RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Comparison of Quantities In Text Exercise is part of RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Maths. Here we have given Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Comparison of Quantities In Text Exercise.
| Board | RBSE |
| Textbook | SIERT, Rajasthan |
| Class | Class 8 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 13 |
| Chapter Name | Comparison of Quantities |
| Exercise | In Text Exercise |
| Number of Questions | 8 |
| Category | RBSE Solutions |
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Comparison of Quantities In Text Exercise
Page No: 147
Question 1.
Rashmi and Rehana picked flowers in basket from garden. In which there were 30% rose, 10% jasmine and rest were marigold. If there were 120 flowers in basket then
(i) What was the number of marigold flowers?
(ii) What was the number of jasmine flowers?
(iii) By what percentage were rose flowers less than jasmine flowers?
Solution:
(i) Percentage of marigold flowers
= 100% – (30% + 10%)
= 100% – 40%
= 60%
No. of marigold flowers = 120 x \(\frac { 60 }{ 100 }\) = 72
(ii) No. of jasmine flowers = 120 x \(\frac { 10 }{ 100 }\) = 12
(iii) Percentage of Rose flowers = 30%
Number of Rose(RBSESolutions.com)flowers = \(\frac { 30 }{ 100 }\) x 120 = 36
Number of Jasmine flowers = 12
Difference of number of rose and marigold flowers = 72 – 12 = 60
Hence, rose flowers were less than jasmine flowers by = \(\frac { 60 }{ 72 }\) x 100
= 83.33%
Page No: 150
![]()
Question 2.
Reena obtained a bill of goods purchased from Khadi Bhandar. Looking at the bill answer the following questions.
| Aazad Khadi Bhandar | |||
| Bill No. 1501 Sir……….. |
Date 5-10-2015 | ||
| Goods/things | Quantities | Rate | Amount |
| 1. Bedsheets 2. kes 3. carpet Total |
4 4 2 . |
80 120 200 . |
320=00 480=00 400=00 1200=00 |
| Subsidy 15% | -180=00 1020=00 |
||
| Vat 10% | 102=00 | ||
| One thousand one hundred and twenty two only | 1122=00 | ||
| Errors and omission expected Signature | |||
What is the mark up price of goods purchased?
—Subsidy is calculated on which price?
—VAT is calculated(RBSESolutions.com)on which price?
Solution:
The total marked price of purchased items = Rs 1200
—Subsidy is given at marked price.
—VAT is taken on the selling price.
![]()
Question 3.
AS compared to Rs. 5000, Rs. 4000 are less by what percentage? Is that percentage similar to percentage by which Rs. 5000 are more than Rs. 4000?
Solution:
Let Rs 4,000 be the x% less than Rs 5,000. Then,
5,000 – (5,000 x \(\frac { x }{ 100 }\)) = 4,000
⇒ 5,000 x \(\frac { x }{ 100 }\) = 5,000 – 4,000
⇒ 50x = 1,000
⇒ \(x=\frac { 1000 }{ 50 }\)
⇒ x = 20
Hence Rs 4,000 is 20% less than the Rs 5,000.
Let Rs 5,000 be y% more as compared to 4,000. Then,
5,000 = 4,000 + 4,000 x \(\frac { y }{ 100 }\)
⇒ 5,000 – 4,000 = 40y
⇒ 1,000 = 40y
⇒ \(y=\frac { 1000 }{ 40 }\)
⇒ y = 25
Hence Rs 5,000 is 25% more as compared to Rs 4,000.
![]()
Question 4.
Bank Pass Book
| Date | Particulars | Credit | Debit | Balance |
| 1.4.13 | Cash | 2000 | – | 2000 |
| 1.4.14 | Interest | 140 | – | 2140 |
| 1.4.15 | Interest | 149.80 | – | 2289.80 |
From entry of passbook tell—
—Interest is added after what period?
—How much interest is added for the first period?
—How much interest is added for the second period?
—Whether amount of interest is same for every year?
Solution:
Interest is credited after 1 year.
—Rs 140 is credited in first year.
—Rs 149.80 interest(RBSESolutions.com)is credited in 2nd year.
—No, interest is not same in each year.
Page No: 157
![]()
Question 5.
Sandeep borrowed Rs. 3000 for 2 years at 8% annual compound interest rate from bank for establishing a biogas plant. If interest is accumulated annually then determine.
(i) What amount has to(RBSESolutions.com)be repaid with 8% annual compound interest rate?
(ii) How much Compound interest is there?
(iii) If this money was borrowed with simple interest then less or more interest was to be paid and how much?
Solution:
(i)
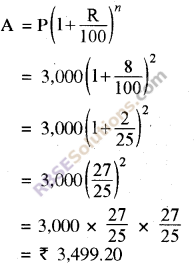
Hence, the amount to be paid is Rs 3,499.20.
(ii) Compound Interest = A – P
= 3,499.20 – 3,000
= Rs 499.20
(iii) Simple Interest
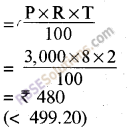
Therefore, if he borrowed money on simple interest, then he would pay Rs 19.20 less as compared to compound interest.
Page No: 158
![]()
Question 6.
Complete the following blanks given in the table.
| Condition of accumulation of interest | Time in Years | Annual Rate | Transformation Period | Transformed Rate |
| Annual | 2 | 10% | 2 | 10% |
| Half yearly | 1½ | 6% | — | 3% |
| Quarterly | 1¼ | 8% | 5 | — |
| Half yearly | 2 | 14% | 4 | — |
| Annual | 1 | 7% | — | — |
| Quarterly | 6 months | 16% | — | — |
Solution:
| Condition of accumulation of interest | Time in Years | Annual Rate | Transformation Period | Transformed Rate |
| Annual | 2 | 10% | 2 | 10% |
| Half yearly | 1½ | 6% | 3 | 3% |
| Quarterly | 1¼ | 8% | 5 | 2% |
| Half yearly | 2 | 14% | 4 | 7% |
| Annual | 1 | 7% | 1 | 7% |
| Quarterly | 6 months | 16% | 2 | 4% |
Page No: 163
Question 7.
Read following statements and find it is direct/inverse relation.
| Statement | Relation |
| 1. A ladder is slipping by the side of wall height of top of ladder from bottom and distance from bottom to top of wall | Inverse Relation |
| 2. Between distance and time of car moving with uniform velocity. | |
| 3. Between number of persons and sufficiency of(RBSESolutions.com)food material in days (when quantity of food material is constant) | |
| 4. Between water and tank and population of village (when amount of water and its distribution is same) |
Solution:
| Statement | Relation |
| 1. A ladder is slipping by the side of wall height of top of ladder from bottom and distance from bottom to top of wall | Inverse Relation |
| 2. Between distance and time of car moving with uniform velocity. | Direct Relation |
| 3. Between number of persons and sufficiency of(RBSESolutions.com)food material in days (when quantity of food material is constant) | Inverse Relation |
| 4. Between water and tank and population of village (when amount of water and its distribution is same) | Inverse Relation |
![]()
Question 8.
Think about such examples about direct and inverse relationship and discuss them with friends.
Solution:
Examples of direct relation –
- Length of cloth and total price
- No. of months and total salary
- No. of hours of production and quantity of production.
Examples of Inverse Relation
- No. of periods in a school and time of periods.
- No. of workers and no. of hours to complete a work.
- No. of production(RBSESolutions.com)machines and no. of necessary days to complete a production
We hope the given RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Comparison of Quantities In Text Exercise will help you. If you have any query regarding Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Comparison of Quantities In Text Exercise, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.