Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Population: Distribution, Density and Growth
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Text Book Questions
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which is the second largest populated country in the world?
(a) China
(b) India
(c) Indonesia
(d) USA
Answer:
(b) India
Question 2.
Which is the biggest agglomeration of the world?
(a) Europe
(b) Asia
(c) Africa
(d) South America
Answer:
(b) Asia
Question 3.
Which country has the highest population density in the world?
(a) Bangladesh
(b) India
(c) China
(d) Taiwan
Answer:
(a) Bangladesh
Question 4.
Physiological density, Le., agricultural density in population density is:
(a) Population ÷ Total surface area
(b) Population ÷ Agricultural land
(c) Farmer population ÷ Agricultural land
(d) Population ÷ Resources
Answer:
(b) Population ÷ Agricultural land
Question 5.
Population migration is the greatest in North America from which continent?
(a) Asia
(b) Europe
(c) South America
(d) Africa
Answer:
(b) Europe
Question 6.
As per 2015, the average population density of the world is:
(a) 57
(b) 42
(c) 47
(d) 55
Answer:
(c) 47
Question 7.
Estimated population of the world by 2025 is:
(a) 781.8 crore
(b) 903.6 crore
(c) 886.9 crore
(d) 960.6 crore
Answer:
(a) 781.8 crore
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 8.
What was the population of the world in the year 2013?
Answer:
The population of the world in the year 2013 was 714 crore.
Question 9.
Which region has the highest concentration of population in North America?
Answer:
The north – eastern part of North America (Great Lakes Area) has the highest concentration of population.
Question 10.
What per cent of world population lives in the northern hemisphere?
Answer:
85% of world population lives in the northern hemisphere.
Question 11.
Which continent has the highest population growth due to migration?
Answer:
North American continent has the highest population growth due to migration.
Question 12.
By how many times has the population of world increased in the last 350 years?
Answer:
In the last 350 years, the population of the world has grown by 13 times.
Question 13.
According to population transition theory, what stage does India come under?
Answer:
According to population transition theory, India comes under the third stage.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 14.
Describe briefly the economic factors that affect the population distribution.
Answer:
The economic factors that affect the distribution of population are as follows:
1. Minerals:
The regions rich with minerals attract industries. Mining and industrial activities produce employment.
2. Urbanisation:
Cities provide good opportunity of educational and medical facilities and also provide good means of transport and communication.
3. Industrialisation:
Industrialisation attracts people on very large scale. In it, not only the workers of industries, but drivers, shopkeepers, workers of banks, doctors,’ teachers and other service sectors are also included.
4. Social and cultural factors:
Some places attract people more for religious and cultural importance, so many people populate such regions.
Question 15.
Write the formulas of major methods of determining population density.
Answer:
According to the major methods of determining the population density, mathematical, economic, working, agricultural and nutritional density are calculated as follows:
(i) Mathematical Density:
The ratio of human population and land is considered in this density. It is calculated by the following formula.
![]()
(ii) Economic Density:
The ratio between total population and total resources. It is measured by this formula.
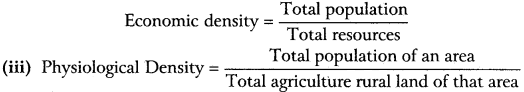
(iv) Agricultural Density:
Area of land used for farming and people living in that area is considered in it.
![]()
(v) Nutritution Density:
It is the area of land producing food crops and total population of that land is considered in it.
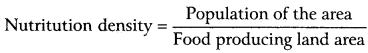
Question 16.
Describe major areas of population concentration in the world.
Answer:
Concentration of population of world population in those areas where climate is favourable, soils are fertile, easy water availability, facility of transportation etc. are available. Such types of areas are – river valley, river made plains and lake groups areas etc.
In the world these types of areas are found in Sikiang, Yangtze Kiang basin in China, Ganga – Yamuna plains of India; Satluj – Sindhu plains of Pakistan, Quanto plain in Japan, Five Lakes group of North America, River built plains in Bangladesh, Niegeria and Ghana in Africa and good condition islands of Indonesia are included.
Question 17.
What do you mean by population growth?
Answer:
The change in the size of population of a particular area between a fixed time period is known as growth of population. The process of population growth may be positive or negative but presently positive population changes are mostly seen in the world. Population growth can be measured and expressed in both total number or percentage.
For knowing the total growth (increase) or relative growth of population, last census year or population of census is subtracted from the present year or the population of census year. By this way, the growth (increase) of population is clarified.
Question 18.
Describe the stages of Demographic Transition Theory?
There are five stages in demographic transition theory. They are:
First Stage:
This is also known as a state of high death rate and high birth rate. In this stage the growth of population is very slow. The countries having this situation; agriculture is the main basis of livelihood.
Second Stage:
In this stage, the birth and the death rate both are high, but due to development of medical facilities the death rate has decreased slowly.
Third Stage:
In this stage, the birth rate is high but the death rate is medium. It means neither higher low. Due to this, the population grows rapidly.
Fourth Stage:
In this stage, the birth rate is at medium pace but the death rate is very low.
Fifth Stage:
In this stage, the birth rate as well as the death rate is very low. In this situation, there is a fear of fall in the population growth. In this stage, the manpower of the nation becomes deficient.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Essay Type Questions
Question 19.
Explain the factors influencing population density distribution in the world.
Answer:
The factors influencing population density distribution in the world are as follows:
- Physical Factors such as event, availability of water, climate and soil.
- Social/Cultural Factors such as religion and culture.
- Economic Factors such as minerals, urbanisation, industrialisation.
Physical Factors :
1. Availability of water:
People prefer to live in areas where fresh water is easily available. Water is used for drinking, bathing and cooking – and also for cattle, crops, industries and navigation.
2. Land forms:
People prefer living on flat plains and gentle slopes because such areas are favourable for the production of crops and to build roads and industries.
3. Climate:
An extreme climate such as very hot or cold deserts is uncomfortable for human habitation. Areas with a comfortable climate, where there is not much seasonal variation, attract more people.
4. Soils:
Fertile soils are important for agricultural and allied activities. Therefore, areas which have fertile loamy soils have more people living on them.
Economic Factors :
1. Minerals:
Areas with rich mineral deposits attract mining and industrial activities, therefore skilled and semi – skilled workers move to these areas for employment and make them densely populated.
2. Urbanisation:
People migrate in the cities for better employment opportunities, educational and medical facilities, and better modes of transport and communication and also for good civic amenities. Mega cities of the world continue to attract a large number of migrants every year.
3. Industrialisation:
Industrial belts provide job opportunities and attract large numbers of people. These include not just factory workers but also transport operators, shopkeepers, bank employees, doctors, teachers and other service providers.
Social and Cultural Factors :
1. Religious factors:
Some places attract more people because they have religious or cultural significance.
2. Political unrest and wars:
In the same way, people tend to move away from places where there is social and political unrest.
3. Government policies:
Many a times, governments offer incentives to people to live in sparsely populated areas or move away from overcrowded places.
Question 20.
Categorize the population from the point of view of population density.
Answer:
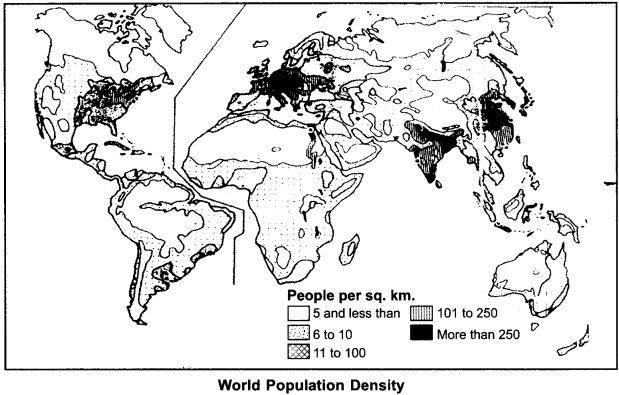
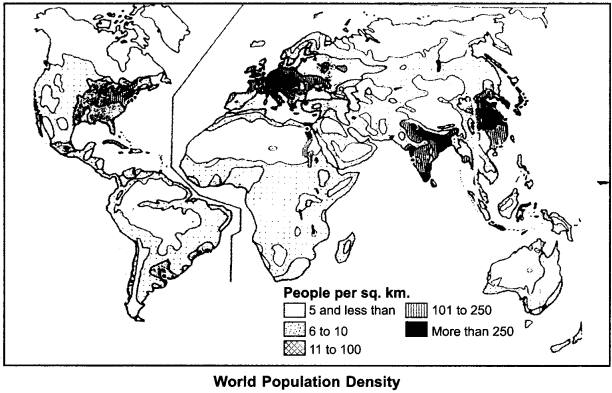
Population density in the world exhibits variations on regional basis. In those regions of the world where distribution of population is more, density is also found to be more there. The level of population density in the entire world exhibits significant variations. At some places in the world, density is 1 person per sq. km., and at other places, it is upto 7797 persons per sq. km. On the basis of these diversities, the world is mainly divided into the following parts with the point of view of population density:
- Very high density regions
- High density regions
- Normal density regions
- Low density regions
- very low density regions
1. Very High Density Regions:
Those areas of world where population density is found to be above 250 persons per sq. km. are included in this category. In this part, world’s three agglomerations are included –
- east, south, and south east Asia.
- western and central Europe.
- North – east America.
Due to favourable condition of climate, plain surface, fertile, soils, water, minerals, modes of transportation, there is high density.
2. High Density Regions:
Those regions of the world, where population density is 101-250 persons per sq. km. are included in this part. Mostly, neighbouring regions of very high density regions are included in this category. Southern, southern-eastern and eastern Europe, central and northern America, coastal area of South America and Africa, internal parts of south – east Asia, north – western China, central India and southern Australia are included in this category.
3. Normal Density Regions:
Those areas of world where population density is found to be between 10-100 persons per sq. km. These are included in this category. Such as grassland areas of Asia, Africa, and South America.
Instable agriculture, livestock, forestory and agriculture near desert area are included.
4. Low density Regions:
Those areas of world where population density is found to be between 1-10 persons per sq. km. Sudan in Africa, Libia, Malagasi, Canada in North America, North Argentiana in South America, Peru, Equador, West Siberia in Asia, Bornio etc. are included in this category.
5. Very Low Density Regions:
Those areas of world where population density is found to be below 1 person per sq. km. are included in this category. 70% area of earth’s land is included in this category. World’s very cold Tundra regions, very hot equatorial regions, very dry desert regions and highly mountainous regions are included in this category.
This classification of population density found in the world has been shown in the following map :
Question 21.
Explain the growth of population in the world.
Answer:
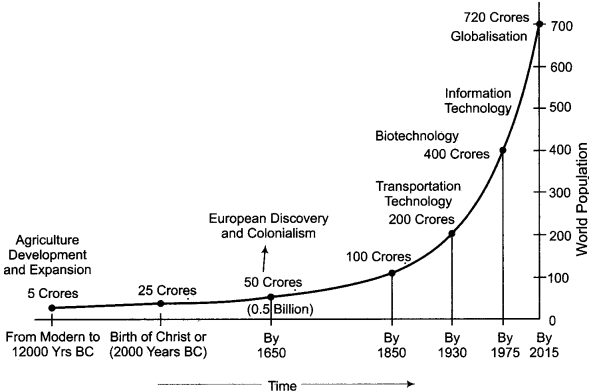
Population growth in the world reflects territorial inequalities. Human existence occurred on earth about one million years ago. Since then, the population of the world has been constantly changing. The study of population growth is mainly divided into the following periods.
- Prehistoric period
- Ancient period
- Medieval period
- Modern era.
1. Prehistoric Period:
The beginning of this period is supposed to from food gathering and hunting occupation. Hunting and food gathering were done in Palaeolithic period on land parts. After the lessening of ice on continents, it is imagined that human extension took place in – Africa, Australia, South Europe, south – west and east Asia. Before presence of human in America, 33 lakh people lived on the earth and in course of time after 15 thousand years, increased upto 53 lakhs. It is estimated that the average population density was 0.04 person per square kilometer of the world.
2. Ancient Period:
Men started agriculture and cattle rearing on some limited parts of land earlier than before six thousand years ago from today. In this way, human civilization has flourished in many parts of the world, and along with agriculture, city development started. In the beginning of the Christian era, total population of the world is imagined to be 20-30 crores. In this way, in Indian sub-continent east Asia, Greek and Roman empire Mesopotamia and along with Egypt a region of extended group of people including Sindhu – Saraswati civilization were present.
3. Medieval Period:
According to history, it is the time period between 700 A.D to 1650 A.D. In 1650 A.D the total population of the world was 55 crores but in after time it got reduced due to obstructions like flood, famine, plague and wars, etc.
4. Modern Period:
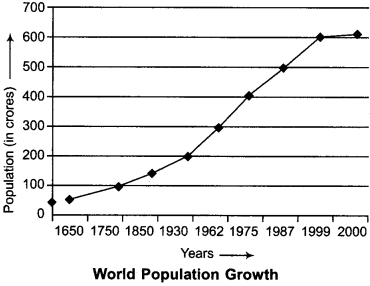
The middle of 17th century is supposed as the beginning of modern period. In 1650 A.D., the total population of world was 55 crore. In 1750, it rose to 72 crores. In 1850 A.D., it went up to 133 crores. In 1950 A.D., the total population of the world was 251 crore. In 2000 A.D., the population was 610 crores, and in 2013, it rose to 714 crore. This increase in world population has been depicted in the following table :
Population Growth in the World:
| Year | Population |
| 10,000 BC | 50 lakh |
| 1 AC | 2000 lakh |
| 1000 AC | 3000 lakh |
| 1750 | 8000 lakh |
| 1850 | 100 crore |
| 1930 | 200 crore |
| 1962 | 300 crore |
| 1975 | 406 crore |
| 1987 | 500 crore |
| 1999 | 600 crore |
| 2000 | 610 crore |
| 2010 | 710 crore |
| 2013 | 714 crore |
| 2015 | 720 crore |
| 2025 | 781 crore |
| 2050 | 903 crore |
Source:
According to UN Population Bureau Source, World Development Report, 2000 and Population Reference Bureau, USA 2013.
Map Based Questions
Question 22.
Show the population growth in world population from 1650 to 2000 by a graph.
Answer:
Question 23.
Show the population density on the world map.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Additional Questions with Answers
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
What per cent of world population lives in the Northern Hemisphere?
(a) 57%
(b) 85%
(c) 60%
(d) 48%
Answer:
(b) 85%
Question 2.
What was the world population in the year 2001?
(a)417 crore
(b)546 crore
(c)613 crore
(d) 745 crore
Answer:
(c)613 crore
Question 3.
Which is the biggest populated continent in the world?
(a) Asia
(b) Africa
(c) Europe
(d) South America
Answer:
(a) Asia
Question 4.
In which agglomeration does maximum population of the world reside?
(a) European
(b) American
(c) Asian
(d) African
Answer:
(c) Asian
Question 5.
Asian agglomeration is mainly spread in:
(a) Between 5° to 10° northern latitudes
(b) Between 10° to 40° northern latitudes
(c) Between 30° to 60° northern latitudes
(d) Between 10° to 40° southern latitudes
Answer:
(b) Between 10° to 40° northern latitudes
Question 6.
Which of the following is the most populated country in Europe:
(a) France
(b) Italy
(c) Germany
(d) Polland
Answer:
(c) Germany
Question 7.
Which is the highest populated country in African agglomeration?
(a) Sudan
(b) Ethiopia
(c) Egypt
(d) Nigeria
Answer:
(d) Nigeria
Question 8.
What was the total population of the world in year 1650?
(a) 50 lakh
(b) 55 crore
(c) 100 crore
(d) 406 crore
Answer:
(b) 55 crore
Question 9.
Low birth rate and low death rate is indicator of which stage?
(a) First stage
(b) Third stage
(c) Fourth stage
(d) Fifth stage
Answer:
(d) Fifth stage
Question 10.
How many stages are there in demographic transition theory?
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 6
Answer:
(c) 5
Matching Type Questions
Match column (A) with column (B).
Question 1.
| Column (A) Poulation distribution | Column (B) Area |
| (i) High density region | (a) Equatorial zone |
| (ii) Normal density region | (b) Relief region |
| (iii) Low density region | (c) Eastern Asia |
| (iv) Very low density region | (d) Mineral reserve region |
Answer:
(i) c, (ii) d, (iii) b, (iv) a.
Question 2.
| Column (A) World agglomeration | Column (B) Location |
| (i) Asian agglomeration | (a) 30° – 45° Northern latitudes |
| (ii) European agglomeration | (b) Nile river valley, Zambia region |
| (iii) American agglomeration | (c) 10° – 40° Northern latitudes |
| (iv) African agglomeration | (d) 40° – 60° Northern latitudes |
Answer:
(i) c, (ii) d, (iii) a, (iv) b.
Question 3.
| Column (A) Year | Column (B) World Population |
| (i) 1000 | (a) 610 crore |
| (ii) 1850 | (b) 500 crore |
| (iii) 1987 | (c) 100 crore |
| (iv) 2000 | (d) 720 crore |
| (v) 2015 | (e) 30 crore |
Answer:
(i) e, (ii) c, (iii) b, (iv) a, (v) d.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why is the study of population distribution and density a challenging task?
Answer:
Right from the very beginning, population distribution has regional expansion and due to the increasing number of political and administrative units, study of population distribution and density has become a challenging task.
Question 2.
What is population distribution?
Answer:
Population distribution means spatical distribution of human or group of people. It shows how humans settle on the earth. Population distribution is of primary importance for analytical study of population. Under this, study of population is done on the basis of spatial distribution.
Question 3.
Why Is human at the central place in human geography?
Answer:
Human is at the central place in human geography because it is the human who utilizes his natural and cultural environment, gets influenced by them and makes changes in them. It is the human who uses the natural resources and builds the culture.
Question 4.
What is population density?
Answer:
The density of population is the ratio of the number of people residing in the region to that area. Normally, population density means number of population lives in per sq. km. area.
Question 5.
How is unequal distribution of population visible?
Answer:
80% population of the world lives on only 20% land while the remaining 20% population lives on 80% land part, which shows its unequal distribution.
Question 6.
What is the population number in the continents of the world?
Answer:
According to 2013 data, population in Asia continent is 430 crore, in Africa 110 crore, in Europe 74 crore, in Northern America 55.7 crore, in Southern America 40 crore and in Oceania 3.8 crore.
Question 7.
Write the names of world’s top ten most populated nations.
Answer:
World’s top ten populated country’s are: China, India, USA, Indonesia, Brazil, Pakistan, Russia, Bangladesh, Japan and Nigeria.
Question 8.
Into how many parts has the world been divided with the point of view of population distribution?
Answer:
With the point of view of population distribution, the world has been divided into high density regions, normal density regions and very low density regions.
Question 9.
Where is very low population distribution found?
Answer:
Very low population distribution is found in world’s very cold areas, dry deserts, highland areas, equatorial regions and mid latitudinal desert areas.
Question 10.
Which factors affect population distribution?
Answer:
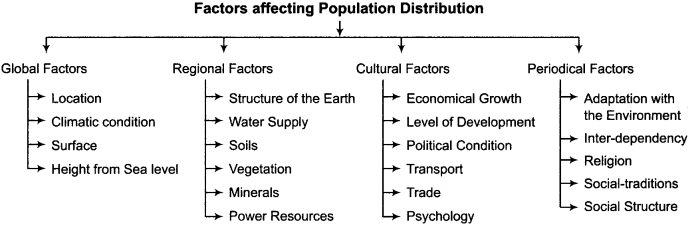
The factor’s which affect population distribution are: global factors, regional factors, cultural factors and periodical factors.
Question 11.
Which global factors affect population distribution?
Answer:
In global factors: location, climate condition, surface and height from sea level are included.
Question 12.
Which regional factors affect population distribution?
Answer:
The regional factors are: structure of earth, water supply, soils, vegetation, minerals and sources of energy.
Question 13.
Which cultural factors affect population distribution?,
Answer:
They are economic condition, level of development, political condition, psychological condition, transport and trade.
Question 14.
Which periodic factors affect population distribution?
Answer:
They are: adaption with the environment, interdependency religion, social recognitions and social structure.
Question 15.
What is agglomerations?
Answer:
Agglomeration is a big group of population. These areas are found near river’s plain and lake based area. Areas of favourable climate and plain surface area.
Question 16.
Write the names of world agglomerations.
Answer:
There are: Asian agglomeration, European agglomeration, American agglomeration and African agglomeration.
Question 17.
Asian agglomeration has been divided into how many parts?
Answer:
Asian agglomeration has been divided into three parts:
- Eastern Asia
- South – eastern Asia
- Southern Asia.
Question 18.
What is meant by Monsoon Asia?
Answer:
Monsoon climate condition is witnessed in Asia from Pakistan to India, Myanmar, Thiland, Indonesia, Vietnam, China, Japan and Korea. Due to this condition, this entire region is called Monsoon Asia.
Question 19.
Which are the major problem of Asian agglomeration?
Answer:
The major problems of Asian agglomeration are: rapid population growth, unemployment, lack of food, housing, medicine, low education facility and extreme poverty.
Question 20.
Where is the European agglomeration most densely populated?
Answer:
European agglomeration is most densely populated between 45° – 55° northern latitudes besides a parallel belt of coal.
Question 21.
Where is the American agglomeration most densely populated?
Answer:
Most of the population (80% population) of American agglomeration is settled between 30° – 40° North latitudes in the east of 100° western longitudes.
Question 22.
Why population growth is controlled in American agglomeration?
Answer:
Due to complete control on birth rate and death rate and prohibition on immigration, population growth remains controlled here.
Question 23.
Where is centralisation of population found in African agglomeration?
Answer:
In African agglomeration, population is mainly centralised in Nile river valley region, on Guinea Coast between Zambia and Niger river valley and in southern and eastern parts of South Africa.
Question 24.
Why is the notion of density of population significant?
Answer:
The notion of density of population is significant in order to form the plan of economic progress and social and cultural progress of every country.
Question 25.
What is mathematical density?
Answer:
The ratio of human population and total land area is considered in mathematical density.
Question 26.
What is economic density?
Answer:
The productive capacity of resources of land and people living on that land is considered in economic density.
Question 27.
What is agricultural area density?
Answer:
Land used for agriculture and the number of people living on that land is considered in agricultural area density.
Question 28.
What is agricultural density?
Answer:
Surface area of land used for farming and number of people living in that area is considered in agricultural density.
Question 29.
What is nutritional density?
Answer:
It is the area of land producing food crops and total population of that land which is considered in nutritional density.
Question 30.
Where is world’s highest and lowest population density found?
Answer:
World’s lowest population density is found in Mangolia (1 person per sq. km) and highest density is found in Singapore (7797 person per sq. km).
Question 31.
Into how many parts has the world been divided in context to population density?
Answer:
In context to population density, the world has been divided into five parts – very high density regions, high density regions, normal density regions, low density regions and very low density regions.
Question 32.
Why is very high density found in some regions of the world?
Answer:
Due to favourable conditions such as healthy climate, levelled plains, fertile soil, availability of water, mineral wealth, industrial development and facility of modes of transportation, very high density is found in some regions of the world.
Question 33.
Which are the high density areas of the world?
Answer:
They are: south, south-east and eastern Asia, coastal area of Africa, internal area of Asia, northern – western China, south Australia and central India.
Question 34.
Which factors affect population density?
Answer:
Physical factors (location, availability of water, climate and soils), economic factors (minerals, urbanisation and industrialisation) and social-cultural factors etc. affect population distribution.
Question 35.
What are the reasons for population growth?
Answer:
Decline in death rate, migration, industrial development, assured availability of food, favourable climatic condition, technological development and high birth rate are the major reasons for population growth.
Question 36.
Write the names of stages of Demographic Transition Theory.
Answer:
There are five stages of Demographic Transition Theory:
- Stage 1 : Stage of high birth rate and high dealth rate.
- Stage 2 : Stage of high birth rate and declining dealth rate.
- Stage 3 : Stage of high birth rate and medium dealth rate.
- Stage 4 : Stage of medium birth rate and low dealth rate.
- Stage 5 : Stage of low birth rate and low dealth rate.
Question 37.
Write the names of countries which are in first stage of demographic transition.
Answer:
Sudan in Africa, Congo, Ghana, Angola, Rhodesia, Nigeria, Guatemala, etc. are included in first stage of demographic transition.
Question 38.
Write the names of countries which are in fourth stage of demographic transition.
Answer:
New Zealand, Australia, Chili, Argentina, USA, Malaysia, Thailand, China and Bangladesh are included in this category.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-I)
Question 1.
Why has the importance of study of population increased in geography?
Answer:
Along with the development of human civilization on the earth, the distribution of population is not found to be equal at all places due to the complexities found in it. Population distribution has regional expansion and due to the increasing number of political and administrative units, the study of population distribution and density has become a challenging task, but study of population distribution and density is an important subject of human geography. Due to the central role of the human, importance of study of population in geography has increased.
Question 2.
What is the different between population distribution and population density?
Answer:
Normally population distribution and density are understood to be similar, but these are two different concepts. Population distribution means spatial distribution of population. It shows surfacial condition of human settlement. But population density means ratio between population and land area. It is a measure of population. It describes number of people living in per unit area.
Question 3.
“World population Is distributed unequally.” Clarify this statement.
Answer:
- World population is distributed unequally. In context to the population of Asia, George B. Kracy says that, “In Asia, less people reside at very large number of places and very large number of people reside at very less number of places.”
- Broadly, 90 per cent of the world population lives in about 10 per cent of its land area.
- The 10 most populous countries of the world contribute about 60 per cent of the world’s population.
- 85 per cent world population lives in Northern hemisphere while only 15 per cent population lives in Southern hemispheres.
Question 4.
Describe the regions of normal population.
Answer:
Such geographical regions where the ecological conditions are favourable for mankind, regions of normal population develop there. Here, at many places, people also adapt to the environment. Due to the availability of copper in the Andes, Chukai, Kamra of Chili, due to uranium deposits in Uranium city of Canada, and due to the gold mines in Australia, regions of normal dense population have developed there.
Question 5.
Mention the characteristics of Asian agglomeration.
Answer:
Following are the main characteristics of Asian agglomeration:
- It is the world’s largest agglomeration.
- This agglomeration shows agriculture based economy.
- This agglomeration is also known as Monsoon Asia.
- It is located between 10° – 40° northern latitudes.
- Rapid population growth rate is found here.
- High birth rate is also found here.
Question 6.
Give the main characteristics of European agglomeration.
Answer:
Following are the main characteristics of European agglomeration:
- This is the world’s second biggest agglomeration.
- This agglomeration is equipped with modern cities and industries.
- It is located between 40° – 60° northern latitudes. Its high density is found between 45° – 55° northern latitudes with a parallel belt of coal.
- Both birth and death rate are found to be low here.
- Population growth is in stable condition in this agglomeration.
Question 7.
Write the main characteristics of American agglomeration.
Answer:
Following are the main characteristics of American agglomeration:
- This is the world’s third biggest agglomeration.
- It is the world’s newest and developed agglomeration.
- This agglomeration developed due to migration of European population.
- 80 per cent population of this agglomeration resides between 30° – 45° northern latitudes in the east of 100° western longitude.
- In this agglomeration, population is controlled. Because both birth and death rate are controlled here and also there is prohibition on migration here.
Question 8.
At which areas do we find high population density in the world?
Answer:
There are some parts or areas of the world where population density is found to be above 250 persons per sq. km. These are known as high population density. Three regions of this type are found in the entire world.
- eastern, southern, and southern – eastern Asia.
- Western and Central Europe.
- Northern-eastern America.
All these regions are densely populated due to plains made by rivers, mineral deposits and location of lakes.
Question 9.
Describe two physical factors which affect population density in the world.
Or
Describe two regional factors which affect distribution of population in the world.
Answer:
Availability of water:
Availability of water is the most,important factor for various human activities. Due to this reason, world river valleys are densely populated.
Landforms:
Landform is the main factor which affects distribution and density of population. Normally, plain areas are highly populated instead of bad land areas. Because plain areas are suitable for residence, industrial development and transportation.
Question 10.
How does climate affect the population distribution?
Answer:
People want to live in regions with favourable climate. Adverse climate of places situated at greater heights and cold deserts are inconvenient for human settlement. People like to settle in such regions where there is no extreme seasonal variation. Less population is found in regions of unfavourable climate. This is the reason that right from ancient times, human settlement is more in mediterranean regions owing to favourable climate.
Question 11.
How,does availability of water affect the distribution of population?
Or
How does water supply affect population density?
Answer:
Water is the most important factor for life. People give priority to get settled in such regions where water is easily available. Water is an element with multiple uses. Water is used for drinking, washing, bathing, preparing food, and for animals, crops, industries and boating. This is the reason that due to the availability of water, river valley regions are the most densely populated areas of the world. World’s ancient civilisations – Nile Valley Civilisation, Indus Valley Civilisation and Mesopotamia Civilisation had developed on the banks of rivers.
Question 12.
How does demography affect the distribution of population? Explain with an example.
Answer:
Demography greatly affects the distribution of population. People want to get settled on levelled plains and mild slopes. Such regions are favourable for crop production, road construction and industries. Mountainous and hilly regions are obstructive in the development of transport system, therefore initially they are not favourable for agricultural and industrial development.
Therefore, population is less in these regions. Example: The Ganga plain is one of the world’s most densely populated regions, while the mountainous parts of the Himalayas are regions of very less population.
Question 13.
Which are the economic factors affecting population density?
Answer:
1. Minerals:
Minerals are main factor for affecting population density. Where deposit of minerals are found, a huge population density is seen.
2. Urbanisation:
Good civil facilities, sources of employment, etc. are main reasons for high population density.
3. Industrialisation:
Due to industrialisation, a huge number of employment opportunities have developed.
4. Agriculture:
A positive or negative pattern of agriculture in a particular area affects the distribution and density of population. Positive conditions are responsible for high population density.
Question 14.
How does urbanisation affect the density of population?
Or
“Population increases as a result of urbanisation”. Clarify this statement.
Answer:
Large cities develop due to urbanisation and abundant opportunities of employment, facilities related to education and healthcare and better modes of transport and communication are available. Better civil facilities and urban life attract people towards the cities. As a result, people migrate from rural regions towards urban regions. Large cities of the world attract people in large numbers every year.
Question 15.
Industrial regions are areas of dense population. Why?
Answer:
Industrial areas provide opportunities of employment to people. Various types of factories attract people in large numbers, due to which people get settled nearby the industrial areas. Among these, labour class, drivers, conductors, shopkeepers, bank employees, doctors, teachers and other service providers are included. For example, Kobe-Osaka region of Japan is densely populated due to the concentration of various industries.
Question 16.
How do social and cultural factors affect the density of population?
Answer:
Some places of the world attract people due to religious or cultural reasons. If conditions are unfavourable at some places, then the people vacate such places and move away from there. People do not want to live in regions of social or political unrest. Customs and traditions, food habits, festivals and occasions and racial traditions of a particular religion also affect the density of population.
Question 17.
Describe the pattern of population growth in modern times.
Answer:
The modern period is considered to start from the middle of the 17th century. At this time, i.e., in 1650, the world population was approximately 55 crore. By 1750, this population increased to 72 crore. After this period, the rate of population growth increased and in 1850, world population increased to 133 crore. By 1950, the world population increased to 251 crore. World population unexpectedly increased to 610 crore by the time we reached the year 2000. By 2013, world population further increased to 714 crore.
Question 18.
How did science and technology help in increasing the population?
Answer:
Steam engine replaced human labour and human energy, which provided mechanical energy for wind and water due to which agricultural and industrial productivity increased. As a result of this, the problem of starvation and famine ended and vaccination against epidemics, improvement in healthcare facilities and sanitation has rapidly made a decline in death rate across the world. In this way, science and technology provided encouragement to population growth.
Question 19.
What Is meant by Demographic cycle?
Answer:
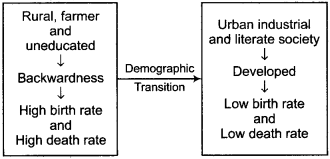
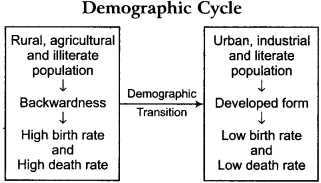
When an agricultural rural society transforms into a technology- based urban society, demographic tendencies also undergo a change. These changes occur in various stages, which are collectively known as the demographic cycle.
Question 20.
Describe the characteristics of first stage of demographic transition.
Answer:
Following are the main characteristics of first stage of demographic transition:
- In this stage, both birth and death rate are high.
- In this stage, countries show economic backwardness.
- In first stage, countries’ dependency upon agriculture is more visible.
- In this stage, population growth is found to be low due to high birth rate and high death rate.
- Currently, Sudan, Congo, Ghana, Angola, Rhodesia, Nigeria and Guatemala etc. countries are included in this stage.
Question 21.
Write a note on fifth stage of demographic transition.
Or
Write the characteristics of fifth stage of demographic transition.
Answer:
This is the last stage of demographic transition. Following are the main characteristics of this stage:
- In this stage, both birth and death rate are found to be low.
- Due to low difference in birth rate and death rate, population is stable.
- This stage shows educated and developed condition of population.
- In this stage, level of technology is found to be at high level.
- In this stage, human power in the world becomes weaker.
- The fear of possibility of decline in population exists in this stage.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-II)
Question 1.
Study of human is the most important on the earth why?
Or
Why is the human the main point of study of geographers?
Answer:
Human is the center point in study of human geography due to his central role. Human uses the natural and cultural environment. Human changes and affects this condition. Land, water, soil, minerals, vegetation and animals are also used by human. Production, agriculture, livestock, manufacturing, trade and transport activities are also done by human.
Social organisation, political management and cultural development are done by human. By using natural resources, human creates culture. Thus, study of human is the most important for geographers on the earth.
Question 2.
Clarify the pattern of distribution of population in the world.
Answer:
According to 2013 data, total population of world was 714 crore. Distribution of population is unequal in the world. World’s total 75% population lives in developing countries and rest 25%, population lives in developed countries. With continental point of view, Asia is the largest populated continent of the world.
In Asia, 430 crore population lives, after this Africa is at the second place with 110 crore population. In Europe 74 crore, in north America 56 crore, South America 40 crore and in Oceania 3.8 crore population resides.
Thus, distribution of population is dense or sparse at different places. In a continent, many places are densely populated or many places are sparsely populated. In world’s top ten populated countries – China, India, USA, Indonesia, Brazil, Pakistan, Russia, Bangladesh, Japan and Nigeria are included in which 60% population of the world lives. Out of these 10 countries, 7 countries are situated in Asian continent.
Question 3.
Describe world’s densely and sparsely populated regions.
Or
Describe the high and low population density regions of the world.
Answer:
World’s densely populated regions:
Densely populated regions of the world are: Eastern part of Asia, South and South-East Asia, North-East part of North America and North – Western part of Europe. In these areas, density of poulation is found to be above 250 persons per sq. km. All these areas are favourable in terms of geographical and economic conditions.
World’s sparsely populated regions:
Low density is found in unfavourable climatic zones, and in the regions of unfavourable physical, economic, social-cultural aspects. Such areas are : North and South polar zone, arid and cold deserts, equatorial zone, high rainfall areas, dense forest areas, and hilly areas. In these areas, population density is found to be 1 or below 1 person per sq. km.
Question 4.
Describe the factors affecting population distribution through a table.
Answer:
Factors affecting population distribution are given below:
Question 5.
Describe the African agglomeration.
Answer:
According to 2013 estimates, 110 crore people lives in the African agglomeration. 15.4% people of the world’s total population lives in this agglomeration. In context to size, it is at the second place after Asia. Centralisation of population in this agglomeration is seen in some specific regions only because 70% part of the African continent lies barren due to desert conditions and dense forests.
Centralisation of a large population is witnessed on its one-third part only. In these regions, Nile river valley region, Guinea Coast situated between Zambia and Niger river valleys and South Africa and eastern coastal part is included. Nigeria is the most populated nation in this agglomeration. After this, Ethiopia, Egypt, South Africa and Tanzania are numbered in.
Question 6.
Describe the inequal distribution of population density in the world on continential basis.
Or
“Density of population exhibits variations in continents.” Explain.
Answer:
In the world, distribution of density of population is also in accordance with the distribution of population. This exhibits unequal and disproportionate tendencies. At places, where settlement of population is found to be more, the density is also naturally found to be more.
Significant diversity is found in population density across the world. On one hand, population density even less than 1 person per sq. km. is found in Sahara, Greenland, Siberia and Mongolia, while on the otherhand, population density of 7797 persons per sq. km. is found in Singapore.
According to World Population Bureau, Washington, in 2015, population density of the world stands at 47 persons per sq. km, but due to regional inequality, population density is 116 persons in Asia, 32 persons in Europe, 27 persons in Africa, 16 persons in North America, 20 persons in South America and 3 persons per sq. km in Oceania.
Question 7.
Give a brief description of the tendencies of population growth at world level.
Answer:
In the beginning of the 21st century, world population was recorded to be more than 600 crore. It took centuries to reach upto this massive size of population. In the initial periods of human civilization, population increased at a slow rate, but during the last 100 years, population of the world has recorded an unexpected increase.
Around 8000 to 12000 years before, after the evolution and beginning of agriculture, the size of population was very small. At that time, the world population was around 80 lakh. In the first Christian century the world population was less than 30 crore.
But the increase in trade at global level during 16th and 17th century provided a basis for rapid growth in population. Around 1750, when industrial revolution took place in Holland, at that time, world population was around 55 crore. In 18th century after the industrial revolution, world population increased at a very high rate, it is also called as population explosion. The current technical development has provided assistance in reducing the death rate and has provided a basis for rapid population growth.
Question 8.
Write a note on the period in which the population doubled in the world.
Answer:
In the initial periods of human civilization, the world population was very less. Around 8000 to 12000 years before, after the evolution and beginning of agriculture, the size of population was very small. In around 10000 BCE, the entire world population was around 50 lakh. In 150 CE, world population increased to 25 crore.
In 1650, world population increased to 50 crore. From the above mentioned facts, it is clear that in 150 CE, world population was 25 crore, and it took a period of 1500 years to double upto 50 crore. In 1850, population increased to 100 crore and it took only 200 years to double up. After this, decline is being witnessed at a rapid rate in the period in which the population in the world is getting doubled.
In 1930, world population was 200 crores which doubled up in 80 years, and which, after 45 years, again doubled to 400 crore in 1975. Keeping in view the population increase rates of the present time, it was expected that the 400 crore population of 1975 will take a time of around 37 years to double up to 800 crore, but this belief proved to be wrong. At present, the world population has reached upto 720 crore (according to 2015 data).
Question 9.
How is the solution of the problem of population possible?
Or
How can the problem of population be resolved?
Answer:
The problem of population can be resolved with the help of the following measures:
- Optimum utilisation of natural resources and increasing economic production.
- Industrialisation, development of modes of transport and communication, mining industries and manufacturing industries, mechanisation, and control upon production of coal, petrol and electricity.
- Creating awareness by spreading education and maximum spread of scientific and technical training.
- Modernisation of agriculture.
- Utilisation of marine resources.
- Population should be settled in less populated regions.
- Awareness should be created for late marriages, family planning and restraint on offspring.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 3 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the pattern of unequal distribution of world population.
Or
Analyze the facts which exhibit unequal distribution of population in the world.
Answer:
The population which resides on earth’s surface shows variations on regional basis due to being controlled by various factors. This unequal distribution of population found in the world has been explained through the following points:
1. World’s two – third population resides on its approximately 14 per cent part. According to another estimate, almost 57 per cent population of the world resides on its 5 per cent land part.
2. World’s two – third part is almost desolate. Only 10% population resides on 90% part. Centralisation of 90% of population is thereon 10% land part.
3. 85% population of the world is found in the Northern Hemisphere and 15% population is found in the southern hemisphere.
4. Around three – fourth of world population lives in Asia and Europe continents. More than 60% population of the world lives in the Asian continent. Only half per cent of World Population resides in Oceania.
5. Around 80% population of the world lives between 20° to 60° northern latitudes. Less than 1% of world population resides in the north of 60° latitude.
6. Around 75% part of world population is settled on the edges of the continents. Centralisation of population declines towards the central parts of the continents.
7. Around 80% of world population resides in regions situated at upto the height of 500 m from sea level.
It is dear from the above fact that many extremely large regions of the world are sparsely populated, while certain relatively smaller regions are excessively densely populated.
Question 2.
Classify the world with the point of view of population distribution.
Or
With the point of view of population distribution, into how many parts has the world been divided?
Answer:
With the point of view of population distribution, the world has been divided into the following parts:
1. Very high population density regions:
There are five such regions of the world, where population density is very high. In these regions, China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan and Hong Kong in eastern Asia, India, Pakistan,’ Sri Lanka, Bangladesh and Nepal in Southern Asia, entire South-eastern Asia, Great Britain, Germany. Holland, Belgium, France, Ireland, Denmark, Spain and Haly in North-Western Europe and North – Eastern USA, South – Eastern Canada in estern and Northern America are included. Population has rapidly increased in North America after the industrial revolution of 1779 CE.
2. Normal Density Regions:
Ecology provides normal conditions of life for population in such geographical regions. Here, human has adapted to the environment also at various places. Even after adverse physical conditions of the Andes mountains, due to the availability of copper, in Khukai and Kamra in Chile, due to uranium deposits in Uranium city of Canada and due to the presence of gold mines in Australia, dense population is found at all these places.
3. Low density regions:
These regions are spread on 70% part of the world. Only 5% of world’s population resides here. Population is less here due to adverse conditions of location, relief and climate.
4. Very low density regions:
Climate and hardness of the surface are the major reasons for less or no population in regions in a large part of the world. Very cold, high deserts, high land areas, equatorial dry forests and sub latitudinal desert regions are included in this. Here, tribal people reside in less number.
Question 3.
Describe agglomeration of the world.
Or
Describe the grand populated region of the world.
Answer:
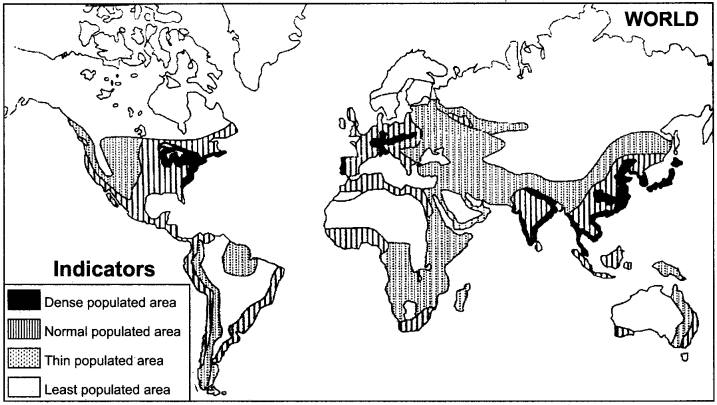
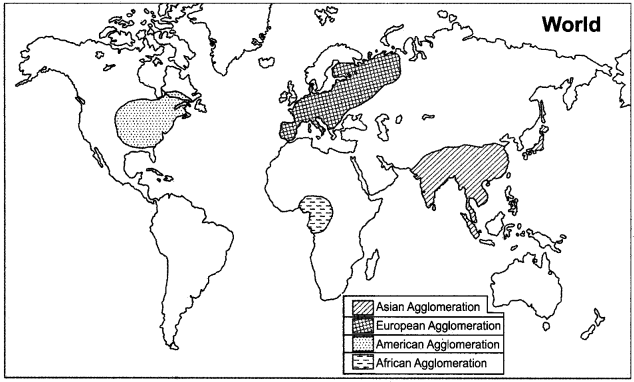
It is clear from the geographical analysis of world population distribution that approximately 80 per cent of world population resides between 20° to 60° northern latitudes. 50 per cent of earth’s surface is not favourable to live, in, so it is almost deserted. In this way, a large part of world population resides in four vast regions. Which are very suitable parts on continents to live in.These vast habitated regions are called agglomerations. These major agglomerations are:
- Asian agglomeration
- European agglomeration
- American agglomeration
- African agglomeration.
The brief description of these four agglomerations is given as below :
1. Asian Agglomeration:
Situation:
This agglomeration is located between 10° to 40° North latitudes. Many fertile plains are built here by the soil brought by several rivers. Except Japan, all the Asian countries have the economy based on agriculture.
Area:
It’s extent is in the west, from Pakistan to India, Myanmar, Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam to China, Japan and Korea towards the east. In this whole region, Monsoon climate is found. Therefore, it is also called Monsoon Asia. Asian agglomeration has further been divided into three sub – divisions:
- East Asia – China, Japan, Korea.
- South – East Asia – Thailand, Myanmar, Indonesia, Philippines, Vietnam.
- South Asia – India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, Sri Lanka.
Speciality:
Rapid increasing population, dependency on agriculture at large scale, large unemployment, lack of settlement and food, and poverty are some of the conditions seen in this region.
2. European Agglomeration:
Situation:
European agglomeration lies between 40° to 60° North latitudes. It is highly dense between the 45° to 55° latitudes in the North. It is seen in the edge of coal belt. Modern industries and metropolitan cities have been mostly developed in this region.
Area:
This area extends to Russia, Great Britain, France, Spain, Netherland, Poland, Belgium, Czechoslovakia, and Hungary.
Speciality:
European agglomeration has the highest population after Asia. In Russia 74.0 crore population resides out of which 75% part of population lives in European agglomeration. There is both low birth and death rate. About 70 per cent of its population is urban.
3. American Agglomeration
Situation:
This agglomeration is located in the North-East part of America. 80 per cent population of this agglomeration dwells in the Eastern part of 100° longitudes and between 30° to 45° Northern latitudes.
Area:
This agglomeration is spread in the North-Eastern part of America and Eastern coastal part of Canada. Concentration point of the agglomeration is the lakes region of North America. Mexico, Guatemala, Cuba, Dominican and Haiti are included in it.
Speciality:
It is the third largest agglomeration of the world. It is not only the newest, but also a developed agglomeration. About 90 per cent population of this agglomeration comes from the European part of continent by migration.
4. African Agglomeration
Situation:
The extension of African agglomeration is found in a certain form. The Nile River Valley is the centre of ancient civilisation. Besides, eight mineral resources play an important role to make this agglomeration developed.
Area:
The concentration of this agglomeration is found in three regions. First, Nile River Valley region, second, Guinea coast between Zambia and Niger River Valley, and third one, South Eastern coastal part of South Africa, Nigeria, Egypt, South Africa, Tanzania, Ethiopia, Sudan, Kenya, Algeria, Morocco, Uganda, etc. countries are included in this assemblage.
Speciality:
It is the most backward agglomeration of the world. The highest birth and death rates of the world are found in this region.
The four great agglomerations of the world are shown in the following map :
Question 4.
Interpret the reasons of population growth.
Or
Which are the reasons responsible for population growth?
Answer:
From the tendencies of population growth in the world, it is known that population has grown in all the continents, but the fate of population growth is not equal in all the continents. During the 99% part of period of existence of human on the earth, population and its growth rate has been extremely less. But in the last 350 years, world population has grown at a very high rate. In the last 50 years, many countries in the world have touched the verge of population explosion. Following are the factors responsible for population growth in the world:
1. Decline in Death Rate:
Control on death rate is the most important reason for population growth in the world. Due to the expansion of scientific achievements and healthcare and medical facilities in the last 50 years, infectious diseases and epidemics have been checked successfully, due to which there has been a rapid decline in the death rate and this has provided a base to population growth.
2. Assured Supply of Food Items:
Due to assured and regular supply of food grains and other food items in the world, the growth rate of population has been affected. Excessive increase in agricultural production has taken place due to mechanised and itensive farming, expansion of irrigation facilities, use of HYV seeds, etc. The number of famines has also declined significantly.
3. Industrial Development:
Due to industrial development, all-round development in various sectors such as mining, energy, production, industry, transportation, trade, technology, etc. has taken place in which opportunities of employment have increased. The general standard of living of human has improved due to which population has increased.
4. Scientific and Technical Development:
Population has increased as the new inventions have made human life full of comforts and facilities.
5. Peace and Security:
Normal progress has gained momentum in the world due to the establishment of peace and security and population has continued to increase.
6. Migration:
Due to high birth rate in comparison to death rate, population started rising rapidly and the Europeans started migrating towards North America, South America and Australia in large numbers. Therefore, population increased in these continents due to migration.
Question 5.
Describe the trend of population growth in the world.
Or
Which types of variations are exhibited by the tendency of population growth?
Or
Describe the characteristics of population growth.
Answer:
Population has increased in all the continents, but in some continent it has grown rapidly, while in some other continent this growth has been slow. Following are the major characteristics of population growth:
1. From 1650 to 1750, normal growth took place in Asia and Europe while population had decreased in Africa. Till that time, population in North and South America was very less.
2. From 1750 to 1900, population growth took place in all the continents, but more increase took place in Asia, Europe and North America.
3. After 1900, in the 20th century, the rate of population growth has risen very sharply. Most of the growth has taken place in North America and Asia. In the last 80 years, population of Asia has doubled while the population of North America has increased four times. Population has started decreasing in Europe.
4. In the last few years, population growth has not been equal in all the continents. Population of the entire world has increased 7 times in the past three centuries. Almost three-fourth of the world population lived in Asia and Europe three centuries earlier, and same is the case evey today.
5. Population of North and South America has increased further. In North America, population increased 364 times in three centuries. In South America, it has increased to 14 times and the slowest growth has been recorded in Africa where it has increased only three times.
Question 6.
Population growth has become an issue of concern for the world. Why?
Or
The problem of population has now become a considerable problem. How? Explain.
Or
Why is there an immediate need to resolve the problem of population?
Answer:
Day by day, the problem of population is getting intensified, and all developed countries have become concerned on this issue. Following are the reasons for this problem becoming an issue of concern:
1. Extremely rapid and horrifying growth:
In present time, the world population is increasing very rapidly. Such growth did not take place before. If it continues to grow at this rate, then in 2040, the world population will increase to 1400 crore, which will be a horrifying condition.
2. Limited resources:
The quantity of those natural resources which fulfill the needs of the population is limited. And because the population is growing rapidly, it will exploit these resources and their quantity will end soon.
3. Centralised Distribution:
Distribution of population in the world is not equal at all places. There are only a few parts, where population is centralised. 90% population resides on only one-third land part of the earth. Therefore, due to increase in population, burden on one part of the earth is increasing more and more. The standard of living of people is very low in China, Japan, Korea, India, Pakistan, Indonesia, etc. Various problems have also emerged in these countries.
4. Despair in un – settled Land Parts:
The surface area of un – settled land part of the earth amounts to almost 70% of the total surface area of the earth. In future also, there is no possibility of human settlement or an increase in it in this part. So, these regions will remain useless with the point of view of utilization of resources.
5. Natural and Human Prohibition:
When the natural resources of a region are not able to bear the burden of the population there, then starvation hits such region. Due to poverty, the standard of living declines so much that death rate increases due to diseases, epidemics and lack of basic necessities, the population starts declining. Such condition proves to be socially and economically dangerous for a nation.
Question 3.
Explain the Demographic Transition theory.
Or
Describe the various stages of Demographic Transition theory.
Answer:
Demographic transition theory is used to describe the population of a region and to perform future estimates of population. Description of the process of a society passing through various stages is done by this theory. There are various patterns of changes taking place in the population of a nation. Every nation has to pass through these phases.
Generally, in its initial phase, a nation/society passes through rural, farmer, illiterate and backward phase and proceeds towards literate, urban, industrial and developed form. During this time, population transforms from high birth rate and high . death rate to low birth rate and low death rate. This change in population takes place in various phases, which is collectively called the demographic cycle.
Demography Cycle:
Graphical representation of the stages of Demographic Transition:
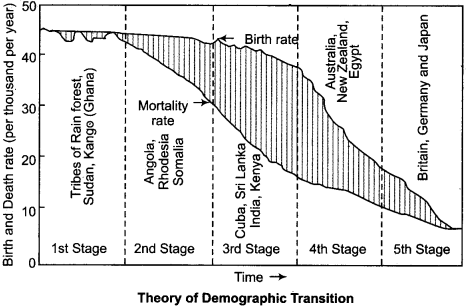
- Stage 1. High birth rate and high death rate.
- Stage 2. High birth rate, high death rate but falling or declining.
- Stage 3. High birth rate and medium death rate.
- Stage 4. Medum birth rate and low death rate.
- Stage 5. Low birth rate and low death rate.
The Demographic Transition Model does not take into account of migration.