RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Physical and Chemical Changes of Substances are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science. Here we have given Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Physical and Chemical Changes of Substances.
| Board | RBSE |
| Textbook | SIERT, Rajasthan |
| Class | Class 7 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 4 |
| Chapter Name | Physical and Chemical Changes of Substances |
| Number of Questions Solved | 44 |
| Category | RBSE Solutions |
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Physical and Chemical Changes of Substances
Textbook Exercise
Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct option:
Question 1.
Example of physical change is?
(a) rusting
(b) melting of ice
(c) formation of curd
(d) browning of apple after cutting
Answer:
(b) melting of ice
Question 2.
Example of chemical change is?
(a) lightening of bulb
(b) milky change of lime water
(c) water changes into water vapour
(d) melting of ghee
Answer:
(b) milky change of lime water
Question 3.
Why are doors painted in our house?
(a) to protect from sun rays
(b) to make it dust proof
(c) to prevent from rusting
(d) to protect from birds
Answer:
(c) to prevent from rusting
Question 4.
The chemical formula of rust is?
(a) Fe2O3
(b) Fe
(c) FeO
(d) FeSO4
Answer:
(a) Fe2O3
Fill in the blanks:
1. To make solution of sugar is a ………… change.
2. Generally physical changes are ……… .
3. Conversion of wheat grains into wheat flour is a ……….. change.
4. When carbon dioxide is passed in lime water, it turns milky. This is a …………. change.
Answers:
1. Physical
2. Temporary
3. Chemical
4. Chemical
Match the Columns
| Column – 1 | Column – 2 |
| 1. Lightening of bulb | (a) chemical change |
| 2. Rusting | (b) physical change |
| 3. Getting crystals from alum | (c) crystallisation |
Answer:
1. (b)
2. (a)
3. (c)
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write the reaction of oxygen with magnesium.
Answer:
Magnesium burns in oxygen to give magnesium oxide.
2Mg +O2 → 2MgO
Magnesium oxygen magnesium oxide
Question 2.
What is crystallisation?
Answer:
Crystallisation is a process that separates a pure solid in the form of its crystals from a solution. The crystallisation method is used to purify solids. Crystallisation is an example of physical change
Question 3.
Which factors are responsible for rusting?
Answer:
Two factors are responsible for rusting:
- Moisture
- Air
Question 4.
What will be the colour of product after reaction of starch and Iodine?
Answer:
The colour of product after reaction of starch and Iodine is Violet.
Question 5.
What kind of change tearing of paper is?
Answer:
Tearing of paper is a physical change.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the chemical change and physical change with proper Example.
Answer:
Physical Change: Properties like size, shape, state (solid, liquid or gas), temperature, pressure etc., are physical properties. Those changes in which only physical properties of a substance changes are called physical changes. For example, lightening of bulb is a physical change.
Chemical Change: The change in which new substance is formed and chemical composition of a substance is changed is called a chemical change. A substance loses its identity in a chemical change and cannot be get back into its original form. For example, burning of candle, formation of curd etc.
Question 2.
Explain crystallisation with the help of labelled diagram.
Answer:
Crystallisation: A process that separates a pure solid in the form of its crystals from a solution is called crystallisation. No new substance is formed, only crystals of the substance are formed. Therefore, crystallisation is an example of physical change.
To obtain a big crystal, a small piece of alum is hanged in the solution of alum with the help of a thread. After sometime, we observe that piece of alum becomes bigger in size. This is due to the fact that small pieces of alum gets deposited on alum.
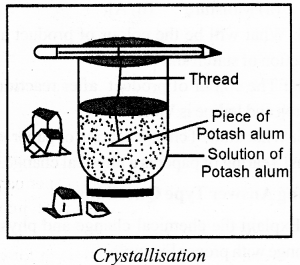
Question 3.
Explain the process of rusting and how could it be prevented?
Answer:
Rusting: If an iron piece is kept open for sometime, a brown layer is obtained on the surface of iron. This brown layer is rust and the process is called rusting. Rust is not iron but a new substance iron oxide is formed as a chemical reaction.
The process of rusting can be represented as:
Fe + O2(in air) + H2O → Fe3O3
Iron oxygen water Iron oxide
For rusting of iron, air and moisture are two important factors. Rust gradually destroys iron. As iron is used in structure of ships, cars, trucks, bicycle etc and in the formation of bridges and big buildings. Therefore, to prevent rusting, it is necessary to protect it from air and moisture both.
A simple solution to this is painting, oiling, greasing etc. Iron can be prevented from rusting by applying a layer of Chromium or zinc. To protect iron and steel from rusting, a layer of zinc is applied on it. This process is known as Galvanisation. Stainless steel is obtained by mixing carbon, manganese, nickel and chromium with iron. It is hard and resistant to rust.
Question 4.
Write down four examples of physical and chemical changes from our daily life.
Answer:
Examples of physical changes:
- Making of squash by mixing sugar in water.
- Making of salt powder by grinding solid piece of salt.
- Wetting of clothes.
- Freezing of water in freezer of refrigerator.
Examples of chemical change:
- Burning of candle.
- Making of curd from milk.
- Dissolution of lime in water for white washing.
- Formation of ash by burning of wood.
Intext Questions
Question 1.
Are all the changes taking place in substances permanent, temporary or reversible? (Page 35)
Answer:
All changes taking (Reversible) and Permanent (Irreversible).
Question 2.
Do you know how the baking soda is formed? (Page 39)
Answer:
Solvay process is used for this. Baking soda is also known as sodium bicarbonate. In this process carbon dioxide, water, amononia and brine solution in its concentrated form are used as raw materials.
Question 3.
Do you see the crystals of alum? (Page 39)
Answer:
Add alum powder to water and heat till it get dissolved completely in the solution. After some time we will see the crytals.
Activity
Activity 1: (Page 36)
Question 1.
What do you observe?
Answer:
Wax starts melting.
Remove the bowl from the flame and let it cool down.
Observation: After sometime we can see that wax again changes to solid on cooling.
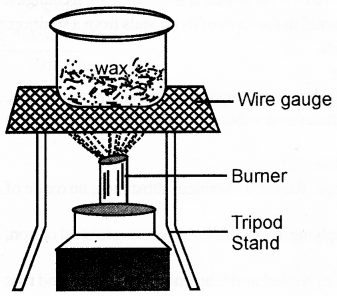
Melting of wax
Conclusion: We can say that melting of wax is a temporary change. Change from solid to liquid called state change.
Activity 2: (Page 36)
Question 1.
Can you solidify the water formed by melting of ice.
Answer:
Yes, water can be converted to ice again by keeping in freezer of refrigerator.
Activity 3: (Page 37)
Question 1.
Did the rubber change to its original from?
Answer:
Yes, Rubber gets back to its original form. Therefore, it is also a temporary change.
Activity 4: (Page 37)
Question 1.
Is it also a temporary change?
Answer:
Yes, it is also a temporary change.
Other Important Questions
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Temporary change is:
(a) burning of coal
(b) burning of candle
(c) glowing of bulb
(d) burning of kerosene
Answer:
(c) glowing of bulb
Question 2.
Permanent change is
(a) setting of curd
(b) melting of ghee
(c) freezing of water
(d) formation of vapour
Answer:
(a) setting of curd
Question 3.
Reversible change i s
(a) formation of vapour on heating of milk
(b) formation of butter from churning curd
(c) ripening of fruit
(d) falling of leaves from trees
Answer:
(a) formation of vapour on heating of milk
Question 4.
The piece of alum becomes bigger when another piece of alum is suspended in its solution. This process is known as:
(a) Ionisation
(b) Transformation
(c) Crystallisation
(d) Polymorphism
Answer:
(c) Crystallisation
Question 5.
Crystallisation is a
(a) Chemical change
(b) Physical change
(c) Irreversible change
(d) All the above
Answer:
(b) Physical change
Fill in the Blanks:
1. Conversion of liquid to vapour is a ………….. change.
2. Those changes in which physical properties of substances changes are called ……………… changes.
3. The changes taking place around us are generally of ……….. types.
4. The substances cannot get back into their original form in a …………… change.
Answer:
1. Physical
2. Physical
3. two
4. Chemical
Very Short Answer type Questions
Question 1.
Potato and Apple when kept in open for sometime after cutting becomes brown. Which type of change is it?
Answer:
Chemical change.
Question 2.
Water vapour, which type of change is this? Temporary or permanent.
Answer:
Temporary.
Question 3.
Define temporary change.
Answer:
The conversion of a substance from one state to another is called temporary change.
Question 4.
What are the physical properties of a substance?
Answer:
Size, shape, state, temperature, pressure etc., are physical properties of a substance.
Question 5.
Write an equation to represent a chemical change.
Answer:
2Mg + O → 2MgO
Question 6.
Write the name of new substance formed when magnesium is burnt in air.
Answer:
Magnesium oxide.
Question 7.
Write the formula of rust.
Answer:
Fe2O3
Question 8.
Write the components of stainless steel.
Answer:
Carbon, Manganese, Nickel, Chromium and iron.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write the examples of two physical and chemical changes seen by you.
Answer:
Physical Change:
- formation of ice
- hail from clouds
Chemical change:
- yellow stain of vegetable becomes red in contact with soap.
- Mehndi becomes red after drying.
Question 2.
Explain the change of state with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
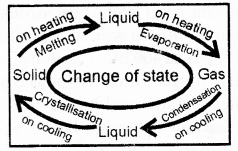
Question 3.
Explain reversible and irreversible changes giving examples.
Answer:
Those changes which are possible in reversible direction also are called reversible changes. Reversible changes are not permanent changes. Examples: conversion of water into ice and vice-versa. Those changes which are possible in forward direction only are called irreversible changes. These changes are permanent. For example: setting of curd, digestion of food etc.
Question 4.
Why crystallisation is called a physical change?
Answer:
In the process of crystallisation, no new substance is formed, only a bigger substance is obtained in its crystal form. For example, to obtain a big crystal, a small piece of alum is hanged in the solution of alum with the help of a thread. After sometime, we observe that piece of alum becomes bigger in size.This is due to the fact that small pieces of alum gets deposited on alum. In this chemical composition of alum is not changed. Therefore, it is a physical change.
Question 5.
Write two equation to represent a chemical change.
Answer:
- Wax + Oxygen → carbon dioxide + water vapour
- Lime water Ca(OH) + carbon dioxide (CO2) → milky water (CaCO3) new substance
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
The iron pillar of Mehrauli, Delhi is known as magic pillar. What is the reason of its not being rusted?
Answer:
In Delhi, near Qutub Minar in Mehrauli, an iron pillar is situated which is constructed by ironsmith around 400 BC. This iron pillar is 8 m high and its weight is 6 ton. The pillar is protected even after centuries and it is not rusted. This shows that our ancestors had developed a technique to prevent rusting.
Researches shows that a layer of iron oxide is present on its surface. They had mixed phosphorous at the time of its formation. It had been painted by mixture of different substances and was heated strongly. Apart from Delhi, Sun temple in Konark, Odissa; Mukambika temple in Kollur in Karnataka, Dhar in Madhya Pradesh etc., are also the examples of ancient metal work.
Question 2.
Explain the reason: Colour of apple changes when left open after cutting.
Answer:
Colour of apple changes when left open after cutting: Iron is present in apple. Iron present in apple changes to iron oxide after reacting with oxygen present in air. As a result, the colour of surface which is cut is changed to brown.
Question 3.
Write short note on:
- Fire in a glass of water (during magic shows).
- Formation of dense white fumes in a magic show.
Answer:
1. Fire in a glass of water during magic shows: In this magic, magician puts a sodium piece in the glass of water. Sodium reacts vigorously with water and form hydrogen gas. Heat is also released in this process.Fire is seen due to burning of hydrogen gas with the heat released.
Sodium + water → sodium hydroxide + hydrogen + heat
2. Formation of dense white fumes in a magic show: In this magic, magician had ammonium hydroxide solution in one glass and hydrochloric acid in another glass. When both the solutions are mixed, white fumes of ammonium chloride are formed deu to reaction.
Ammonium hydroxide + Hydrochloric acid → Ammonium chloride + water (white fumes)
We hope the RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Physical and Chemical Changes of Substances will help you. If you have any query regarding Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Physical and Chemical Changes of Substances, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.