RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Temperature and Heat are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science. Here we have given Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Temperature and Heat.
| Board | RBSE |
| Textbook | SIERT, Rajasthan |
| Class | Class 7 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 15 |
| Chapter Name | Temperature and Heat |
| Number of Questions Solved | 81 |
| Category | RBSE Solutions |
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Temperature and Heat
Text book Exercise
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Which material is used in laboratory thermometer?
(a) Sodium
(b) Mercury
(c) Melted aluminium
(d) Shining water
Answer:
(b) Mercury
Question 2.
In a heat transfer method, when molecules themselves move from one place to another to transfer heat, it is called.
(a) Conduction
(b) Convection
(c) Radiation
(d) Conduction and radiation both
Answer:
(b) Convection
Fill in the blanks with suitable words
1. Degree of hotness or coldness of an object is called………………..
2. A metal spoon is dipped into icecream pan for few moments then it will become…………….
3. A layer of copper is adhered at the bottom of steel pan, because copper is good………….. of heat.
4. The heat flows from………….. temperature object to…………. temperature object.
5. Air and water are………….. of heat.
Answer:
- temperature
- cold
- conductor (best conductor)
- higher lower
- bad conductor.
In the following statements, Tick T against those which are True and F against those which are False.
1. If we add 1 litre of 35° C water into 1 litre of 55° C water then the mixture will have a temperature of less than 30° C (T/F)
2. Utensils for cooking food are made up of metals because metals are good conductors of heat. (T/F)
3. The houses, which have outer walls painted with white colour are less hot in summer days. (T/F)
Answer:
- False
- True
- True
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Explain the difference between heat conductor and insulator with examples.
Answer:
Those materials through which heat is transferred easily are called good conductor or conductors of heat.
For example- Metals like aluminium, iron, copper etc. are good conductors of heat opposite to these materials which do not transfer heat easily through them are called bad conductors or insulators. For example wood, plastics Ebonics, woollen clothes are bad conductors of heat.
Question 2.
What are the different methods for heat transfer? Explain the difference in each.
Answer:
There are three methods for heat transfer. They are :
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation.
Difference between conduction, convection and Radiation
| Sr. No. | Conduction | Convection | Radiation |
| 1. | Medium is necessary for conduction of heat | Medium is necessary for convection | Medium like (Solid, Liquid Gas) is not necessary for radiations |
| 2. | Heat is transferred from one atom to the next atom | Particles themselves receive heat and move to other place | Particles (atoms/molecules) are not required |
| 3. | Particles (atoms) do not leave their place | Particles (Molecules) after gaining heat from the source leave their place | Particles are not required |
| 4. | Transfer of heat in this method is possible from all directions | Transfer of heat may zig-zag or circular current | Transfer of heat is always in a straight line |
| 5. | Transfer of heat occurs slowly | Transfer of heat occurs slowly | Transfer of heat is fast equal to the speed of light |
| 6. | There is no need of any type of wave for transfer of heat | Waves are not required | Heat is transferred by electromagnetic waves like light |
Question 3.
When we put objects in sunlight, why do black objects get more heated up as compared to lustrous objects although having same size and shape?
Answer:
Black objects are the best absorbs of heat while lustrous objects are best reflectors of heat. That is why black object absorbs maximum heat that incidents on them, while lustrous object reflects maximum heat falling on them. That is why when black and shiny objects of same size are put in sunlight, the black object becomes hotter by Sun’s radiation as compared to lustrous or shiny objects.
Question 4.
Give reasons for formation of hot currents in sea?
Answer:
Sun rays falls directly near equator as compared to the poles. As a result ocean water at equatorial line is hotter as compared to near the poles. This water being hotter remains on the surface and flows towards polar regions. The heat that flows in such a way is called hot water current. Just opposite to it, the water around the poles is heavy due to its coldness. It flows from poles to equatorial circle. These type of currents are called cold water current.
Question 5.
Why is the handle of cooking utensils made with ebonite or wood? Give reason.
Answer:
Handies of cooking utensiles are made up of wood or ebonite. It is because during cooking utensils made of metal become hot and can not be handled. Since ebonite or wood are bad conductor of heat, do not become hot, and we can hold them easily. So, the handles of cooking utensils are made with ebonite or wood.
Question 6.
With the help of a diagram, explain heat conduction procedure.
Answer:
We take a broken spoke of a bicycle or thin iron wire and fix some small pieces of wax on it at an equal distance. Now we put one end of the wire on a table and put a brick or stone over it as shown in figure below. Now we heat other end of wire by a burning candle. We see on heating piece of wax near the candle melts and drops first and then next and so, on. On heating one end of wire heat is transferred to other cooler end. This method of transmission of heat is called conduction. In solid, transfer of heat takes place by conduction.
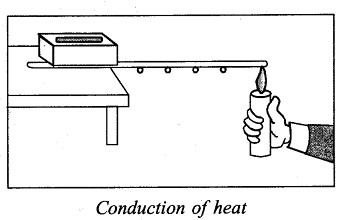
Question 7.
How are we protected in winter by wearing woollen clothes. State the reason.
Answer:
Air is bad conductor of heat. Air gets trapped in the small holes present in woollen clothes. Wool and air both being bad conductor of heat does not allow body heat to go out and thus we are protected from cold in winter.
Practical Work
Question 1.
Take same sized pots and fill it with same amount of water, oil, sand and salt etc. for similar time period in sun. Measure the temperature of each and tell which one becomes rapidly hot and why?
Answer:
When same amount of water, oil, sand and salt are placed in equal sized pots and then are placed in sunlight, it is observed that salt becomes heated first and then sand, water and oil respectively.
Question 2.
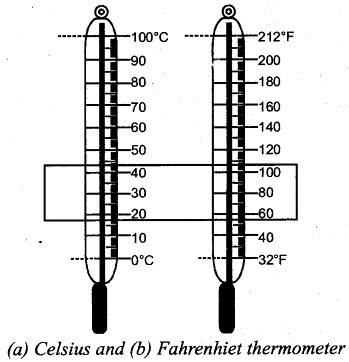
Make a chart of thermometers having Fahrenhiet and Celsius scales and display it Fahrenhiet.
Answer:
Display the following fig. I of Celsius and Fahrenhiet thermometers on a drawing sheet.
Question 3.
With the help of a thermometer find out the melting point of ice and boiling point of milk.
Answer:
The process of changing of a solid into liquid on heating is called melting. The temperature at which a soild completely changes into liquid state is called its melting point.
To find melting point of ice: We heat ice filled beaker kept on a tripod stand by sprit lamp. When ice is completely changed into water we measure its temperature by thermometers and note it. This temperature is called melting point of ice. We find that the melting point of ice is 0°C. When any liquid is heated, it boils and this process is called boiling and the temperature at which a liquid starts boiling is called its boiling point.
To find the boiling point of milk: We take milk in a beaker and heat it by sprit lamp on a tripod stand. When milk starts boiling, we measure the temperature of milk by thermometer. The temperature at which milk starts boiling is called boiling point of milk.
Question 4.
Measure the temperature of normal water and sugar containing water and compare them.
Answer:
We take normal water in one beaker and sugar mixed water in another beaker and heat them by sprit lamp on tripod stand separately. When normal water and sugar mixed water starts boiling we note temperature separately and find that the boiling point of normal water is 100° C while that of sup r mixed water is more than 100° C. It depends on the amount of sugar dissolved in water.
InText Questions
Question 1.
We come across a number of objects everyday. Some of them are hot and some others are cold. List the names of some object. Mark these as hot or cold in the table given below. (Page-146)
Answer:
| S. No. | Name of Object | Hot or Cold |
| 1. | Ice | Cold |
| 2. | Icecream | Cold |
| 3. | Cold Drink | Cold |
| 4. | Boiling Water | Hot |
| 5. | Boiling Oil | Hot |
Activities
Activity-1 (Page-146)
Question 1.
What do you feel ?
Answer:
When both the hands are dipped in pot B containing normal water, left hand feels it hot while right hands feel it cool.
Question 2.
Whether the water in pot ‘B’ is hot or cold?
Answer:
We are not able to decide whether water in pot B is hot or cold. Because at the same point of time our one hand feels it cool and other feels it hot.
Question 3.
What does the experiment performed in this activity shows (Proves)?
Answer:
This experiment shows that our sense of touch is not reliable to decide about the hotness or coldness of an object.
Question 4.
How do we know, how much hot an object really is?
Answer:
By measuring the temperature of an object by thermometer, we can find how hot an object is really.
Question 5.
What is temperature ?
Answer:
The property of hotness or coldness of an object as compared to other objects is called temperature.
Activity-2 (Page-147)
Question 1.
Observe carefully laboratory thermometer and fill the maximum and minimum values/ temperature printed on it?
Answer:
On the laboratory thermometer, the maximum value printed is 110°C and the lowest value is -10°C Usually a laboratory thermometer has -10° C to 110° C mark on it. It is called the range of thermomter.
Question 2.
How is temperature measured by thermometer?
Answer:
Dip the bulb of thermometer in a liquid and wait till the level of mercury become stable. Note this reading. It is the temperature of that liquid. Let us do and observe Dip the bulb of thermometer in the three pots A, B and C (filled with water) respectively. In activity-1 and wait, till the level of mercury becomes stable.
Conclusion: We observe that the temperature of pot C is the maximum, temperature of water in Pot B is less than of C, while the temperature of water in pot A is the minimum (below 0°C).
Activity-3 (Page-148)
Question 1.
What is body temperature of a healthy person?
Answer:
Usually, the body temperature of a healthy person is 37° C.
Question 2.
Clinical thermometer is washed with an antiseptic solution before, it is used, why ?
Answer:
To make clinical thermometer free of any sort of infections, it is washed with antiseptic solution, before it is used.
Question 3.
Clinical thermometer is given a strong jerk every time before measuring temperature, Why?
Answer:
To bring down the mercury level to its low position a jerk is given to thermometer every time.
Activity-4 (Page-150)
Question 1.
What is the difference in temperature of both water ?
Answer:
The temperature of normal water has increased while the temperature of boiled water has decreased.
Question 2.
What conclusion do you draw from above experiment?
Answer:
From the above experiment we conclude that heat flows from a body of higher temperature to a body of lower temperature.
Question 3.
What change you noticed in the temperature of hot and cold water? ‘
Answer:
The temperature of hot water has decreased and that of cold water has increased.
Question 4.
Why does the temperature of both the containers become equal at the end of experiment?
Answer:
The exchange of heat between hot and cold water containers till the tempertaure of both become equal. Therefore, at the end of experiment temperature of both the containers becomes equal.
Activity-5 (Page-151)
Question 1.
What happens if other end of spoke or wire is heated by burning candle?
Answer:
Wax pasted on wire starts melting.
Question 2.
Which piece of wax melts first and fell down?
Answer:
The piece of wax close to burning candle falls first.
Question 3.
What is the transfer of heat in solids called?
Answer:
Transfer of heat in solids is called conduction.
Activity-6 (Page-151)
Question 1.
Upper end of which of the object has become hot?
Answer:
Heat is easily transferred in the objects made of aluminium, steel spoon, iron wire, Therefore, upper end of these things have become hot.
Question 2.
What are good conductors of heat?
Answer:
Those substances in which heat is transferred easily are called good conductors of heat.
Question 3.
Plastic and wood on heating become less hot. Give reason why?
Answer:
Materials like plastic and wood are bad conductor of heat therefore, on heating, heat is not transferred. So they become less hot.
Question 4.
Cooking utensils are made of metals and their handles are covered by materials like wood or ebonite why?
Answer:
Metals are good conductors of heat, food is cooked easily in the utensils made from metals. Therefore cooking utensils are made of metals which are conductor of heat, so handles of cookwares are covered with ebonite or wood to protect our hands from burning.
Question 5.
Stainless steel pots has a copper base why?
Answer:
Copper is the best conductor of heat. Therefore, to cook food quickly a layer of copper is pasted at the bottom of pans made of steel.
Question 6.
During summers, why is it less troublesome to walk bare foot on mat or carpets as covering of heated floor?
Answer:
Mats and carpets are bad conductor or insulator of heat, They do not absorb heat from heated floor. Therefore, it is less troublesome to walk on them during summer.
Activity-7 (Page-152)
Question 1.
Why does colourful current set up in water?
Answer:
When bottom of the pot is heated the water molecules at the bottom gain heat and move up with coloured water and the colder molecules at the top move down. This is repeated so long water is heated. As a result colourful currents form set.
Question 2.
What is called this method of transfer of heat?
Answer:
This method of transfer of heat is called convection.
Question 3.
How is heat transferred in convection method?
Answer:
In convection method the molecules of liquid move itself to transfer heat from one place to another.
Question 4.
By which methods heat is transferred in air?
Answer:
In air heat is transferred by convection method.
Other Important Questions
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
Conductivity of heat is more in:
(a) Wood
(b) Iron
(c) Copper
(d) Soil
Answer:
(c) Copper
Question 2.
Heat is transferred with faster speed in:
(a) Conduction
(b) Convection
(c) Radiation
(d) By its own
Answer:
(c) Radiation
Question 3.
Heat reaches from the sun to the earth:
(a) By conduction
(b) By convection
(c) By radiation
(d) By conduction and convection’s
Answer:
(c) By radiation
Question 4.
Bad conductor of heat is:
(a) Iron
(b) Copper
(c) Aluminium
(d) Ebonite
Answer:
(d) Ebonite
Question 5.
By which method, heat is transferred in air?
(a) By conduction
(b) By convection
(c) By radiation
(d) By conduction and convection
Answer:
(b) By convection
Fill in the blanks :
1. In weather reports…………. thermometer is used.
2. Exchange of heat between two objects take place till their temperature becomes…………
3. The transfer of heat in solid takes place by ……..methods.
4. In liquid and gas transferred heat takes place by……….. methods.
Answer:
- maximum-minimum
- equal
- conduction
- convection
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is temperature?
Answer:
The degree of hotness or coldness of an object as compared to other objects is called temperature.
Question 2.
Which device (instrument) is used to find temperature of an object?
Answer:
Temperature is measured by thermometer.
Question 3.
Which thermometer is used to measure the temperature of human body.
Ans:
Temperature of human body is measured by clinical thermometer.
Question 4.
What is the average temperature of human body?
Answer:
Average temperature of human body is 37°C or 98.6F.
Question 5.
What precautions should be taken while using thermometer?
Answer:
Thermometer bulb should not be kept over flame or near flame or in sunlight of longer time otherwise it may break or blast.
Question 6.
By which method heat is transferred in solids?
Answer:
In solids heat is transferred by conduction method.
Question 7.
By which method heat is transferred in liquids and solids?
Answer:
In liquid and solids heat is transferred by convection method.
Question 8.
By which method heat from the sun reaches to the earth?
Answer:
From sun to the earth heat reaches by the method of radiation.
Question 9.
In which method of heat transfer, medium is not necessary?
Answer:
In radiation method, medium is not necessary.
Question 10.
Why do woollen garments protect us from cold?
Answer:
Air tod woollen clothes are bad conductor of heat. Thus they protect us from cold.
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
What is thermometer? How many types of thermometers are there?
Answer:
Temperature of an object is measure by device which is called thermometer. Thermometers are of different types. They are: Laboratory thermometer, Gas thermometer, Alcohol thermometer and Digital thermometer etc.
Question 2.
Use of digital thermometer is more safe why?
Answer:
Mercury is a poisonous (Toxic) material, if the mercury thermometer breaks, Mercury will be scattered here and the item is their. If mercury Ms on some food item and consumed mistakenly, it will cause great harm to the body. Therefore, now a days use of digital thermometer is more common in place of mercury thermometer.
Question 3.
How long exchange of heat between two objects takes place?
Answer:
Exchange of heat between two objects takes place till, the temperature of both of the object becomes and remains equal. In other words, the exchange of heat between a hot body and a cold body will occur till, the temperature of both of the bodies become same.
Question 4.
What is importance of ventilation in the homes? .
Answer:
The air that we exhale (breath’out) is warmer and has low density as compared to the normal air. The warmer and lighter (low density) air rises up towards ventilations near roofs and escapeds and fresh air is filled in the room, through doors and windows because fresh air is heavy with higher density.
Question 5.
How do air blow?
Answer:
Air blows from an area of a higher air pressure towards an area of lower air pressure. This flow of air from one place to another is called wind. When at any place the earth becomes heated more, then air becomes hot and rises up and expands. As a result air pressure of that area becomes low. So air from near by cooler (high air pressure) region flows towards hotter (low air pressure) region, That is how air blows from an area of higher air pressure to an area of lower air pressure.
Question 6.
What do you mean by sea breeze and land breeze?
Answer:
During the day, the land because heated up more than the sea water. The cool air from the sea blows towards the land. It is called sea breeze. On the other hand, at night land becomes cooled fast, so the air from land blows towards the sea, this is called land breeze.
Question 7.
Days are very hot and nights are cold in deserts. Why?
Answer:
Sand is the best absorber of heat as well as it also releases heat very fast (a best releaser of heat) during days, sand absorbs more heat therefore, days are very hot and at night sand releases heat easily, so, night are cold in desert. Therefore, in desert days are hot and nights are cold.
Question 8.
Why is it comfortable to wear white clothes in summer and coloured clothes in winter?
Answer:
White clothes reflect maximum heat that incident on them and only a small part of heat is absorbed by white clothes, making us to feel comfortable in summer.
On the other hand, coloured (deep coloured/ black) clothes absorbs maximum heat that incidents on them and only a small part of heat is reflected, which makes us feel warm during the winter.
Question 9.
Why the cloudy nights are warmer than the night with clear sky?
Answer:
During the day the earth becomes hot due to radiation from the sun and the heat from the earth goes in the space so, the temperature of the earth is reduced. But if the sky is cloudy, the heat radiated by the earth at night is reflected back on the earth which increase the temperature of the environment. That is why clear sky nights are cool as compare to cloudy nights.
Question 10.
Mountains are cooler even in summer. Why?
Answer:
The surface of mountains is not plane and most parts of the mountain remain covered with shadows, also Sun’s radiation incidents in an inclined manner. As a result sun rays spread over a larger area,. The solar radiation that incidents per unit area is very less. Therefore, the mountain surface becomes least heated. So, mountains remain cooler even in summer.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by transmission of heat? Describe different methods of heat transmission.
Answer:
When objects having different temperature are placed in contact to each other, then transmission of heat takes place from the object with higher temperature towards the object having lower temperature. This flow of heat due to temperature difference is called transmission of heat.
Methods of Heat Transmission
There are three methods of transmission of heat:
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
1. Conduction: The method of transmission of heat in which heat is transferred from one atom to the next atom. The atoms do not leave their place is called conduction of heat.
For Example: Transmission of heat in metals and mercury takes place through conduction.
2. Convection : Convection is that method of heat transmission in which the particles of medium (molecules) receive heat and move towards the place of lower temperature and other particles from colder place move to take their place.
For Example: Transmission of heat in liquids and gases takes place through convection.
3. Radiation: The method of heat transmission in which heat is transferred from a body of high temperature to a body of lower temperature with out affecting the medium is called radiation. Radiation do not need any medium like solid, liquid or gas for transmission.
Question 2.
What are the uses of convection method of heat transmission?
Answer:
Uses of Convection:
1. Ventilation: The air that we breath out is warmer and has lower density as compared to normal air and it expands. Being warmer it rises forward ventilation near the roof and escapes out and fresh air. Fresh air is heavier because of more density enters the room throw windows and doors.
2. Chimneys: The smoke produced in homes and factories are hotter and lighter. Then normal air. Such hot and light air rises up and removes out through chimney.
3. Oceanic Currents: Around the equatorial lines, the sun rays fall directly as Compared to poles. Therefore, water is hotter in ocean near equator as compared to the poles. This heat from surface moves towards the poles. The hot water that flows in such way is called hot water current. Opposite to it, the water around the poles is heavier due to coldness. It flows from poles to equatorial circle. This type of current is called cold water current.
4. Airflow: Air flows from a region of higher pressure to a region of lower air pressure. When a place becomes very hot, the air of that place becomes lighter and rises up and creates vacuum. To occupy this vacuum place air from the high air pressure areas rushes towards, Thus air flows from a colder place to a hotter place. This flow of air is called wind.
5. Sea breeze: During the day, the land becomes heated up more than sea water. The cooler air from the sea blows towards the land. It is called sea breeze. But at night the land becomes colder fast. The cool air from land blows towards the sea side. This is called the land breeze. In summer during monsoon moisture laden air blows from the ocean for the same reason and rain fall occurs.
Question 3.
Which activities take place when heat radiation falls on any object?
Answer:
The following activities occur when heat radiation falls on an object.
1. Reflection: When radiated heat incidents on an object, a part of heat is reflected back. This is called reflection of heat. Polished surface/shiny surfaced materials like metals are good reflector of heat.
2. Absorption: Apart of radiant heat is absorbed by the object. As a result, the object become hotter and its temperature is increased. Because of this reason we feel hot when we go out in summer. To protect ourselves from heat we use umbrella or take shelter of shadows. Black coloured or deep coloured clothes absorb more heat as compared to white Coloured objects.
3. Transmission: When radiation falls on an object, a part of heat is also transmitted along with reflection and absorption.
We hope the given RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Temperature and Heat will help you. If you have any query regarding Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Temperature and Heat, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.