RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Blood Circulation are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science. Here we have given RBSE Rajasthan Board Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Blood Circulation.
Rajasthan Board Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Blood Circulation
| Board | RBSE |
| Class | Class 8 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 7 |
| Chapter Name | Blood Circulation |
| Number of Questions Solved | 50 |
| Category | RBSE Solutions |
Blood Circulation Textbook Questions Solved
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
- Amount of water in the blood plasma is about:
(a) 70%
(b) 90%
(c) 10%
(d) 45% - Red blood corpuscles are also known as:
(a) RBC
(b) WBC
(c) Platelets
(d) Pulse - Which of the following causes red colour of the blood?
(a) filerin
(b) antigen
(c) haemoglobin
(d) platelets - How many times does the heart of an adult man beats?
(a) 50 times
(b) 72 times
(c) 110 times
(d) 120
Answers:
- (b)
- (a)
- (c)
- (b)
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- …………….kills the bacteria that enters into the body.
- There are……………groups of blood.
- Impure blood is brought back to the heart by……………
- Blood containing carbon dioxide is purified in the ……………
Answers:
- WBC
- four
- veins
- lungs
Blood Circulation Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the corpuscles that clots the blood.
Answer:
Thrombocyte.
Question 2.
What keeps the blood in liquid form?
Answer:
Plasma.
Question 3.
How many chambers are there in the heart?
Answer:
Four.
Question 4.
How many types of antigens are there?
Answer:
Two.
Blood Circulation Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the various blood vessels.
Answer:
- Artery
- Veins
- Capillaries
- Arterioles
- Venules
Question 2.
How many types of blood corpuscles are there? Name them.
Answer:
There are three types of blood corpuscles they are:
- RBC or erythrocytes.
- WBC or leucocytes.
- Thrombocytes or platelets.
Question 3.
Why are white blood cells called the soldiers of body?
Answer:
WBC are called the soldiers of our body because they protect our body from disease viruses and bacteria.
Question 4.
Write the functions of blood.
Answer:
Function of blood:
- It carries O2 and CO2 in our body.
- Nutrient and waste product are carried by it.
- It protects our body from disease from foreign viruses and bacterias.
- If body gets injured it stop bleeding by making blood clots.
- Carries antigens and antibodies.
- Maintain the body temperature.
Question 5.
What will happen if clot is not formed on injury?
Answer:
If there were no platelets in the blood, then in case of an injury, bleeding will not stop as blood clot will not be formed. It will result in death due to heavy loss of blood from body.
7 Blood Circulation Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the structure of heart with diagram.
Answer:
The heart is a hollow muscular organ in the middle of the chest that pumps blood around the body supplying cells with oxygen and nutrients. It does pumping without break. Its size is like our fist. It is divided into four chambers, to avoid mixing of O2 and CO2 mixed blood, the upper two part are called auricles and lower two ventricle. A muscular wall, called the septum divides the heart lengthwise into left and right.
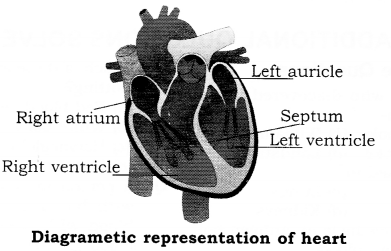
A valve divides each side into two chambers-an upper atrium and a lower ventricle. When the heart muscles contract it squeezes blood through the atria and through the ventricles. Oxygenated blood from the lungs flows from the pulmonary veins into the left atrium, through the left ventricles and then out via the aorta to all parts of the body. Deoxygenated blood returning from the body flows from the vena cava into the right atrium through the right ventricle and then out via the Pulmonary artery to the lungs for reoxygenation. At the rest heart beats between 60 – 80 times a minute. During exercise or a time of stress or excitement the rate may increase to 200 beats a minute contraction and expansion of heart is called heart beats or pulse. Doctors by counting these beats of heart or pulse presumes the status of health.
Question 2.
Write a short note on
(a) Blood group
(b) Blood bank
Answer:
(a) Blood group:
On the basis of the presence of antigens and antibodies Karl Landstiener had divided the human blood into four groups -A, B, AB, and O.
Human blood groups:
| S.NO | Blood group | Antigen | Antibody |
| 1. | A | A | b |
| 2. | B | B | a |
| 3. | AB | A and B | None |
| 4. | O | none | a and b |
Importance of blood group: Due to the knowledge of blood group blood donation has been proved as a boon for the society. By this if the blood is required for the accidental victims and sick persons then blood of appropriate group could be made available by the blood banks or registered voluntary blood donors easily. They are important in the field of law and justice. By taking samples and tests of DNA, culprits could be caught. Deficiency of blood in the body is fulfilled by blood donation and given that blood to person who has deficiency.
(b) Blood Bank:
As far as possible blood should be taken from relatives but if it is not possible then blood could be receive from blood bank opened by government. In government, hospital of every district or private blood bank run by social service institution. To preserve blood in the blood bank, sodium citrate is mixed. It can be preserved for 30 days in blood banks.
Blood Circulation Additional Questions Solved
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1 .
The scientist who discovered blood transportation:
(a) Leuvan Hooke
(b) William Harvey
(c) Robert Hooke
(d) Landstiener
Question 2.
Blood is purified in:
(a) Heart
(b) Lungs
(c) Liver
(d) Kidneys
Question 3.
One of the following is an antigen not found in human blood
(a) A
(b) B
(c) Rh
(d) O
Question 4.
The person who is a universal donor with blood group-
(a) A
(b) B
(c) AB
(d) O
Question 5.
Which of these is responsible for blood clotting?
(a) Red blood cells
(b) White blood cells
(c) Haemoglobin
(d) Platelets
Question 6.
A person injured in a road accident, with blood group ‘O’ can be given blood with, which of the following blood group:
(a) from ‘A’ and ‘O’
(b) from ‘B’ and ‘O’
(c) from ‘AB’ and ‘O’
(d) only from ‘O’
Question 7.
The thinnest blood vessels in the human body are
(a) arteries
(b) veins
(c) capillaries
(d) any of these
Question 8.
Veins can be differentiated from arteries because the veins
(a) have valves
(b) have hard walls
(c) have pure blood in them
(d) have thick walls
Question 9.
When you feel your pulse, what you actually feel is blood rushing through the-
(a) arteries
(b) veins
(c) capillaries
(d) all of these
Question 10.
Blood cells that protect the body from diseases-
(a) RBCs
(b) WBCs
(c) Blood platelets
(d) all of these
Question 11.
The device used to hear the heartbeat is called
(a) thermometer
(b) stethoscope
(c) sphygmomanometer
(d) microscope
Question 12 .
The deficiency of haemoglobin causes
(a) blood cancer
(b) anaemia
(c) weakness
(d) flow blood
Question 13.
Human heart beats in a minute:
(a) 60 times
(b) 62 times
(c) 70 times
(d) 92 times
Question 14.
Blood carries
(a) oxygen
(b) food
(c) waste
(d) all of these
Question 15.
RBC’s are WBC’s in size:
(a) larger than
(b) smaller than
(c) equal to
(d) some time larger, sometime smaller
Answers:
1. (b)
2. (b)
3. (d)
4. (d)
5. (d)
6. (d)
7. (e)
8. (a)
9. (a)
10. (b)
11. (b)
12. (b)
13. (e)
14. (d)
15. (b)
Blood Circulation Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which scientist is given the credit of discovering blood groups?
Answer:
Scientist name Karl Landsteiner discovered blood group.
Question 2.
Name the blood group in which antibodies are absent.
Answer:
Blood group AB.
Question 3.
Name the ‘universal recipient’ and ‘universal donor’ blood groups.
Answer:
Universal recipient – blood group AB
Universal donor – blood group O.
Question 4.
Where are antigens and antibodies found in blood?
Answer:
Antigens are present in red blood corpucles while antibodies are found in blood serum.
Question 5.
What is the function of blood platelets?
Answer:
The main function of blood platelets is to help in clotting of blood. It control the blood flow during any injury.
Question 6.
Name the doctor who invented stethoscope?
Answer:
In 1816 doctor named R. Laennec in France invented stethoscope.
Question 7.
Name the diseases caused by blood infection?
Answer:
Blood infection cause diseases like AIDS, anaemia, polycythemia, hepatitis etc.
Question 8.
Define pulse rate.
Answer:
The number of heart beats per minute is called pulse rate.
Question 9.
Write the main function of arteries and veins.
Answer:
Arteries take the blood away from the heart and veins bring the blood back to the heart.
Question 10.
What is heart beat?
Answer:
Contraction of auricles and ventricles makes a sound called heart beat.
Blood Circulation Solutions Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define blood transfusion.
Answer:
Blood transfusion is a process in which blood is given to an injured person who need blood immediately due to excessive blood loss. It is used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of blood. Before a recipient receives transfusion compatibility testing between donor and recipient blood must be done.
Question 2.
Why is blood necessary to all the parts of body?
Answer:
Blood is needed by all the parts because it contains nutrients of food and oxygen in it. It supplies the oxygen and nutrients, food to various parts of the body to provide essential energy which help the body to perform various functions.
Question 3.
Write the main function of platelets.
Answer:
Platelets play an important role in the clotting of blood by blocking the flow of blood in case of any injury. They are small and irregular cells.
Question 4.
How does oxygenated and deoxygenated blood not mixed together in heart?
Answer:
There is no mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in the heart because of a partition called septum. This partition completely separates the left and the right side of the heart. The heart has a number of valves that allow blood to flow in one direction only.
Question 5.
What is the relationship between the rate of heartbeat and pulse rate?
Answer:
Each time the ventricles in the heart contract, a pulse or wave effect is felt due to expansion. The artery expands to accommodate the pressurized blood pumped into it. It recoils immediately as the pressure eases. Since the pulse is a result of ventricular contraction, the rate of pulse is exactly the same as the heart beat.
Question 6.
What are the criteria for donating blood?
Answer:
- 18 years to 60 years.
- weight above than 45 kg.
- not suffering from the serious diseases like Hepatitis B or C, Syphilis, Malaria or any other such disease.
- not donate blood since last three month.
- not gone through a surgery in last six months.
- haemoglobin is more than 12.5.
- blood pressure is normal.
- body temperature is 37.50 and pulse rate is normal.
- not pregnant woman.
Question 6.
What precautions should be taken after blood donation?
Answer:
Precautions after blood donation:
- Take liquid substances like milk, juice etc. upto 24 hours after blood donation.
- Do not exercise and extra labour is avoided after blood donation up to 24 hours.
Question 7.
What is AIDS? Write its full form. By which test it can be detected?
Answer:
AIDS is an incurable syndrome.
Full form of AIDS is – Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome. AIDS can be detected by ELISA test.
Blood Circulation Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write the characteristics of each blood group. Prepare a table giving information about the suitable blood group to be given to patient, for successful blood transfusion.
Answer:
On the basis of the presence of antigens, Landsteiner classified blood into four groups which are called blood group ‘A’, “B’, ‘AB’ and ‘O’.
(a) Blood group A-People containing Blood group A possess antigen-A in their red blood corpuscles and antibody-b in their serum. The blood group of about 25% people in Bharat is “A”.
(b) Blood group B-People with blood group B possess antigen B in the red blood corpuscles and antibody a in their serum. About 35% people in Bharat have ‘B’ blood group.
(c) Blood group AB-People with this blood group possess both Antigen-A and Antigen-B in their red blood corpuscles but antibodies are absent in their blood serum, approximately 10% people in Bharat have ‘AB’ type of blood group. The capillaries join up to form the veins which carry the blood back to the heart.
(d) Blood group ‘O’-Both antigen A and antigen B are absent in the red blood corpuscles of people having blood group ‘O’ but both antibody-a and antibody-b are present in their serum. Because of the absence of any antigen, this blood group has been named as Zero group (O). Now a days, this is called as a “O” blood group. About 35% person in India have ‘O’ blood group.
| S.No | Blood group | Antigens present on RBC. (Ag) | Antibodies present in serum (Ab) |
| 1. | A | A | b |
| 2. | B | B | a |
| 3. | AB | A and B | None |
| 4. | O | None | a and b |
Can give blood to:
“A’ and ’ AB’
‘B’ and ‘AB’
Only ‘AB’
‘A’ ,’B’ , ‘AB’ and ‘ O ‘(all)
Can receive blood from:
A and O
B and O
‘A’ ,’B’ ,’AB’ and ‘O’ (all)
‘O’
Question 2.
Name the constituent of blood. Discuss the importance of each constituent.
Answer:
Blood is a highly specialised medium of transport consisting of blood cells suspended in a fluid medium called plasma. Blood is about 7% of the human body weight and an average adult has a blood volume of about 5 litres.
- Plasma: Plasma is a pale yellow- coloured liquid containing 92% water. The remaining 8% liquid is mostly proteins and small amounts of other dissolved materials. Plasma carries carbon dioxide, proteins, glucose, urea, minerals and hormones.
- Blood cells:
There are three tyes of blood cells:- Red Blood Cells: RBCs are small bi-concave disc-shaped cells present in large numbers. RBCs contain haemoglobin which combines with oxygen and helps in transportation of oxygen. Haemoglobin is a red- coloured pigment which gives blood its red colour.
- White Blood Cells: WBCs help the body to fight diseases by destroying infectious agents. They are known as soldiers of our body. They are larger than RBCs, but are fewer in number.
- Platelets: Platelets play an important role in the clotting of blood by blocking the flow of blood in case of any injury. They are small irregular cells.
Question 3.
Differentiate between arteries and veins. What is the importance of capillaries in the circulatory system.
Answer:
Arteries:
- Their walls are thick and elastic
- They have no valves.
- Blood flow with high pressure.
- They carry oxygen rich pure blood from heart to all the body parts.
Veins:
- Their walls are thin.
- They have valves.
- Blood flows at low pressure.
- They carry carbon dioxide rich impure blood from body parts to the heart. Capillaries are the thinest blood vessel, they have very thin wall through which oxygen, digested food, carbon dioxide and other waste products are exchanged between the blood and the surrounding cells. The capillaries join up to form the veins which carry the blood back to the heart.
Question 4.
Explain the working of heart.
Answer:
The heart is divided into four chambers. The top chamber with comparatively thinner wall are called auricles. The two lower chambers with thick muscular wall are called ventricles.
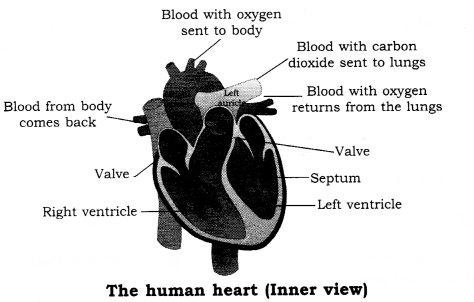
- The right auricle receives carbon dioxide-rich blood from the various parts of the body. The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs, where carbon dioxide is removed and oxygen is absorbed.
- The left auricle receives oxygen-rich blood as it comes back to the heart from the lungs. The left ventricle pumps this blood to the rest of the body. The right side of the heart is completely separated from the left side with the help of a partition called septum, so that the two types of blood do not mix.
- The heart has a number of valves that allow the blood to flow in one direction only. Figure shows the complete circulatory system in the body. The blood enters the right side of the heart and is pumped to the lungs where it gives up carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen. This oxygen- rich blood travels back to the left side of heart. It is again send to all other parts of the body and the process is repeated again and again.
Information related to the blood:
| Blood group of Doner | Blood group of Receptor | |||
| A | B | AB | O | |
| A | ✓ | X | ✓ | X |
| B | X | ✓ | ✓ | X |
| AB | ✓ | X | ✓ | X |
| O | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
NOTE:
Symbol (✓) Means blood can be given Symbol (x) means blood cannot be given. The person of group AB can receive blood from any one.
The person of group O can give blood to any person. In this way group AB is the universal receptor while group O is the universal donor.
We hope the given RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Blood Circulation will help you. If you have any query regarding RBSE Rajasthan Board Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Blood Circulation, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.