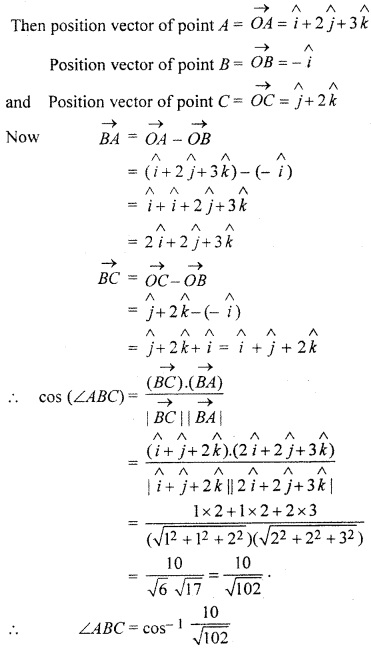Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 Vector Ex 13.5
Question 1.
Find the value of
![]()
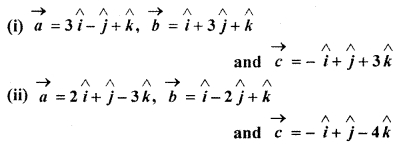
Solution:
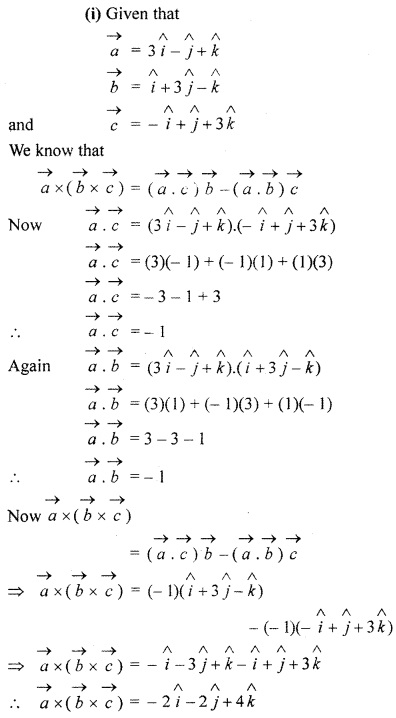
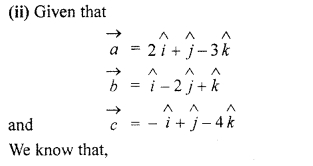

Question 2.
Prove that
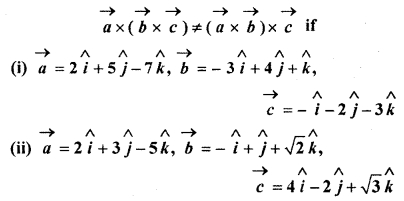
Solution:
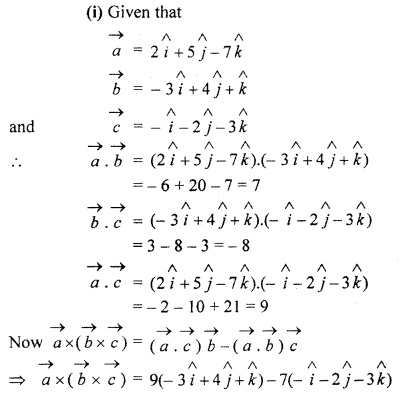

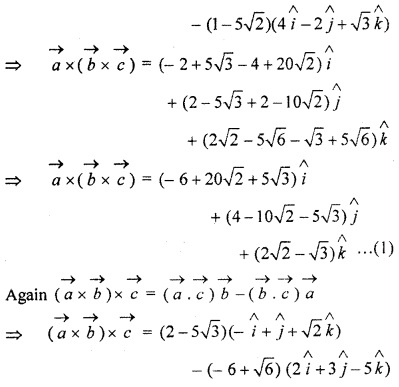
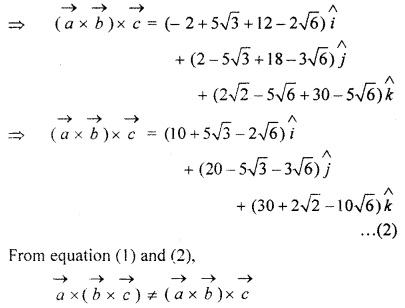
Question 3.
Evaluate the formula
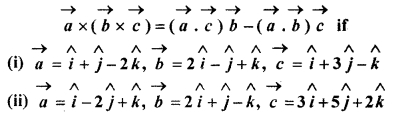
Solution:
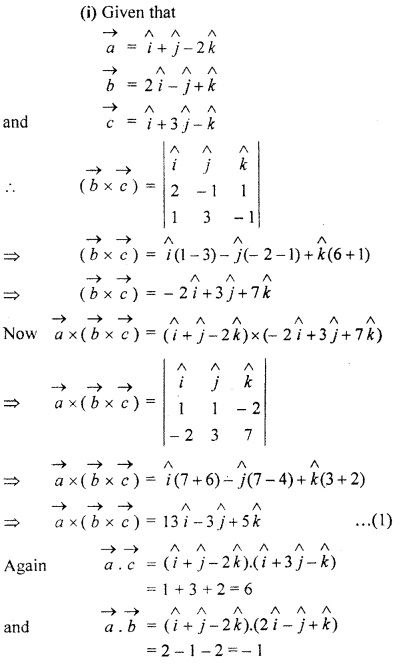


Question 4.
For any vector \(\overrightarrow { a } \), prove that:
![]()
Solution:
We know that
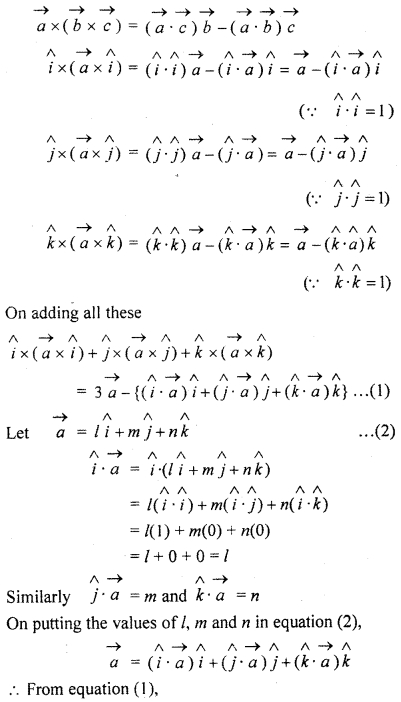
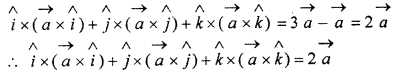
Question 5.
Prove that
![]()
Solution:
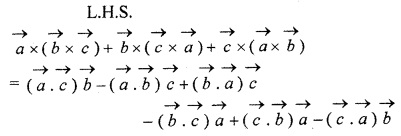
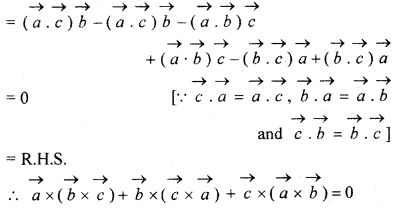
Question 6.
Prove that \(\overrightarrow { a } \),\(\overrightarrow { b } \),\(\overrightarrow { c } \) are coplanar if \(\overrightarrow { a } \) × \(\overrightarrow { b } \), \(\overrightarrow { b } \) × \(\overrightarrow { c } \), \(\overrightarrow { c } \) × [/latex], \(\overrightarrow { a } \) are coplanar
Solution:
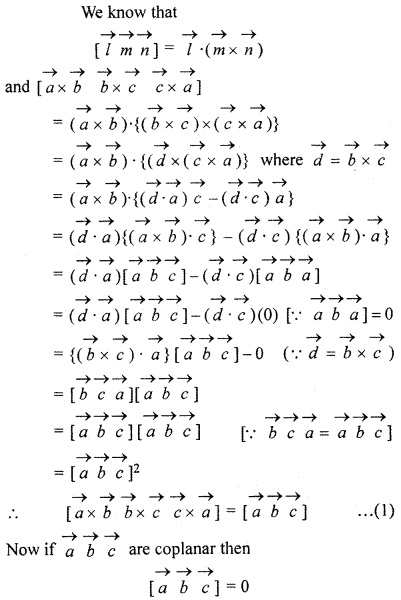
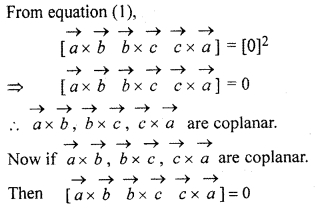

Question 7.
Prove that
![]()
Solution:
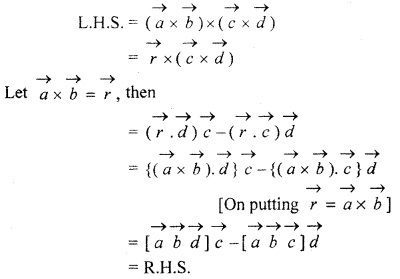
Question 8.
If magnitude of two \(\overrightarrow { a } \) and \(\overrightarrow { b } \) are √3 and 2 respectively \(\overrightarrow { a } \) and. \(\overrightarrow { b } \) = √6, then find the angle between \(\overrightarrow { a } \) and \(\overrightarrow { b } \)
Solution:
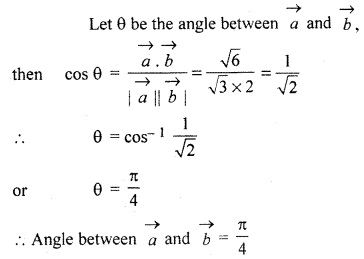
Question 9.
Find the angle between the vectors
![]()
and
![]()
Solution:
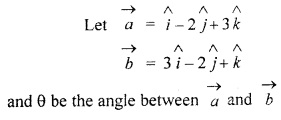

Question 10.
Find the projection of vector
![]()
Solution:

![]()
Question 11.
Find projection vector on vector
![]()
on vector
![]()
Solution:

Question 12.
Find the value of
![]()
Solution:
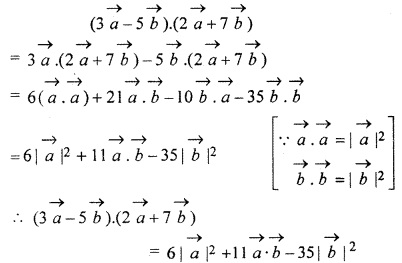
Question 13.
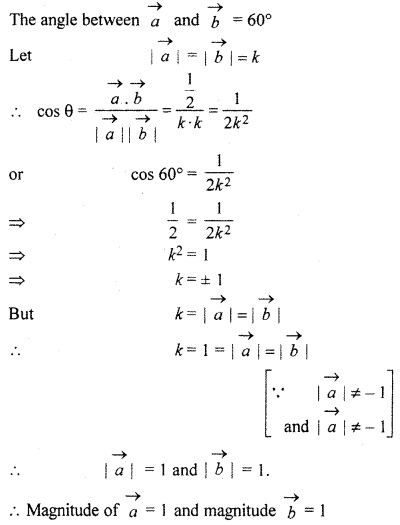
Find the magnitude of two vectors \(\overrightarrow { a } \) and \(\overrightarrow { b } \), if their magnitude are equal and angle between them is 60° and their scalar product is \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)
Solution:
According to question
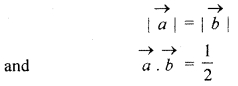
Question 14.
If for a vector \(\overrightarrow { a } \), (\(\overrightarrow { x } \) – \(\overrightarrow { a } \) ).( \(\overrightarrow { x } \) + \(\overrightarrow { a } \) ) = 12, then | \(\overrightarrow { x } \) |.
Solution:
According to question,
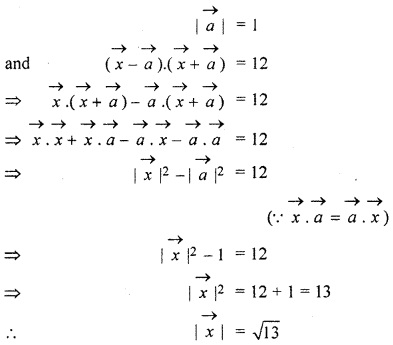
Question 15.
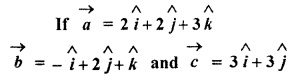
such that \(\overrightarrow { a } \) + λ \(\overrightarrow { b } \) is perpendicular on \(\overrightarrow { c } \), then find the value of λ.
Solution:
According to question \(\overrightarrow { a } \) + λ \(\overrightarrow { b } \) is a perpendicular to \(\overrightarrow { c } \)
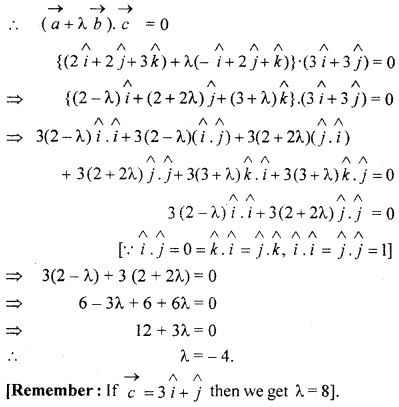
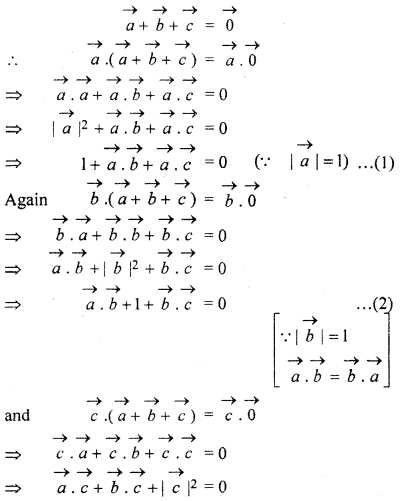
Question 16.
If vertices \(\overrightarrow { a } \), \(\overrightarrow { b } \), \(\overrightarrow { c } \) are such that
\(\overrightarrow { a } \) + \(\overrightarrow { b } \) + \(\overrightarrow { c } \) = \(\overrightarrow { 0 } \)
then, find the value of \(\overrightarrow { a } \) . \(\overrightarrow { b } \) + \(\overrightarrow { b } \) . \(\overrightarrow { c } \) + \(\overrightarrow { c } \) . \(\overrightarrow { a } \)
Solution:
According to question

Question 17.
If vectors/1, B, C of triangle ABC are (1, 2,3), (-1,0, 0,), (0, 1, 2) respectively, then find ∠ABC.
Solution:
Let O be the origin.