RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 7 Environmental Regions (Zones) is part of RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Social Science. Here we have given Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 6 Social Science Chapter 7 Environmental Regions (Zones).
| Board | RBSE |
| Textbook | SIERT, Rajasthan |
| Class | Class 6 |
| Subject | Social Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 7 |
| Chapter Name | Environmental Regions (Zones) |
| Number of Questions | 40 |
| Category | RBSE Solutions |
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 6 Social Science Chapter 7 Environmental Regions (Zones)
Textbook Activity Based Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is meant by environmental regions? Explain. (Page 52)
Answer:
Environmental regions are those exclusive places, which have similarity in some specific conditions. Due to the similarity of these exclusive conditions, the environment of one region is different from the others.
Question 2.
Why had the earth been divided into various environmental regions? (Page 52)
Answer:
Environmental conditions of various regions situated on the earth’s surface are different. Due to this variation in environmental conditions, the earth’s surface has been divided into various environmental regions.
(Page 54)
Question 1.
List the plants found nearby you and also list their uses to us.
Answer:
Various types of plants and trees are found nearby us. Mango, mahua, neem, sheesham, banyan, peepal, etc. are the major ones among them. Trees are of special importance for human life. Under direct benefits, fodder for animals, wood for fuel, wood for construction of houses, etc. are obtained, and along with this, in indirect form, they free the environment from the pollution and build a healthy environment. Precious oxygen is derived from them which is life-giving for the living beings and they also attract rainfall and protect soil erosion.
Question 2.
Out of the different environmental regions, shown in the lesson, in which environmental region do you reside? (Page 55)
Answer:
We reside in the plains and come under lowlands or low altitude lands, where there is even land, fertile soil and most of the population over here is dependent upon agriculture. Animal husbandry is conducted as an allied occupation for their use in agriculture and in order to fulfill our own needs.
Question 3.
What is the effect of our nearby environment on us? Discuss. (Page 55)
Answer:
Human being is the product of his own environment. His working, his thinking and his way of living life adapts to the environment in which he fives. His education and knowledge is also influenced by the type of environment. Environment also influences the residence type of mankind, his eating habits, physical structure and culture etc.
Question 4.
Why do people cut forests? What is the effect of this reckless deforestation? Discuss. (Page 55)
Answer:
At present time, population is at a continuous rise. The feeling of accumulating things is rigidly employed among people. As a result of this, reckless cutting of forests is taking place. In order to fulfill his requirements, obtain agricultural land, obtain land for housing purposes of the ever increasing population or for public works done by the government, mankind is cutting trees recklessly, due to which, environmental pollution is on a rise and biodiversity is depleting.
Some wild animals are on the verge of extinction due to which natural balance is deteriorating. As a result of this, changes such as increase in temperature, increase in sea water level, lack of rainfall, climate changes are taking place. Therefore, it is required that steps should be immediately taken for conservation of forests.
Textbook Exercise
Question 1.
Choose the correct option
(i) The grasslands of Prairies are found in
(a) Europe
(b) Asia
(c) Australia
(d) North America
Answer:
(d) North America
(ii) Which is located on the North Pole?
(a) The Arctic Ocean
(b) The Antarctica Ocean
(c) The Atlantic Ocean
(d) Australia
Answer:
(a) The Arctic Ocean
Question 2.
Match the zones with their area of latitudes:
| Zone | Position of Latitude | ||
| 1. | Hot zone | a. | 66 1/2° to 90° North and South |
| 2. | Cold zone | b. | 23 *6° to 66 *6° North and South |
| 3. | Temperate zone | c. | 0° to 23 1/2° North and South |
Answer:
1. (c), 2. (a), 3. (b).
Question 3.
Write about the difference(s) between the forest areas and grasslands.
Answer:
Forest areas and grasslands are two different environmental regions. Following are the major differences between them
| Forest Areas | Grasslands |
| Rainfall is more here. | Rainfall is comparatively less here. |
| Large trees, plants are found here. | Grasses are found here. |
| Forests are of many types, such as evergreen forests, deciduous forests, etc. | On the basis of shape of grasses, grasslands are also of various types. For example – the Prairies (North America) have grasses of long height, while grasses of short height are found in Steppes grasslands. |
| Tribal people reside in forest areas. | Pastoralists (shepherds) temporarily reside in grasslands. |
| Large wild .animals and small insects are found in the forests. | Sheep, goats, cows, etc. are grazed in grasslands. Wild animals are not found here. |
Question 4.
In how many zones is our earth divided? ’ Write their main characteristics.
Answer:
On the basis of temperature, our earth has been divided into the following temperate zones
1. Hot zone or Torrid Zone – Hot zone expands in both the hemispheres between 0° to 23 1/2° latitudes.
Following are the major characteristics of this zone:
- Sunrays fall directly, especially perpendicular, on all the regions, at least once in a year.
- Climatic change is almost negligible here. Same climate is there, both in summer and winter.
2. Temperate zone – This zone expands in both the hemispheres between 23 1/2° to 66 1/2° latitudes.
Following are the major characteristics of this zone:
- The sun is never on the head here.
- Difference between the day. and the night increases. Four seasons occur here- summer, winter, autumn and spring.
3. Cold zone – This zone expands in both the hemispheres between 66 1/2° to 90° latitudes up till the North and South Pole.
Following are the major characteristics of this temperate zone:
- These are the coldest regions. Temperature is less than 0° for most of the time. On the poles here, 6 months have days and six months have night.
- Due to rigid climate, very less population resides here.
Question 5.
What are the differences between the environment of the hot zone and the cold zone?
Answer:
Following is the difference between the environment of the hot zone and the cold zone:
| Hot Zone | Cold Zone |
| 1. It is located between 0° to 23 1/2° northern and southern latitudes. | It is located between 66 1/2° to 90° northern and southern latitudes. |
| 2. Temperature is more around the year here and the climate is hot and humid. | These are cold regions. Most of the months in a year experience temperature less than 0°. |
| 3. Days are lengthier across the year. Difference between the day and night is extremely less. | Difference between the day and night is more here. At the poles there are days of 6 months have and night of six months. |
Question 6.
How many types of deserts are there in the world? Compare them.
Answer:
Desert is of two types – hot desert and cold desert. Following are the major differences between both of them:
- Sandy plains are found in hot desert and temperature is more there, while cold desert is the region led with snow and temperature remains less than 0° there.
- Thorny bushes are found in hot desert regions, while lack of trees is noticed in cold desert regions.
- Cow, ox, camel, goat, pony, etc. are reared in hot desert regions, while ‘yak’ is the major animal to be reared in cold desert regions.
Question 7.
Why is Rajasthan called as ‘Land of Sand Dunes’?
Answer:
The Thar Desert is situated in Rajasthan, so sandy soil is found at most places here. At various places, dunes of sandy soil are formed by winds. Along with this, these dunes are transported from one place to another and various types of shapes are formed by sand. Thus, Rajasthan is called as the ‘Land of Sand Dunes’.
Question 8.
Explain with the help of examples the vegetation’s of desert regions.
Answer:
Due to lack of rainfall in desert regions, Rohida and Khejadi trees are found here. Mostly, thorny bushes are found here, which have pointed and needled leaves. These plants adapt themselves to spines according to the environment there. The process of vaporization takes place in the pointed parts. In order to sustain the life of plants, thick leaves retain abundant amount of moisture in them. Small thorny bushes of her, nagfani, dandathor, khair and various types of cactus, keekar and babool are included in vegetation of the desert regions.
Other Important Questions
Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Part of man-made environment are
(a) Rivers
(b) Natural vegetation
(c) Soils
(d) Occupations
Answer:
(d) Occupations
Question 2.
In which temperature zone is Brazil (South America) situated?
(a) In hot zone
(b) In temperate zone
(c) In cold zone
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) In hot zone
Question 3.
Terrace-shaped lands are formed in
(a) Highlands
(b) Lowlands
(c) Forest regions
(d) Dry and humid regions
Answer:
(a) Highlands
Question 4.
A representative region of dry and humid regions is
(a) Himalaya mountain
(b) Ganga – Yamuna plains
(c) Amazon Basin
(d) Thar Desert
Answer:
(c) Amazon Basin
Question 5.
Steppes grass plains are situated in
(a) Africa
(b) Australia
(c) Eurasia
(d) South America
Answer:
(c) Eurasia
Match the following
| 1. Sweden | (a) Tea and fruit plantations |
| 2. Highland | (b) Europe and Asia |
| 3. Dry and humid region | (c) Seal and Walrus |
| 4. Steppes | (d) Igloo |
| 5. Polar region rainforests | (e) Temperate |
| 6. Eskimo | (f) Cold zone |
Answer:
1. f, 2. a, 3. e, 4. b, 5.- c, 6. d .
Fill in the blanks
1. Temperature ………………. from the Equator towards the poles.
2. There are ……………… found between the climate, vegetation and lifestyle of one temperature zone also.
3. Our natural and ………………. environment surrounds us from all the sides.
4. Climate makes the environment of the earth ………………… .
5. Large land part covered with trees-plants and bushes is called …………….. .
Answer:
1. decreases
2. variations
3. man-made
4. diversified
5. forest region
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by environment?
Answer:
The cover of natural and man-made components which surrounds us is known as the environment.
Question 2.
Which zones are found in low, mid and high latitudes?
Answer:
Hot zone is found in low latitudes, temperate zone is found in mid latitudes and cold zone is found in high latitudes.
Question 3.
Give some examples of highland environment.
Answer:
Himalayas in northern India, Nilgiri and Annamalai hills in southern India, hilly areas in north-eastern India are major examples of highland environment.
Question 4.
Write the names of plain regions formed by rivers in India.
Answer:
Ganga – Yamuna plains, Brahmaputra plains, Satluj – Indus plains, Ghagghar plains, Chambal, Banas and Mahi plains are included in these plain regions.
Question 5.
Write the names of some regions which represent forest region.
Answer:
Mediterranean Africa, South – East Asia and land parts of South America are major regions which represent forest region.
Question 6.
Write any two characteristics of desert regions.
Answer:
- Rainfall is less here
- Here, vegetation is found in the form of thorny bushes.
Question 7.
What is the reason behind temperature being more on the Equator and excessive cold at the poles?
Answer:
The sunrays fall directly on the Equator, so temperature is found to be more in regions around it, while due to the sunrays falling slanting upon the poles, excessive cold is experienced there.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write the names of major nations situated in hot/torrid zone.
Answer:
Mainly Philippines, Indonesia, India, Sri Lanka, Brazil, Nigeria, Ghana, Ecuador, Myanmar, Thailand, Cambodia, Singapore, Malaysia, etc. are included in hot zone.
Question 2.
What are environmental regions? Explain.
Answer:
Environmental regions are such large regions where similarity is found between the environmental conditions and components i.e. there is similarity in climate, soil, vegetation, etc. All these components collectively form such an exclusive region which is different from the nearby land parts.
Question 3.
Why are people living in high altitude regions more dependent on animal husbandry?
Answer:
Following are the reasons for people living in high altitude regions being more dependent on animal husbandry:
- Uneven and excessively sloped land is found in these parts.
- High mountainous regions are significantly colder.
- Unfavorable conditions are present in these regions.
Question 4.
Write the names of temperate zone grazing lands.
Answer:
Grazing lands are those places where sheep, goats, cows, etc. animals are reared. Such grazing lands and grasslands are known by different names in different countries. In North America, they are called Prairies and in Europe and Asia they are called Steppes.
Question 5.
What is the difference between plains formed by rivers and sandy plains?
Answer:
Following is the difference between plains formed by rivers and sandy plains:
| Plains formed by rivers | Sandy plains |
| 1. These are formed by rivers. | These are formed by weathering, erosion and oddments. |
| 2. Normal or more than normal rainfall takes place in these parts. | Rainfall is very scarce in these parts. |
| 3. In these, facility of irrigation is available through rivers during dry period. . | Normally, there is lack of irrigation facility in these parts. |
| 4. These are the most fertile parts. | These are usually infertile. |
Question 6.
Throw light on the environment of humid regions in brief along with examples.
Answer:
Amazon Basin is a representative area of humid region. Rainfall takes place in these regions around the year. Various types of trees-plants and animals are found in the forests. The climate is sultry here. Swampy land is also found here. These types of regions are unfavorable with human health point of view.
Question 7.
Why is the land of plain parts fertile?
Answer:
When rivers flow down into the plains from the mountainous regions, they bring along a lot of soil with them from upper regions due to their velocity and deposit it in the plains. Along with this, various types of carbonic substances and dust of minerals are also deposited along with the soil due to which this soil becomes extremely fertile.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the environmental characteristics of high altitude land in brief.
Answer:
Highlands are the symbol of mountainous environment. Temperature is found to be less in high mountainous regions, because along with increase in height, temperature continues to decline. Snow is also present at places of extreme height. Mountainous regions are the origin place of rivers. Due to steep slope, rivers flow here at extreme velocity and form waterfalls in their way. There is absence of leveled land in mountainous regions. People build their houses in parts with lesser slope. Mountainous slopes are cut to form terrace-shaped farms on which, vegetables in lesser amount and tea and fruit plantations are found. Agricultural work is almost negligible in high mountainous regions, so the residents of these regions are engaged in occupations associated with forestry and animal husbandry.
Question 2.
What is meant by environmental stress?
Answer:
The environment is mainly formed due to the mutual coordination of natural and man-made components. Both of these have been complimentary to each other. But at present time, due to mankind being extremely ambitious, he is insensibly exploiting the natural resources in an extreme manner, due to which, environmental pollution and deforestation have taken place and otir natural heritage has been destroyed and this process continues even today due to which various environmental problems have emerged in the entire world. These are known as environmental stress.
Question 3.
Write major characteristics of polar region.
Answer:
Poles are present on both the edges of the earth. Arctic Sea is present on the North Pole and Antarctica continent is present on the South Pole. Sunrays fall slanting on the poles, so the quantity of solar heat is always less here, due to which they remain covered with snow for the entire year. There is lack of vegetation here. Eskimos tribal people reside here in such rigid geographical conditions. They build small houses made of snow and heat them from inside and live there. These houses are called ‘Igloo’. Fishing is their main occupation and way of earning livelihood. Seal, walrus and polar bear are also found here.
Map Based Question
Question 1.
Show various temperature zones on the map of the world.
Answer:
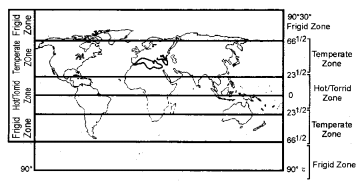
We hope the RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 7 Environmental Regions (Zones) will help you. If you have any query regarding Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 6 Social Science Chapter 7 Environmental Regions (Zones), drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.