RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Chapter 2 Atmosphere and Climate are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Social Science. Here we have given Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 7 Social Science Chapter 2 Atmosphere and Climate.
| Board | RBSE |
| Textbook | SIERT, Rajasthan |
| Class | Class 7 |
| Subject | Social Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 2 |
| Chapter Name | Atmosphere and Climate |
| Number of Questions Solved | 53 |
| Category | RBSE Solutions |
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 7 Social Science Chapter 2 Atmosphere and Climate
Exercise from text book
Question 1.
Choose the correct options.
(1) The name of hot zone cyclone in USA is:
(a) Hurricane
(b) Tornado
(c) Typhon
(d) Willy willies
Answer:
(a) Hurricane
(2) In which layer airplanes flies?
(a) Troposphere
(b) Ionosphere
(c) Stratosphere
d) Exosphere
Answer:
(c) Stratosphere
Question 2.
Fill in the Blanks :
(1) The amount of ………. gas is maximum in atmosphere.
(2) The ………. is the instrument for measuring velocity of wind.
(3) The radio waves are reflected back from …….. of atmosphere.
(4) ………….is the name given to hot air blowing in summer season in Rajasthan.
Answer:
1. Nitrogen
2. Anemometer
3. Ionosphere
4. Loo.
Question 3.
What is the difference in season and climate?
Answer:
The short duration state of atmosphere of a particular place is called season. On the other hand the long lasting weather conditions of a place is known as its climate. There is continuous change in weather conditions in a short duration however change in climate takes pace very slowly and its first-hand experience is not possible.
Question 4.
How many types of rain are there? Name them.
Answer:
Rain is of three types, namely : Convectional rain, C)rographic or mountain rain and Cyclonic rain.
Question 5.
Define wind and explain its types.
Answer:
The movement of air from high pressure to low pressure is called wind.
Winds are of following three types :
(1) Permanent winds : Those winds which flow in a fixed direction and in a fixed area are called permanent winds. They are of three types : Trade wands, westerly winds and polar winds.
(2) Seasonal winds or weather winds : Those winds which change their direction after a specific time of weather conditions are called seasonal along with weather winds. For example : Monsoon winds in India change their directions as per seasons. The land and sea breeze blowing in coastal regions are example of seasonal winds.
(3) Local winds : The winds which blow’ on a specific time of a day or of a year in small areas are called local winds. Loo (in Rajasthan), Chinook (Rocky mountains), Kohan and Mistral winds (in Europe) etc are main local winds.
Question 6.
Write difference between cyclone and anticyclone?
Answer:
Both cyclone and anticyclone are dependent on air. Their major differences are given below :
(1) The center of the cyclone has low air pressure and the air flows in a cyclone from the outer walls to the center while in an anti-cyclone the center has high air pressure and the wind blows from center to the outer walls.
(2) Normally cyclones are generations of the sea and make rainfall in the coastal areas, whereas anti cyclone have divergent wind blow due to which the areas where they blow’ are clear and dry.
(3) Cyclones are of two types Tropical cyclones and Temperate cyclones. The temperate cyclones move at slower pace due to which they are less harmful whereas tropical cyclones have a tremendous force and speed and are much more destructive than temperate cyclones. Anti cyclones move through mid latitudes with the help of tetragonal winds from west to east. They do not bear rains and the climate is clear.
Question 7.
Explain organization of atmosphere?
Answer:
The major constituents of atmosphere are
- Gases
- Water vapour
- Dust particles.
(1) Gases : Are major constituent of atmosphere. Some major gases are Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon and Carbon dioxide. Apart from these atmosphere also has Helium, Ozone, Hydrogen, Neon, Krypton and Methane. Nitrogen and Oxygen are the highest in Question uantity with 99% of total gases.
(2) Water Vapour : It is the second most important constituent of atmosphere found onlv in troposphere. Water vapour is responsible for rain, fog, frost and dew’ in the atmosphere.
(3) Dust Particles : The third important constituent of atmosphere are various dust particles. The rays are refracted through these dust particles. The blue sky, the red skv during sunset and sunrise is all due to dust particles present in the atmosphere. They play an important role in condensation.
Question 8.
Draw the diagram of layer of atmosphere and write the main significance of it.
Answer:
Based on temperature and distance the atmosphere is divided into 5 layers :
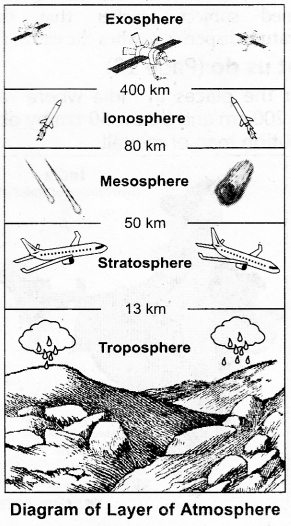
(1) Troposphere
(2) Stratosphere
(3) Meso-sphere
(4) Ionosphere
(5) Exosphere.
(1) Troposphere : This is the lowest layer of the atmosphere. Its average height is considered to be 13 km. Major part of heavy gases and water vapour is found in this layer. Weather phenomena such as rain, fog, frost, storm and hailstorm take place in this layer.
(2) Stratosphere : It extends above troposphere upto a height of 50 kms. It has clear skies so airplanes tend to fly in this layer. Ozone gas is found in the lower layer of stratosphere and blocks the harmful ultraviolet rays coming from the sun.
(3) Mesosphere : It spreads upto 80 kms above stratosphere. The comets and asteroids coming towards the earth are burnt in this layer.
(4) Ionosphere : It spreads from 80-400 kms above mesosphere. The radio signals relayed from earth are reflected back to earth from this layer.
(5) Exosphere : This is the outermost layer of the atmosphere. It comprises mainly of Hydrogen and Helium gases. Nothing much is known about this layer of atmosphere.
Activities from textbook
Let us do (Page 12)
Question 1
List the main gases and their percentage by observing the picture of atmosphere.
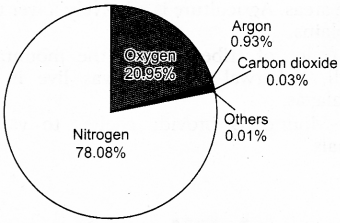
Answer:
The main gases in atmosphere and their amount in percentage is as follows :
| S.No | Main Gases | Amount (percentage %) |
| 1. | Nitrogen | 78.08 |
| 2. | Oxygen | 20.95 |
| 3. | Argon | 0.93 |
| 4. | Carbon dioxide | 0.03 |
| 5. | others | 0.01 |
Question 2.
Write a brief essay on importance of gases present in atmosphere.
Answer:
The main gases present in atmosphere are nitrogen, oxvgen, argon and carbon dioxide. Apart from these the other gases found in the atmosphere are helium, ozone, hvdrogen, krypton, methane, etc. Oxygen sustains life which is used by all living organisms for breathing. The carbon dioxide exhaled by organisms is used by plants and trees for making their food. This helps to maintain the stability of amount of gases present in atmosphere. Ozone gas laver protects us by absorbing harmful ultraviolet rays emitted by the sun.
Let us do (Page 13)
Question 1.
Name the layers of atmosphere.
Answer:
The layers of atmosphere are : Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Ionosphere, Exosphere.
Question 2.
Fill the following blanks.
| S.No | Name of the layer | Height | Main Importance |
| 1. | ………….. | ……….. | ……………. |
| 2. | …………. | ………. | ……………… |
| 3. | ………… | ……….. | ……………… |
| 4. | …………. | ………… | …………….. |
Answer:
| S.No | Name of the layer | Height | Main Importance |
| 1. | Troposphere | 13km | Weather activities, i.e., clouds, rainfall, storms, etc. occur in this layer. |
| 2. | Stratosphere | 13-50km | No seasonal activities occur. Aeroplanes fly in this region. Ozone layer is found here which protect the earth from ultraviolet rays. |
| 3. | Mesosphere | 50-80km | his layer burns up the meteors that enter the earth’s atmosphere. |
| 4. | Ionosphere | 80-400km | For communication, it is very important. The radio waves from earth are reflected back from this laver. |
Let us do (Page 14)
Note :
Try to understand taking help from concerned subject teacher that the high temperature disperses reaches the earth. (Page 14)
Let us do (Page 18)
Question
List the places in India where rainfall is above 200 cm and below 50 cm by observing distribution mao of rainfall.
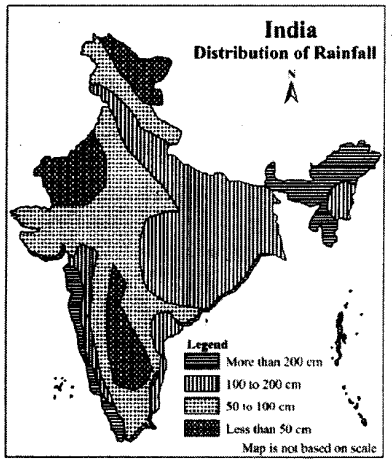
(i) Places with above 200 cm rainfall : Assam, Mizoram, Meghalaya, Manipur, Tripura, Arunachal Pradesh, Western Ghats (From south Gujarat to Kerala), etc.
(ii) Places with less than 50 cm rainfall : Western Rajasthan, Ladakh, Lahaul Spiti Valley interior Maharashtra, Telangana, Vidarbha, etc.
Let us do (Page 19)
Question 1.
Collect the data of temperature of your area from newspaper and study its change. Find out why the change in temperature occurs.
Answer:
After collecting temperature readings for one week from local newspaper it was found that each day temperature changes. Due to earth’s daily rotation and yearly revolution speed the change in temperature takes place.
Question 2.
With the help of your teachers or parents find out when the maximum rainfall occur in which region in your area and that season occur in which month of the year?
Answer:
In our region the maximum rainfall occurs in rainy season and this season is active from the month of June to September.
Other important questions
(A) Multiple Choice Question
Question 1.
Which gas is the primary cause of global warming?
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Oxygen
(c) Carbon-dioxide
(d) Argon
Answer:
(c) Carbon-dioxide
Question 2.
Water vapour is mainly found in :
(a) Troposphere
(b) Stratosphere
(c) Mesosphere
(d) Ionosphere
Answer:
(a) Troposphere
Question 3.
Which layer of atmosphere is called as Question uiet and calm layer?
(a) Troposphere
(b) Stratosphere
(c) Mesosphere
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Stratosphere
Question 4.
The ultraviolet rays are absorbed by:
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Oxygen
(c) Ozone
(d) Helium
Answer:
(c) Ozone
Question 5.
Following is an instrument to measure temperature:
(a) Barometer
(b) Thermometer
(c) Anemometer
(d) Compass
Answer:
(b) Thermometer
Question 6.
Snowfall in the form of rain occurs in :
(a) Hot deserts
(b) Poles
(c) Temperate regions
(d) EQuestion uatorial regions
Answer:
(b) Poles
Question 7.
In China and Japan tropical cyclones are called:
(a) Hurricane
(b) Williuiclie
(c) Tornado
(d) Typhon
Answer:
(d) Typhon
(B) Fill In the Blanks
Question 1.
Atmosphere is made up of a number of ……….. gases, and dust particles.
Question 2.
In the absence of dust particles ………. is not possible.
Question 3.
The short term environmental conditions of a specific place is called ……………
Question 4.
The earth derives energy from the sun during the day in the form of ………….
Answer:
1. water vapour
2. condensation
3. season,
4. short wave radiations.
(C) Very Short Answer Type Question
Question 1.
What is the main cause of global warming?
Answer:
The increase in carbon dioxide in atmos-phere is the main cause of global warming.
Question 2.
Describe the factors affecting the distribution of rains?
Answer:
Important factors are
- The direction of mountains
- Distance from the sea
- Form of earth surface
- Winds, etc.
Question 3.
What are wind vane and Anemometer?
Answer:
The instrument which points to the direction of the wind is called windvane and the instrument which measures the speed of the wind is called anemometer.
Question 4.
What is the cause of high temperature and humidity in the equatorial regions?
Answer:
The sun-rays fall directly and there is more rainfall in the equatorial region. This is the reason behind which are high temperatures and humidity in this region.
Question 5.
Which are India’s highest rainfall areas?
Answer:
Mawsynram and Cherapoonji in Meghalaya are the highest rainfall areas.
Question 6.
What is the rate at which temperature drops with increase in height in the troposphere?
Answer:
The temperature falls 1 °C for every 165 meter in the troposphere (on average).
Question 7.
Into how many types are cyclones divided?
Answer:
Cyclones are divided into two types :
- Cold zone cyclones and
- Hot zone cyclones.
Question 8.
Describe any 3 benefits of rainfall?
Answer:
(i) Rainfall is the onlv sourc e of ground water
(ii) Through rainfall the earth receives clean and clear water
(iii) For the existence of living creatures-plants and animals, rainfall is necessary.
Question 9.
What are the harmful effects of irregular rainfall?
Answer:
Irregular rainfall causes water scarcity drought and famines whereas excessive rainfall can lead to floods in the plains.
(D) Short Answer Type Question
Question 1.
What is the importance of dust particles in atmosphere?
Answer:
Dust particles cause dispersion of sunlight due to which the sky looks blue in colour. The red colour of sky during sunrise arid sunset and the rainbows are also created by dust particles. The clouds are formed when the small droplets of water accumulate around the tiny dust particles, and the condensation process is possible only because of dust particles.
Question 2.
How does moisture, get converted into rainwater?
Answer:
Water present in atmosphere as vapor. It is also knows as moisture or water vapour. As the temperature of atmosphere increases, its capacity to hold water vapour, also increases. The amount of humidity is more in air during rainy season. As the water vapor rises it gets cola and so water vapour holding capacity of air reduces and water vapour condenses into water droplets. Cloud is the group of these water droplets. When these droplets get big they come to the earth by gravitational force and fall on the earth as rain.
Question 3.
What is the structure of an anti-cyclone and its wind direction?
Answer:
There is high pressure at the centre of an anti-cyclone and tne pressure reduces in the outward direction.
In each anticyclone, winds flow from centre to outward direction and is clockwise in the northern hemisphere and anticlockwise/ counter-clockwise in the southern hemisphere.
Question 4.
What are the rules of radiation?
Answer:
Each object which is hot, emits radiations. As per the rule of radiation, the hotter objects will emit short waves and less hot objects will emit long waves. Therefore, radiation from sun is in the form of short waves and earth emits long wave radiations.
Question 5.
How do winds get their names?
Answer:
Winds’ names are based in their flowing direction. Winds are known by the name of direction from which they flow. For example, winds which blow from east are known as easterly winds and winds which blow from west are known as westerly winds. Winds which blow from mountain are known as mountain breeze and winds which blow from valley are known as valley breeze.
Question 6.
Name the regions which receive rainfall above 200 cm. and below 50 cm. in India.
Answer:
Regions in India which receive rainfall above 200 cm. are-Konkarn and Malabar coast in western ghats, Bihar, West Bengal, Assam, Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram Manipur and Tripura etc. and regions in southern foothills of the Himalayas.
Regions in India which receive rainfall below 50 cm. are-western Haryana, western Rajas-than, Raylaseema of Tamilnadu, Ladakh, etc.
Question 7.
How do sea and forest affect the climate?
Answer:
Sea has an intense impact on the climate of the coastal regions. The climate of coastal region is the same and moderate throughout the year. Due to high amount of evaporation from the sea, the coastal areas receive heavy rainfall. Similar to the evaporation from sea, process of transpiration occurs in plants and trees which results in heavy rainfall in area which has plenty of plants and trees. Along with this, the climate in these areas is even throughout the year. On the other hand areas where there is less amount of plants and trees, experience a very hot or cold climate.
(E) Long Answer Type Question
Question .1
What is air pressure? What are the factors which affect air pressure.
Answer:
The force exerted by all the layers of atmos¬phere on the unit area of earth’s surface is called air pressure. On earth surface 1 cm2 of area bears approximately 1 kg air pressure. Air pressure is measured in millibar (mb). Air pressure is measured by an instrument called barometer. Highest amount of air pressure is on Sea-level and air pressure reduces as we move higher.
The air in hotter regions of earth is lighter and thus it rises above which reduces the air pressure in these regions while the air in colder regions is heavy and it stays closer to the ground, therefore, there is high air pressure in these regions. The air pressure has greatest impact on the flow of wind. Winds always flow from high atmospheric pressure areas to low atmospheric pressure areas.
We hope the given RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Chapter 2 Atmosphere and Climate will help you. If you have any query regarding Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 7 Social Science Chapter 2 Atmosphere and Climate, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.