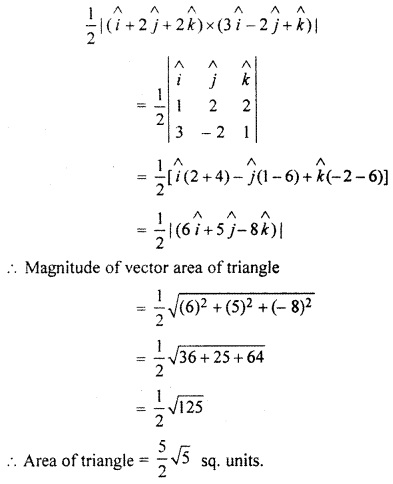Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 Vector Ex 13.3
RBSE Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 13.3 Question 1.
Find vector product of vectors
![]()
and
![]()
Solution:
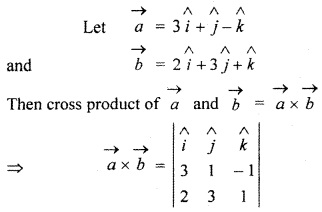
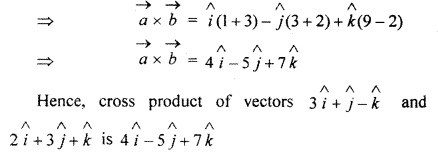
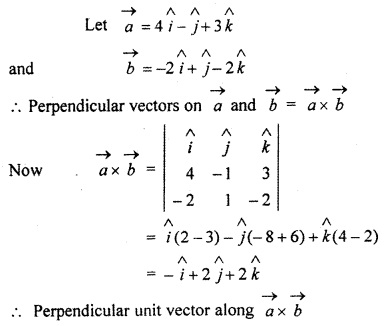
RBSE Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 Question 2.
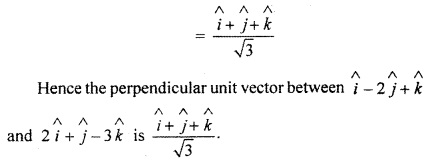
Find perpendicular unit vector of vectors
![]()
and
![]()
Solution:
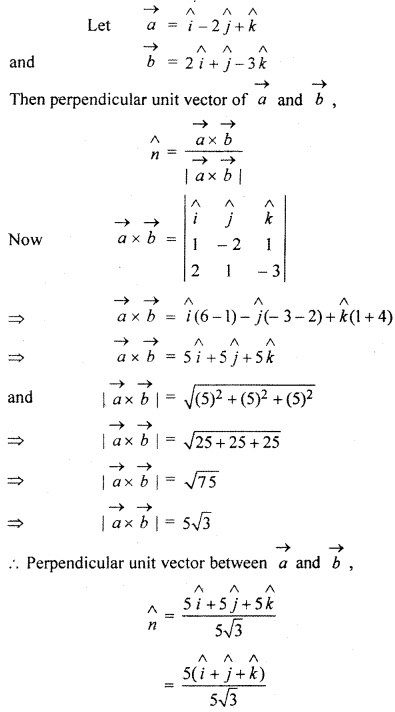
Exercise 13.3 Class 12 RBSE Question 3.
For vectors \(\overrightarrow { a } \) and \(\overrightarrow { b } \), prove that
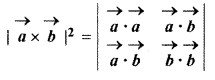
Solution:
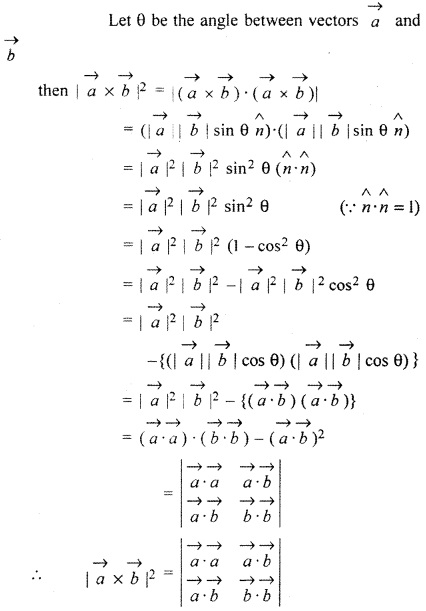
Ex 13.3 Class 12 RBSE Question 4.
Prove that
![]()
Solution:
According to question,
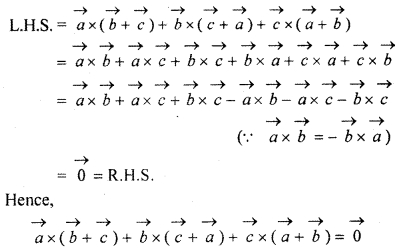
RBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 Question 5.
If \(\overrightarrow { a } \), \(\overrightarrow { b } \), \(\overrightarrow { c } \) are unit vectors, such that
\(\overrightarrow { a } \) . \(\overrightarrow { b } \) = 0 = \(\overrightarrow { a } \) . \(\overrightarrow { c } \) and angle between \(\overrightarrow { b } \) and \(\overrightarrow { c } \) is \(\frac { \pi }{ 6 } \), then prove that \(\overrightarrow { a } \) = ± 2 (\(\overrightarrow { b } \) × \(\overrightarrow { c } \))
Solution:
Given that

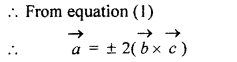
Maths Class 12 Exercise 13.3 Question 6.
Find the value of
![]()
![]()
Solution:
We know that if \(\overrightarrow { a } \) and \(\overrightarrow { b } \) are two vectors and θ is the angle between them, then
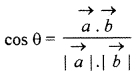
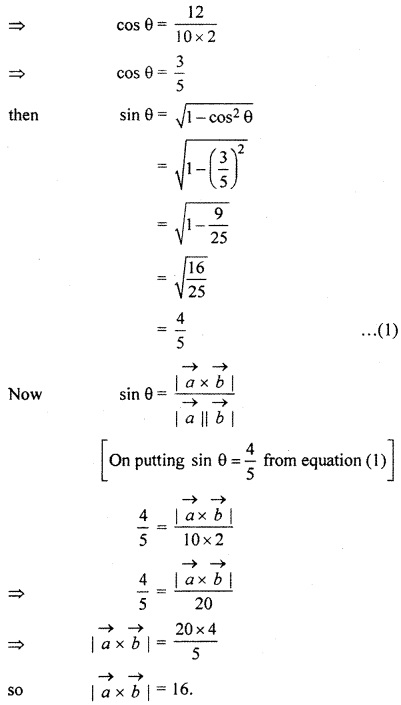
Exercise 13.3class 12 Question 7.
Find vector perpendicular to the vectors
![]()
and
![]()
whose magnitude is 9 unit.
Solution:

Class 9 Math Exercise 13.3 Question 8.
Show that:
![]()
also, explain geometrically.
Solution:

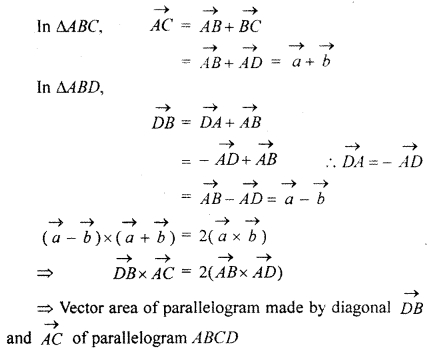
= 2(vector area of parallelogram ABCD).
Thus we conclude that area of parallelogram whose adjacent sides are diagonals of given parallelogram is twice the area of given parallellogram.
Ex 13.3 Class 12 Question 9.
For any vector \(\overrightarrow { a } \), prove that
![]()
Solution:
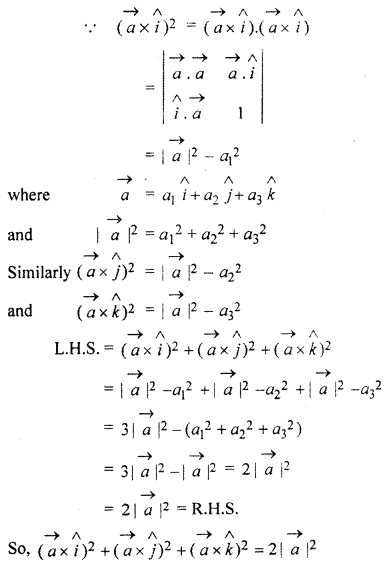
Ex 13.3 Class 10 Question 10.
If two adjacent sides of a triangle are represented by vectors
![]()
and
![]()
then find the area of triangle.
Solution: