, a provision was made for their deduction by 5% per year in the period from 2008 to 2012. Whereas, the European Union member countries, United States of America (on the basis of emission level of 1990) and Japan, this deduction will be by 8%, 7% and 6% respectively.
8. World Earth Conference:
At the headquarters of the United Nations located in New York, on April 22, 2016, on the occasion of the Earth Day, the representatives of more than 170 countries of the world signed the Paris Climate Change Agreement of December, 2015. This historic agreement, together with the agenda of 2030, is an important step in the field of sustainable development.
Along with this, on Dec 12, 2015, at the United Nations Climate Change Conference in Paris, capital of France, there took place the Global Change Agreement on the issues of climate change and sustainable development of agriculture.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 12 Additional Questions with Answers
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 12 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Air pollution is responsible for:
(a) Depletion of ozone layer
(b) Greenhouse effect
(c) Climate change
(d) All these
Answer:
(d) All these
Question 2.
The reason for the release of Red Alert in China on November 30, 2015 was:
(a) Radioactive pollution
(b) Air pollution
(c) Water pollution
(d) Acid Rain
Answer:
(b) Air pollution
Question 3.
Which of the following grade of petroleum is being made available by the Indian government since April 1, 2017 for the prevention of vehicle – borne air pollution:
(a) BS – 2
(b) BS – 3
(c) BS – 4
(d) BS – 5
Answer:
(c) BS – 4
Question 4.
Which of the following diseases is related to air pollution?
(a) Diarrhoea
(b) Hepatitis
(c) Lung disease
(d) Malaria
Answer:
(c) Lung disease
Question 5.
Smoke fog is related to:
(a) Water pollution
(b) Acid Rain
(c) Noise pollution
(d) Air pollution
Answer:
(d) Air pollution
Question 6.
Which of the following is a cause of acid rain?
(a) Water pollution
(b) Soil pollution
(c) Noise pollution
(d) Air pollution
Answer:
(d) Air pollution
Question 7.
Which of the following diseases is related to water?
(a) Conjunctivitis
(b) Diarrhea
(c) Respiratory infection
(d) Laryngitis
Answer:
(b) Diarrhea
Question 8.
In India, ‘Namami Ganga’ project started on:
(a) July 7, 2016
(b) August 8, 2016
(c) September 7, 2016
(d) November 8, 2016
Answer:
(a) July 7, 2016
Question 9.
The biggest source of Noise pollution is:
(a) Operation of vehicles
(b) Loud speakers
(c) Nuclear explosion
(d) Volcanic eruption
Answer:
(a) Operation of vehicles
Question 10.
‘Decibel’ is the unit of:
(a) Air pressure
(b) Noise level
(c) Air temperature
(d) Relative humidity
Answer:
(a) Air pressure
Question 11.
Which of the following rivers is the most polluted?
(a) Brahmaputra
(b) Sutlej
(c) Yamuna
(d) Godavari
Answer:
(b) Sutlej
Question 12.
Which of the following gases is dissolved in the water of acid rain?
(a) Sulphur dioxide gas
(b) Carbon monoxide gas
(c) Nitrous oxide gas
(d) All these
Answer:
(b) Carbon monoxide gas
Question 13.
Which of the following has the most adverse effect on stone and marble?
(a) Air pollution
(b) Ultraviolet rays
(c) Acid rain
(d) Global warming
Answer:
(c) Acid rain
Question 14.
The most affected area from greenhouse effect is
(a) Southern Asia
(b) Eastern Asia
(c) Western Europe
(d) Southern Europe
Answer:
(a) Southern Asia
Question 15.
At present, glaciers retreat velocity is:
(a) 1.7 mm per annum
(b) 2.2 mm per annum
(c) 2.5 mm per annum
(d) 2.8 mm per annum
Answer:
(a) 1.7 mm per annum
Question 16.
The gas most responsible for the depletion of ozone layer is:
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Nitrous oxide
(c) Chlorofluorocarbon
(d) Sulphur dioxide
Answer:
(c) Chlorofluorocarbon
Question 17.
The World Ozone Day is celebrated on:
(a) May 22
(b) September 16
(c) December 2
(d) December 5
Answer:
(b) September 16
Question 18.
The main objective of the organisation named TRAFFIC is:
(a) Protection of bio – diversity
(b) Control on illegal trade of plant and animals
(c) Control on emission of green house gases
(d) Protection of ozone layer
Answer:
(b) Control on illegal trade of plant and animals
Question 19.
Freon is the most deadly chlorofluorocarbon that is used in:
(a) Refrigerators
(b) Air conditioners
(c) Foam manufacturing
(d) In all these
Answer:
(d) In all these
Question 20.
The World Earth Day is celebrated on:
(a) April 18
(b) April 22
(c) May 22
(d) June 5
Answer:
(b) April 22
Question 21.
The organization named NEERI is located in:
(a) Nagpur
(b) Dehradun
(c) Mumbai
(d) Kolkata
Answer:
(a) Nagpur
Question 22.
The headquarters of the United Nations Environment Program is in:
(a) Geneva
(b) New York
(c) Nairobi
(d) Vienna
Answer:
(c) Nairobi
Match the Following
Question 1.
Match the options given in column A with right options given in column B:
| Column A (Organisation) | Column B (Headquarters) |
| (i) United Nations Environment Program | (a) Jodhpur |
| (ii) CAZRI | (b) Switzerland |
| (iii) WWF | (c)Dehradun |
| (iv) Indian Wildlife Institute | (d) Nairobi |
Ans. (i) d, (ii) a, (iii) b, (iv) c.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 12 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What does the word Environment mean?
Answer:
The meaning of Environment is ‘outer cover’, that is, the natural, physical and social cover around us is called the Environment.
Question 2.
What definition of the environment did C.C. Pie give?
Answer:
According to C.C.Pie, “All circumstances which surround the human in a particular place at a particular time, are called the environment”.
Question 3.
What problems have arisen due to the increased imbalance between humans and nature?
Answer:
Due to the increased imbalance between humans and nature, many problems have arisen like earthquakes, volcanoes, floods, droughts, famines, climate change, acid rain, green house effect, ozone layer depletion, barren land, pollution and desertification.
Question 4.
What is the meaning of Environmental Pollution?
Answer:
Any change in the environment which contributes to the degradation of the environment, and which has harmful effects on humans and other organisms is called Environmental Pollution.
Question 5.
What is Pollution?
Or
What is called Pollution?
Answer:
Such an unwanted change in the physical, chemical and biological properties of air, water and soil, which harms natural and cultural elements of the entire environment as well as humans, is called Pollution.
Question 6.
What is the meaning of Biosphere? Or What is called Biosphere?
Answer:
The combined area of life containing component of the atmosphere, lithosphere and hydrosphere is called the Biosphere.
Question 7.
Mention the types of Pollution.
Or
How many types of pollution can be classified on the basis of diffusion of pollutants?
Answer:
- Water Pollution
- Air Pollution
- Soil Pollution
- Noise Pollution
- Thermal Pollution.
Question 8.
What does Air Pollution mean?
Answer:
The presence of pollutants in the atmosphere due to natural or human activities is called Air Pollution. Air pollution causes harm to the life of human beings, plants and animals.
Question 9.
Into how many parts are the sources of air pollution divided?
Answer:
The sources of air-pollution are divided into two parts – natural and unnatural sources.
Question 10.
What are the natural sources of air – pollution?
Answer:
The matter erupted from volcanic explosion, dust of storms and winds, forest fire, eruption of volkanoes are included in natural sources of air pollution.
Question 11.
What are the unnatural sources of air – pollution?
Answer:
- Exploitation of fossil fuels
- Mining
- Industrialisation
- Radioactivity
- Modes of transport
- Smoking.
Question 12.
What is smoke fog?
Answer:
In industrial and urban areas, the polluted gases and pollutant elements which are present in abundant amount in the lower layer of atmosphere, when get mixed with general fog, then the smoke fog is generated. This is more hazardous for human health.
Question 13.
What does Water Pollution mean?
Answer:
Such an unwanted change in the physical, chemical and. biological properties of water, which has adverse effects on humans and all other organisms is called Water Pollution.
Question 14.
What are main causes of Water Pollution?
Answer:
Domestic waste water, agricultural waste, industrial waste, mineral oil, thermal contaminated water, atmospheric particles, radioactive waste, etc. are included in main causes of water pollution.
Question 15.
Name three diseases that occur in humans from water pollution.
Answer:
- Cholera
- Jaundice
- Stomach disorders like Diarrhoea.
Question 16.
Which is the most responsible factor for pollution of the Ganga River in Kanpur city?
Answer:
The pollution in Ganga River in Kanpur city is mainly through the effluents released by leather refinery units.
Question 17.
When was Namami Ganga project started by the Indian government?
Answer:
On July 7, 2016.
Question 18.
What does Noise Pollution mean?
Answer:
When the sound exceeds a certain level and brings harm to a person or group at the physical and mental level, then it is called Noise Pollution.
Question 19.
What does Noise mean?
Answer:
When the intensity and frequency of sound exceeds the level pleasing to the ear, it is called Noise.
Question 20.
What are the main causes of noise pollution?
Answer:
Modes of transport, loud – speakers, sound from industries, noise generated by airplanes and jet aircrafts, thundering of clouds, fireworks, etc. are included in main causes of noise pollution.
Question 21.
What are the harms caused by noise pollution?
Answer:
The negative effects on the brain, irritability, deafness, etc. are the harms caused by noise pollution.
Question 22.
Define Soil Pollution.
Answer:
Reduction in the quality of soil due to natural and human activities is called Soil Pollution.
Question 23.
What is Green house Effect?
Answer:
Green house Effect is a process in which the temperature of the earth steadily increases. The heat that comes from the sun stays on the earth, but that heat cannot be expelled out of the atmosphere.
Question 24.
What does Acid Rain mean?
Answer:
Gases like carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide and nitric oxide, emitted from various production activities of different industries, together with water vapour, through the process of precipitation, falls in the form of rain, which is called Acid Rain.
Question 25.
What are the main causes for increase In the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
Answer:
Deforestation and exploitation of fossil fuels are the main causes which increase the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Question 26.
Which country is the world’s largest green house gas emitter?
Answer:
China.
Question 27.
What is the reduction per decade in the amount of ozone of the stratosphere after 1970?
Answer:
The ozone levels are decreasing in the stratosphere by 4% per decade.
Question 28.
Why is ozone layer called human protection armour?
Answer:
Because it does not allow ultraviolet rays of the sun which are harmful for human health, to reach the earth.
Question 29.
What was the major objective of the Stockholm Conference?
Answer:
The major objective of this conference was to protect the environment of the world.
Question 30.
What was the major objective of the World Earth Conference 2016?
Answer:
The main objective of the World Earth Conference 2016 was to plant trees for the earth.
Question 31.
Where is the institution named CAZRI
located in India?
Answer:
CAZRI is located in Jodhpur.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 12 Short Answer Type Questions (SA -I)
Question 1.
Write the meaning and definition of Environment.
Answer:
The natural and social cover around us is called the environment in the real sense. The environment or circumstances in which the organism lives, is called the environment of that organism. Basic amenities like air, water, food, light and shelter are available for organisms in the environment.
Definition of Environment:
According to C.C.Pie, “All the circumstances which surround the human in a particular place at a particular time, is called his enviornment.” Enviornment is not the name of any one element, but it is the sum total of all the states or elements, which directly or indirectly affect human life and development.
Question 2.
Summarize the responsible factors for environmental problems.
Answer:
Following factors are primarily responsible for the environmental problems of the earth:
- Industrial and technological development made by humans for attainment of their physical pleasure.
- Rapid growth of world population and rapid expansion of the cities and metropolis.
- Rapid and indiscriminate exploitation of the natural resources by developed countries of the world in the past 50 years.
- The increasing tendency of humans to exploit nature.
Question 3.
What is the meaning of Pollution and Pollutants?
Answer:
Meaning of Pollution:
According to E.P Odam, “Such undesirable changes in the physical, chemical and biological properties of the air, water and soil, which harm the natural and cultural elements of the entire environment as well as the humans, is called pollution.”
Meaning of Pollutants:
Such undesirable substances, that, due to their presence, alter any main element of the environment or spread pollution, are called pollutants.
Question 4.
Write the main types of pollution based on the nature of pollutants.
Answer:
There are 10 types of pollution based on the nature of pollutants:
- Air pollution.
- Water pollution.
- Noise pollution.
- Soil pollution (Land Pollution).
- Thermal pollution.
- Radiation pollution.
- Industrial pollution.
- Pollution from garbage.
- Marine pollution.
- Pollution due to domestic waste.
Question 5.
Define air pollution and mention its sources.
Answer:
Air Pollution:
The unwanted substances found in the air reduce air quality and have harmful effects on humans and on the biological world. Such level of air is called air pollution.
Sources of air pollution:
The sources of air pollution are divided into two parts:
1. Natural sources:
Substances erupted by volcanic eruption, dust of storms and wind, forest fire, and land slides in mountains.
2. Unnatural sources:
Industries, modes of transport, smoking, use of chemicals and radioactive substances, etc.
Question 6.
Write the harmful effects of air pollution.
Answer:
The harmful effects of air pollution are as follows:
- Negative impact on human – health.
- Negative impact on natural vegetation; and threat to the existence of living organisms and insects.
- Negative impact on the atmospheric conditions, and taking place of grave problems like climate change, ozone layer depletion and greenhouse effect.
- Canopy of fog created in the cities and metropolises.
Question 7.
Summarize the measures to protect the ozone layer.
Answer:
1. According to the provisions of the Montreal Protocol, production of gases which are responsible for ozone layer depletion has been banned in the world. These gases include chloro – fluoro – carbons, halogen gases, carbon tetrachloride, trichloro ethane.
2. The production of the hazardous chloro – fluoro – carbon named Freon has been banned which is used in refrigerators, air conditioners, in the foams of seats and couches, in aerosol spray.
3. The operation of Concorde aircraft of the United States of America has been banned due to the possibility of depletion of ozone layer.
4. With the objective to promote awareness regarding protection of ozone layer, the World Ozone Day is celebrated on September 16 every year, throughout the world.
Question 8.
Write the major days declared by the United Nations with a view to environmental protection.
Answer:
The following World Days have been declared by the United Nations, with the vision of environmental protection and environmental awareness.
- World Heritage Day – April 18
- World Earth Day – April 22, celebrated on March 20 in the United Nations
- World Bio-diversity Day – May 22
- World Population Day – July 11
- Hiroshima Day – August 6
- World Ozone Day – September 16
- Green Consumer Day – December 28
- Bhopal Gas Tragedy Day – December 2
- World Soil Day – December 5
- World Environment Day – June 5
- National Pollution Prevention Day – December 2
Question 9.
Name major institutions and organizations of India related to environmental protection.
Answer:
Major institutions and organizations of India related to environmental protection are as follows:
- Botanical Survey of India – office at Kolkata; related to the survey of vegetation resources.
- The Wildlife Institute of India (Dehradun) – related to research and training.
- Kalpavriksha – Non Government Organization (NGO) working since 2003 for the protection of bio – diversity and environment.
- CAZRI (Central Arid Zone Research Institute) – centred at Jodhpur.
- FRI (Forest Research Institute) – 1906, Dehradun.
- Indian Wildlife Institute, Dehradun – 1985.
- NEERI (National Environmental and Engineering Research Institute) Nagpur – 1958.
Question 10.
Name the world’s major International Environment Institutes and their headquarters.
Answer:
| Institute | Headquarters |
| UNEP (United Nations Enviromnemt Programme) | Nairobi (Kenya) |
| lUCN-International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources | Glind (Switzerland) |
| TRAFFIC – (International institute that controls illegal trade of plants and animals) | Cambridge (United Kingdom) |
| WWF | Glind (Switzerland) |
| IPCC | Geneva (Switzerland) |
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 12 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-II)
Question 1.
Describe the measures adopted by the Indian Government to reduce air pollution.
Answer:
Following are the important steps taken by the Indian Government for the prevention of air pollution:
1. On June 24, 2016, the National Forest Policy was drafted by the Central Government, under which, green, tax is recommended, and the money received from it will be used to make the forests lush green.
2. Effects are being made by the Central Government to control the pollution on roads by the Green Highway Policy 2015. But absolute freedom from this problem is possible only when, at personal level, every individual understands his role of planting a tree and keeping it alive.
3. For the prevention of pollution by vehicles, from April 1,2017, the Government of India will provide the fuel (petrol) of BS-4 grade, throughout the country, which is currently of BS – 3 grade. From April 1, 2020, the assurance of supply of BS-5 grade fuel, in place of BS – 4 grade, has been given.
Question 2.
Explain the causes and harmful consequences of soil pollution.
Answer:
Causes of Soil Pollution:
- Excessive use of chemical fertilizers.
- Waste from industrial units.
- Garbage – waste from the cities and metropolises.
- Un – dissolved waste from sewage.
- Use of pesticides and insecticides.
Harmful Consequences of Soil Pollution:
- Constant decrease in agricultural land.
- Major diseases caused by this include dysentery, cholera, eye disease and tuberculosis.
- Soil pollution gives rise to other environmental pollutions.
- Land pollution has increased the problem of landlessness.
Question 3.
Explain the consequences of ozone layer depletion.
Answer:
Following are the major consequences of ozone layer depletion:
- Ozone layer depletion causes diseases like skin cancer and cataract.
- Ultraviolet rays destroy plant plankton, due to which there is an adverse effect on the sea food chain.
- Reduction in the quantity and quality of many types of vegetation crops.
- Ultraviolet rays have an adverse effect on the disease resistance capability.
- Due to ozone layer depletion, there will be increase in temperature at the regions near the equator. For this reason, the physical and mental development of the native people will be adversely affected.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 12 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Define Air Pollution. Describe the sources, harmful effects and measures to control air pollution.
Answer:
Definition of Air Pollution:
Due to the natural and human activities, the presence of pollutants in atmosphere, like dust, smoke, gases, mist, vapours, foul smell, etc., which are harmful for human-beings and other living organisms is called Air Pollution.
Sources of Air Pollution:
1. Natural Sources:
Materials erupted from volcanic eruptions, dust of storms and winds, forest fire, and landslides taking place in the mountains.
2. Unnatural Sources:
Exploitation of fossil fuels (coal, petroleum and wood), mining, industries, modes of transport, smoking, use of chemicals and radioactivity.
Harmful Effects of Air Pollution:
- Negative impact on human – health.
- Negative impact on the natural vegetation; and threat to the existence of living – organisms and insects.
- Negative impact on the environmental condition, and occurrence of grave problems like climate change, ozone layer depletion and greenhouse effect.
Basically, air pollution is a slow poison,which is creating a gradual, negative effect form on the entire biotic and abiotic environment.
Effective Measures to Control Air Pollution:
To control air pollution, it is necessary to control the current air pollution level and prevent future pollution. For this, following measures are necessary to be implemented:
- To develop plantation and green belt on at least 33% part of the earth.
- To control pollution emitted by vehicles. For this, from April 1, 2017, in place of BS-3 grade, vehicle fuel of BS – 4 grade is being provided in India.
- To use more of solar powered battery and electric engines (railway) in place of petrol and diesel.
- Ban on cutting of trees; and use of such domestic fuels that do not emit smoke.
- To establish utensils and bricks manufacturing industries outside the city.
- Use of modern techniques in industries for minimising the level of air pollution.
- At personal level, every individual should plant a tree and provide complete protection to it.
Question 2.
What does water pollution mean? Describe the sources, harmful consequences and measures to prevent water pollution.
Answer:
Meaning of water pollution:
Reduction in the quality of water due to mixing of any unwanted external matter in natural water, which has adverse effect on humans and all other organisms, is called water pollution.
Sources of Water Pollution:
Major sources of water pollution are domestic effluents, agricultural waste, industrial waste, thermal contaminated water, atmospheric particles, radioactive waste, leakage of mineral oil, etc.
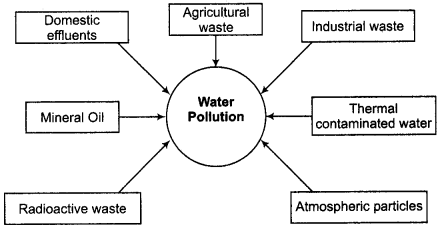
According to an estimate, about 3000 million to 4000 million litres of sewage water from 300 cities of India is being carried into rivers and streams every day, due to which in the related rivers and lakes, water pollution reaches the highest level.

Harmful Consequences of Water Pollution:
1. Along with toxic substances, there are a large number of bacteria and viruses of many diseases in the polluted water, due to which many aquatic creatures die. Also, when humans drink this polluted water, they get infected with cholera, jaundice and stomach-related diseases.
2. Humans also have to face many water-borne diseases merely by taking bath and washing clothes in polluted water.
3. About 65% of the total diseases occurring in human beings in India are due to water pollution.

4. According to a report of the United Nations, “Due to lack of pure water and diarrhoea, 2300 people die every day in the world”.
5. In the last 30 – 40 years, due to sea water-pollution, about 40% of aquatic creatures in the seas and oceans have become extinct.
Measures to Prevent Water Pollution:
- For effective disposal of waste in water, sewage treatment plants should be established in all the cities.
- After treating water having industrial waste, it should be reused in the industries.
- Immersion of dead bodies of animals in rivers should be strictly prohibited.
- In place of chemical farming, organic farming should be highly encouraged.
Question 3.
Write a brief note on Noise Pollution and Soil Pollution.
Answer:
Meaning of Noise Pollution:
When the sound exceeds a certain level and this brings harm to a person or group at the physical and mental level, then it is called Noise Pollution. Generally, all sounds above 80 decibels fall under noise pollution.
Causes (Sources) of Noise Pollution:
Major sources of noise pollution are the horns of modes of transport, loud speakers and sound amplifying devices, sound from industries, sound from airplanes and jet aircrafts, etc.
Harmful Effects of Noise Pollution:
Noise pollution has an adverse effect on the human-brain. This causes irritability, deafness, stress and headaches. The hearing capability of a person who is exposed to extremely loud sound can be permanently damaged.
Soil Pollution:
Meaning of Soil Pollution:
Reduction in the quality of soil due to the natural and human activities is called Soil Pollution or Land Pollution. Soil pollution reduces the fertility power of the land. Soil pollution has an adverse effect on all living organisms of the earth.
Causes of Soil Pollution:
The polluted water, excessive use of chemical fertilizers, industrial waste, waste from the cities and metropolises are the major factors responsible for soil pollution. In the areas of rapid industrialisation in China, the water-sources and adjoining lands have also been most affected by pollution.
Harmful Effects of Soil Pollution:
- This reduces the area of agricultural land continously.
- Dysentery, diarrhoea, cholera, tuberculosis, eye – disease are the major diseases caused due to soil pollution.
- Soil pollution is considered to be the father of other environmental pollutions.
- The availability of useful land decreases in the areas affected by soil pollution.
Question 4.
What is Ozone Layer Depletion? Describe the causes and effects of ozone layer depletion.
Answer:
The ozone layer is present at a height of 15 – 35 km in the stratosphere, which consists of ozone gas. The ozone layer absorbs high energy ultraviolet rays of sunlight, which are harmful for the health of humans and other living organisms. Thus, the ozone layer is also called the earth’s protective shell.
Depletion of Ozone Layer:
It has been found by the research done in the past few decades that the total amount of ozone gas in the ozone layer is decreasing by about 4% per decade, due to which ozone layer is having holes over Antarctica continent, Australia, New Zealand, etc. With the passage of time, at present, similar types of holes are being seen in ozone layer also over North Pole during spring season.
Causes of Ozone Layer Depletion:
In the last 50 years, humans have disturbed the perfect balance of nature by releasing harmful gases and chemicals in the atmosphere, due to which the life – saving ozone layer is continuously depleting. Halogenic gases are primarily responsible for the depletion and destruction of ozone gas in the ozone layer. In this, the major gases are chloro – fluoro – carbons, chlorine, bromine, methyl chloroform and carbon tetrachloride. In the ozone layer, the diffusion of one atom of chlorine destroys one lakh ozone molecules. The atoms of chlorine are formed by the disintegration of chloro-fluoro-carbon.
CFCl3 + UV > CFCl2 (chlorofluorocarbon) + Cl (chlorine)
Besides chlorine, the atoms of bromine also destroy many molecules of ozone, due to which, the amount of ozone in the ozone layer decreases continuously, and this accelerates the process of depletion in ozone layer.
Effects of Ozone Layer Depletion:
- Increase in the number of diseases like skin cancer and cataract in the world due to ozone layer depletion.
- Ultraviolet rays have an adverse effect on the disease – resistance capability of humans and other living organisms.
- Due to ozone layer depletion, there will be increase in temperature at the regions near the equator. For this reason, the physical and mental development of native people will be adversely affected.
- Ultraviolet rays are destroying plant plankton of the sea-water, which is having adverse effect on the sea food chain.
- Due to the influence of ultraviolet rays, the quantity and quality of many types of vegetation crops are decreasing.
Question 5.
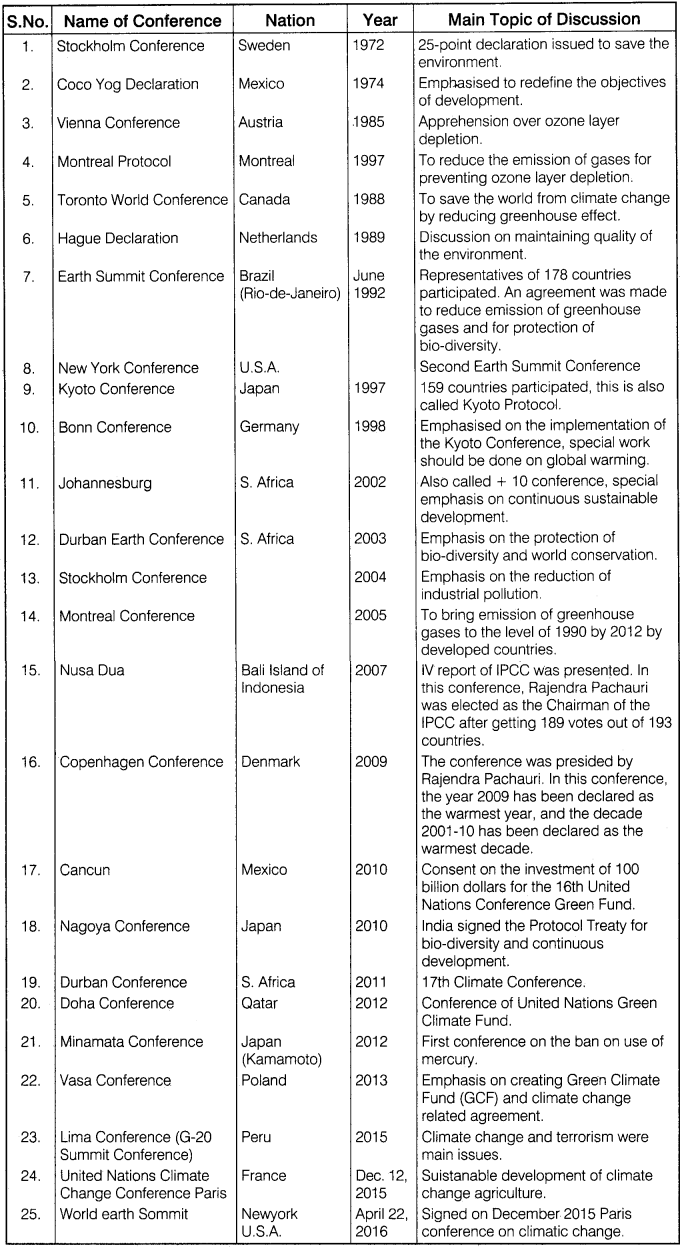
Prepare a table of major environmental conferences of the world, along with their place, year and main topics of discussion.
Answer:
Major Environmental Conferences of the World: