RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 9 Types and Parts of Plants are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science. Here we have given Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 9 Types and Parts of Plants.
| Board | RBSE |
| Textbook | SIERT, Rajasthan |
| Class | Class 6 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 9 |
| Chapter Name | Types and Parts of Plants |
| Number of Questions Solved | 56 |
| Category | RBSE Solutions |
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 9 Types and Parts of Plants
Intext Questions
Question 1.
You might have visited a garden near your house or school, which type of plants have you seen there ? Were all the plants very big ? Were all the plants very small ? Were there some plants equal to your height? (Page 71)
Answer:
Yes, we have seen many types of plants in the garden, out of which some are very small, some are medium sized and some are very big trees.
Question 2.
Examine the plants present in the garden and complete the following table with the help of your teacher. (Page 71)
Answer:
Different type of plants and their names :
| S.No | Types of Plants | Name of the Plant |
| 1. | Very sihall plants like grass | Mint and Doob. |
| 2. | Medium sized plants | Guava and Orange. |
| 3. | Bush sized plants | Rose and Dodendron. |
| 4. | Thorny plants | Opuntia and Acacia. |
| 5. | Flowering plants | Hibiscus and Dahlia. |
| 6. | Fruit bearing plants | Tomato and Brinjal. |
| 7. | Aquatic plants | Hydrilla, Lotus. |
| 8. | Plants with long leaves. | Banana, Aloevera, and Snakeplant. |
| 9. | Vegetable bearing plants | Brinjal, Potato. |
| 10. | Shady plants | Pipal and Banyan. |
| 11. | Plants that climb up by twinning around support | Pea and Grapes. |
| 12. | Wall climbing plants | Bougainveillea, Rangoon creeper. |
| 13. | Small plants grown on the walls. | Moss and Campanula. |
Question 3.
Do you know wich is the smallest flowering plant in the world and which is the world’s largest tree ?
Answer:
The smallest flowering plant is Wolffia. The largest tree in thickness is General Sherman and its scientific name is Sequoia dendron giganteum. The tallest tree is Eucalyptus which is also known as ‘safeda’ in Hindi.
Question 4.
Do all plants have the same life span ? Are some plants short lived while others are long lived ? (Page 73)
Answer:
No, some plants are short lived from 4 to 6 month, some are of 1 – 2 years and some are long lived for many years.
Question 5.
Visit a farm near your house or school, and discuss the following points with the farmer working there. (Page 73)
1. At present which crop is grown in the farm ?
2. When is this crop sown ?
3. W hen are fruits or other edible products obtained from this crop ?
4. What is the time duration between sowing and harvesting the crop ?
5. Which crops ripe in one year ?
6. Which plants have life span of two years ?
7. Which plants or tress have a life span of many years ?
Answer:
- At present, wheat crop is grown in the farm.
- This crop is sown in November – December.
- In April – May.
- The time duration between sowing and harvesting the crop is 5 – 6 months.
- Life span of Jowar, Mustard, Millet and Maize is one year.
- Carrot, sugarcane, cabbage, onion.
- Neem, pine, banyan, mango, pipal etc.
Question 6.
Have you ever seen a plant with soft stem near your house or in a garden ? Are the stems of such plants, strong enough to stand upright on their own ? Do these plants need any support? (Page 74)
Answer:
The plant of bean has a soft stem, it needs a support of a wall or another tree or of a string.
Question 7.
Do you have any curiosity to know about habitat of plants ? Name their types of the basis of habitat. (Page 75)
Answer:
Yes, on the basis of the habitat plants are of two types :
- Aquatic plants
- Terrestrial plants
Let us find Out
Question 8.
With the help of your teacher, make a list of plants grown in garden or pots which are flowering or non – flowering and are grown for decorative purpose in lawns. (Page 76)
Answer:
Various types of flowering and non – flowering plants grown in garden or pots:
| S. No. | Name of flowering plants | Name of non-flowering plants |
| 1. | Rose | Fern |
| 2. | Hibiscus | Moss |
| 3. | Gulmohar | Cycus |
| 4. | Tikoma | Pine |
| 5. | Coronarium | Peacock’plant |
| 6. | Marigold | Cupresus |
| 7. | Jasmine | Sprus |
Question 9.
The main parts of a plant are root, stem, leaves and flower. What are the functions of these plants parts ? (Page 77)
Answer:
- Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil.
- Main function of stem is to carry the water and minerals absorbed by the roots and send them to the aerial parts of the plant.
- Leaves make food by the process of photosynthesis.
- Flower is the generation part of the plant.
Question 10.
Which part of a plant is below the ground ? (Page 77)
Answer:
Root.
Question 11.
Which parts of a plant are found above the ground ? (Page 77)
Answer:
Stem, branches, leaves, flowers and fruits.
Question 12.
Name that part of a plant where exchange of gases takes place ? (Page 77)
Answer:
Leaves.
Question 13.
Do all plants have similar roots ? Is it possible to uproot a big tree ? (Page 78)
Answer:
No, All plants have not similar roots. It is not possible to uproot a big tree.
Question 14.
Is the structure of roots of xerophytic plants and mesophytic plants similar ? (Page 78)
Answer:
In some cases, the structure of roots is similar and in some cases it is dissimilar.
Question 15.
Can you name a root which can be consumed as dish or can be eaten raw ? (Page 79)
Answer:
Carrot and radish are such type of root.
Question 16.
Like roots, does the storage of food occur in the stem also ? Does stem play an important role in the development of the plant ? (Page 80)
Answer:
Yes, the storage of food occurs in the stem also e.g., potato and sugarcane. Stem performs vegetative reproduction.
Question 17.
Do the leaves of all the plants look alike ? Are they similar in size and shape ? (Page 80)
Answer:
No, they don’t look alike they are of different size and shapes.
Question 18.
Do plants perform functions other than photosynthesis and respiration ? (Page 81)
Answer:
Yes, they perform transpiration.
Exercises
Choose the Correct Option
Question 1.
Which one of the following is a biannual plant
(a) wheat
(b) gram
(c) onion
(d)pine
Answer:
(c) onion
Question 2.
How many types of plants are there on the basis of size ?
(a) three
(b) four
(c) two
(d) six
Answer:
(a) three
Question 3.
Which of the following is an aquatic plant ?
(a) Prosopis cineraria (khejri)
(b) water hyacinth
(c) plum
(d) capparis decidua (kair)
Answer:
(b) water hyacinth
Fill in the blanks
1. On the basis of size, plants can be divided into …………. and …………. .
2. Plants respire through the …………. .
3. Climbing plants climb up with the help of ………….. .
4. Roots are of two types (a) ………….. (b) …………… .
Answer:
1. Small, big
2. stomata
3. support
4. (a) Tap, (b) Fibrous.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is photosynthesis ?
Answer:
The process by which leaves of green plants prepare food material in the presence of sunlight, carbon dioxide, water and chlorophyll is called photosynthesis.
Question 2.
In how many categories can plants be classified on the basis of life span ? Name them.
Answer:
On the basis of the life span, plants can be classified into three categories :
- Annual plants.
- Biennial plants.
- Perennial plants.
Question 3.
What is the difference between the stems of herbs and shrubs ?
Answer:
The stems of herbs are extremely soft and can be easily bent while stems of shrubs are hard.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the different categories into which plants can be classified on the basis of size ?
Answer:
On the basis of size, plants can be classified into three categories :
- Herb
- Shrub
- Tree
1. Herb : Herbs are plants of short height, Basil (tulsi) plant found in our houses and turmeric, used as medicine for many diseases are herbs. These plants have very short height (less than 1 meter). Their stems are also green in colour. These short sized plants are extremely soft and can be easily bent. For example : Wheat, rice, basil, turmeric, chilli, tomato etc.
2. Shrub : Shrubs are small and medium sized woody plants and their height is nearly less than 6 meter. Their stem is usually brown in colour. Their main stem branches out near the base. Their stem is often hard. For example : henna, rose, plum etc.
3. Tree : Some plants are very tall and have hard stem with bark. The stems have branches in the upper part, much above the ground, like, mango, Azadirachta indica (neem), banyan and sacred fig (peepal) etc.
Question 2.
Describe the features of plants living in aquatic habitat ?
Answer:
Those plants which are found in water bodies like rivers, ponds, lakes, sea etc are called aquatic plants. For example: lotus, vallisneria, water chestnut, hydrilla, water hyacinth (jal kumbhi) etc. These plants are called hydrophytes. Roots of aquatic plants are less developed. Air chambers in the stem provide buoyancy and help the plants in floating. The leaves of these plants are ribbon like and finely dissected. On the basis of position in water, aquatic plants are divided into three groups :
- Floating plants, like water hyacinth (jalkumbhi).
- Submerged plants, like hydrilla.
- Amphibious plants, like vallinsneria.
Question 3.
Draw a labelled diagram of leaf ?
Answer:
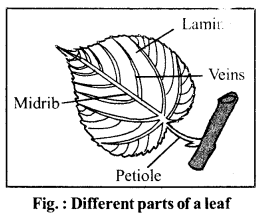
Practical Work
Question 1.
You have studied the classification of plants found in nature on different basis. So, on the basis of these classifications, make a scrapbook of various plants.
Note : Do it yourself.
Question 2.
Label the different parts of the plant given below :
Answer:
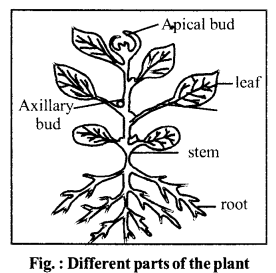
Other Important Questions
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Which is not herb plant
(a) wheat
(b) maize
(c) rose
(d) tomato
Answer:
(c) rose
Question 2.
Which is not shrub
(a) henna plant
(b) plum
(c) capparis decidua
(d) guava
Answer:
(d) guava
Question 3.
Which contains tendril
(a) pea
(b) cucumber
(c) ridged gourd
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Question 4.
Aquatic plant is
(a) hydrila
(b) kapok tree
(c) bamboo
(d) basil
Answer:
(a) hydrila
Question 5.
Fibrous roots are found in
(a) maize
(b) wheat
(c) onion
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Fill in the blanks
1. Turmeric, which is used as medicine is actually a ………………. .
2. Perennial plants are usually large and ………… trees.
3. Plants which are found in water are called ……………. .
4. Those plants which do not have flowers are called ……………. plants.
Answer:
1. herb
2. shady
3. aquati
4. non – flowering
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write specifications of herbs.
Answer:
These short sized plants are extremely soft and can be easily bent.
Question 2.
What is the average height of shrubs ?
Answer:
Less than 6 meters.
Question 3.
Write the names of two shady plants.
Answer:
- Banyan
- Pipal
Question 4.
Write names of two creepers.
Answer:
- Watermelon
- Pumpkin
Question 5.
Write the name of structure which supports Pilvan plant ?
Answer:
Tendril.
Question 6.
Write names of two non – flowering plant.
Answer:
- Moss
- Fern
Question 7.
Name the types of the root.
Answer:
- Tap root
- Fibrous root
Question 8.
Name two plants the roots of which store food in them.
Answer:
- Carrot
- Radish
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are weeds ? Why they are harmful ?
Answer:
Sometimes, in farms or gardens, unwanted plants grow along with the main plant or crop, which are harmful for the growth of the main plant. They harm the main plant by competing for nutrition, respiration sunlight etc. Such unwanted plants are called weeds.
Question 2.
Give three examples of climbers and creepers each.
Answer:
- Climbers : Pea, cucumber, bitter gourd.
- Creepers : Watermelon, pumpkin, muskmelon.
Question 3.
What are aquatic plants ? Give examples with types.
Answer:
Aquatic Plants : Those plants which are found in water bodies like rivers, ponds, lakes, sea etc. are called aquatic plants.
For example: lotus, vallisneria, water chesnut, hydrilla, water hyacnith etc.
On the basis of position in water, aquatic plants are divided into three groups :
- Floating plants, like water hyacinth.
- Submerged plants, like hydrilla
- Amphibious plants, like vallisneria.
Question 4.
What are terrestrial plants ? Write examples with types.
Answer:
Plants found on land are known as terrestrial plants. Terrestrial plants can be classified into the following groups on the basis of their varied habitats.
- Mesophytes, like: neem and bamboo.
- Plants of cold habitat, like : soldanella, lichen etc.
- Dry habitat (xeroyphytes), like prosopis cineraria (khejri), euphordia roleana (thor), opuntia etc.
Question 5.
What are flowering and non – flowering plants ? Give examples.
Answer:
Flowering Plants : Plants which bear flowers are called flowering plants, like rose, china rose, delonix regia (gulmohar), cassia fistula (amaltas) etc.
Non-flowering Plants : Those plants which do not have flowers are called non – flowering plants. For example, fern, mosses etc.
Question 6.
Make a list of modified form of roots for specific functions.
Answer:
| 1. For storing food | carrot, radish, sweet potato |
| 2. For climbing | Money plant |
| 3. For reproduction | Dahlia |
| 4. For providing support | Sugarcane, banyan. |
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Classify plants on the basis of life span with examples.
Answer:
On the basis of life span, plants are broadly divided into three groups :
- Annual plants : Plants that have life span of one year or one season are called annual plants.
For example: maize, sorghum, millet, mustard etc. - Biennial plants : Plants which generally have a life span of two years are called biennial plants.
For example : Onion, Cabbage, Carrot etc. - Perennial plants : These plants live for more than two years and produce wood. These plants usually flower in summer or spring season. Perennial plants are usually large and shady trees.
For example : Neem, pine, banyan etc.
Question 2.
On the basis of ascent, write types of plants.
Answer:
On the basis of ascent plants are of two types :
1. Climbers : Climbers are those plants that need a support to climb up. Some plants have thread-like structures which are called tendrils. Tendrils are the modified form 6 f petiole, leaf of stem. Pea, cucumber, bitter gourd, ridge gourd etc. are climbers.
2. Creepers : These plants have very weak stem. They cannot stand upright. They spread on the ground and grow horizontally and acquire large space. Unlike climbers, they do not have tendrils. For example : Water melon, pumpkin, muskmelon etc.
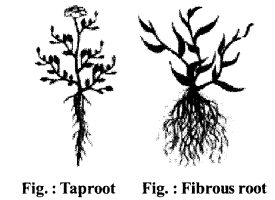
Question 3.
Define taproot and fibrous root with examples. Draw diagram also.
Answer:
Tap root : Tap roots have a main root and other roots arise laterally from the main root.
For example : Mango, neem etc.
Fibrous root : In fibrous roots, no main root is present and all roots appear similar and form a cluster.
For example : Maize, wheat, onion, sugarcane etc.
Question 4.
Write different works of the stem.
Answer:
Different Work of stem :
- The main function of stem is to carry the water and minerals absorbed by the roots and seuding them to the aerial parts of the plants.
- Stem bears leaves, flowers, fruits etc.
- Stems store food material prepared in the leaves.
- Gren stems make food by chlorophyll present in like asparagus.
- Stems adapt the xero – phytic plants by storing water, like cactus.
- They take part in vegetative propagation for example: rose, jasmine.
- they Provide support (tendrils) like : Cocculus pendulus (Peelwan).
Question 5.
What are the main works of leaf.
Answer:
Main works of leaf :
- Leaves of green plants prepare food material in the presence of sunlight carbon dioxide, water and chlorophyll. It is called as photosynthesis.
- Food synthesized by leaves ultimately gets stored as starch in different parts of the plant.
- Stomata are present on the surface of the leaves. Leaves respire through these stomata.
Question 6.
Give a brief biography of professor Shipra Guha Mukherjee.
Answer:
She was born on 13 July, 1938 in Calcutta. She achieved graduate and post graduate degrees from Delhi University. She achieved a Ph.D degree under the guidance of Prof. B. M. Johari on the subject “Tissue Culture of Flowers of Alium Cepa,” Under the guidance of S.C. Maheshwari, she invented a technique for production of haploid plant by culturing stamen from the flowers of Datura innoxia. This technique is utilized in the field of agriculture to develop new varieties of crop plants. She died of brain tumour on 15 September, 2007.
We hope the RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 9 Types and Parts of Plants will help you. If you have any query regarding Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 9 Types and Parts of Plants, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.