Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 11 Work, Energy and Power
Work:
The product of force and displacement (in direction of force) is called work.
Work = Force x Displacement in direction of force
W = F x s
If direction of force is different from direction of displacement then we can find the work done by component of force in direction of displacement.
Let us assume that direction of force makes an angle θ with direction of displacement. Then, component of force in direction of displacement is;
F.cosθ
RBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Notes Work done
W = component of force in direction of displacement x displacement
Or W = F.cosθ x s = F s cosθ = F.S
Work is a scalar quantity, i.e. its value can be positive or negative. If force or component of force is in the direction of displacement then work done is positive. But if force or component of force is in opposite direction of displacement then work done is negative.
Work Energy And Power Class 10 Notes Unit of Work:
If force is expressed in Newton and displacement is expressed in meter, then unit of work is Joule.
Work = Newton × meter = Joule
If force is expressed in Dyne and displacement is expressed in centimeter then unit of force is erg.
Work = Dyne×cm = erg 1 Joule = 1 N x 1 m = 10s Dyne x 102cm = 107erg
RBSE Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Energy:
The capacity to do work is called energy. Thus, work is the measure of energy and hence unit of energy is same as that of work. Energy too is a scalar quantity. If 1 Joule of work is to be done then required energy for this would also be 1 Joule.
RBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Types of Energy:
Some major forms of energy are as follows:
- Mechanical Energy: The energy in an object because of movement or position, or both is called mechanical energy.
- Heat Energy: The mobile energy in micro particles due to heat is called heat energy. These micro particles transfer energy from high temperature to low temperature,
- Chemical Energy: Energy obtained from chemical reactions is called chemical energy. For example, a battery provides energy because of chemical reaction. Similarly, energy from LPG or coal is obtained because of chemical reaction.
- Electrical Energy: Energy produced by electric charge is called electrical energy. Most of the household appliances work because of electrical energy. Gravitational Energy: Energy in an object due to gravitational force is called gravitational energy. Gravitational energy is responsible for falling water in waterfalls.
- Nuclear Energy: The energy produced by nuclear fission or fusion is called nuclear energy.
Work Energy And Power Class 10 Notes In Hindi Mechanical Energy:
The sum of kinetic energy and potential energy in an object gives the mechanical energy of that object. Mechanical energy gives an object the capacity to do work.
RBSE Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Kinetic Energy:
The energy in an object due to its motion is called kinetic energy. Let us assume that an object of mass m is moving at uniform velocity μ and a force F is applied on it in the direction of motion then the object is displaced to distance s. Let us assume that the work done on the object increases its speed to ν and acceleration of object becomes. Then work done is equal to change in kinetic energy of object.
![]()
If initial velocity of the object is zero, i.e. the object starts from rest and obtains the velocity v then;
![]()
It can be said that the kinetic energy of an object of mass m and velocity v is;
![]()
Work And Energy Class 10 Notes Potential Energy :
The energy in an object due to the position of the object is called potential energy. Potential energy gives the capacity to do work to an object. The work done in putting an object in a specific position from normal position, gives the measure of its potential energy.
Class 10 Science Ch 11 Notes Potential Energy in Gravitational Field :
When an object is lifted up to a height then some work is done against acceleration due to gravity. The work done on object increases the energy of object. This energy gets stored in the object in the form of potential energy. If an object with mass m is lifted to height h from earth then the minimum force required to do this should be equal to its weight, i.e. w = mg.
Potential energy of object at height h = work done against gravitational force
= Force × Displacement = mgh
Work Energy And Power Class 11 Notes Pdf Potential Energy of a Simple Pendulum :
When a simple pendulum is displaced from its mean position to a particular side, its centre of gravity is raised. The work done on pendulum in this gets stored as potential energy in pendulum.
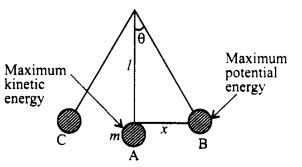
The pendulum moves ahead from its mean position due to this kinetic energy. While doing so, its kinetic energy reduces to zero and potential energy increases to maximum when pendulum reaches another extreme (point B). The pendulum swings back to its mean position due to the potential energy.
If mass of pendulum is m and pendulum is suspended by a thread of length / then potential energy of pendulum for displacement x can be obtained as follows:
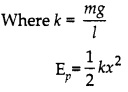
Similarly, when a spring with spring constant k is displaced to x distance from its mean position (under elastic limits) then potential energy of spring is;
![]()
Work And Energy Class 9 Notes Electrical Energy
The energy in charged particles is called electrical energy. When a particle becomes charged then an electrical field is created around it. This electrical field applies a force on charged particles nearby and makes them move. Thus, transmission of energy takes place through particles in motion.
- The electrical field around a positively charged particle repels other positively charged particles but attracts negatively charged particles.
- Positively charged particles possess potential energy because of their position. When electrical field applies a force on these particles, they move in a certain direction. For example; we need to apply an external force in order to move a positively charged particle from negatively charged source. This process would increase the potential energy of positively charged particles. When the external force is removed, the positively charged particle would move from area of higher potential energy to area of lower potential energy. Thus, a positively charged particle would naturally move towards negatively charged source. While doing so, potential energy of charged particles changes into kinetic energy. This kinetic energy is obtained in the form of electrical energy.
Different types of electric plants are used for production of electricity. Some of them are as follows.
Thermal Power Plant: In a thermal power plant, heat energy is obtained from chemical energy of coal. The heat energy is utilized to convert highly pure water into steam. The steam is utilized to rotate the turbine and thus electricity is produced by generator which is attached with turbine.
Work Energy And Power Class 9 Pdf Nuclear Power Plant:
Nuclear fission is carried out in a nuclear power plant. The heat generated from nuclear fission is utilized to convert water into steam. The steam is utilized to rotate the turbine and thus electricity is produced by generator which is attached with turbine.
- Hydel Power Plant: In a hydel power plant, potential energy of water is increased by making a dam. When water is released from the dam, potential energy of water changes to kinetic energy. This kinetic energy is utilized to rotate the turbine and thus electricity is produced by generator which is attached with turbine.
- Wind Power Plant: In a windmill, kinetic energy of air is utilized to rotate the turbine and thus electricity is produced by generator which is attached with turbine. Wind energy is a renewable energy and hence is environment friendly.
- Solar Power Plant: Energy from sun is converged at a point with the help of lens and mirrors and is changed into heat energy. This heat is utilized to produce steam which is utilized to rotate the turbine and thus electricity is produced by generator which is attached with turbine.
- Photovoltaic Power Plant: In a photovoltaic power plant, solar panels are installed at open spaces or on rooftops. These panels contain photovoltaic cells. When sunlight falls on these cells, the cells gain photons from light and bring the electrons in excited state. These charged particles provide electricity to circuit in the form of electric current.
RBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Question Answer Conservation of Energy :
As per law of conservation of energy, the total energy of an isolated system always remains constant. Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed. We can only change the form of energy.
As per law of conservation of mechanical energy, the mechanical energy of a system remains conserved. If kinetic energy of the system is increased then potential energy decreases, and vice- versa is also true.
If change in potential energy and kinetic energy is respectively ΔEP and ΔEK then;
ΔEP=- Δ Ek
Or, ΔEp+ΔEk = 0
Or, Total mechanical energy Em = Ep+Ek
In reality, there is some fall in mechanical energy during the whole cycle. This reduction is because of action of some non-conserving forces, like friction, viscosity, etc. These forces convert some of the energy into sound, heat, etc. Thus form of energy of the system changes but total energy of the system remains constant.
![]()
Class 10th Chapter 11 Science Notes Dissipation of Energy:
When energy changes from one form to another then some of the energy is dissipated in the form of heat, light, sound, etc. Dissipation of energy means that energy is converted into some forms which are undesirable and which are not required by us. The total energy remains conserved but because of useless dissipation of energy it is impossible to make a cent per cent efficient system.
Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Notes Power:
Power is defined as the rate of doing a work. It is a scalar quantity.
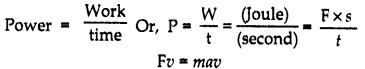
Work Energy Power Class 11 Notes Unit of Power:
The unit of power is Watt which is named in honour of James Watt; the inventor of steam engine.

Another unit of power is horse power which is equal to 746 W.
Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work And Energy Electrical Power:
The rate of transfer of electrical energy in electric circuit is called electric power. On a commercial scale, the electricity distribution company measures the consumption of electricity in the form of kilo Watt Hour. One kilowatt hour is called one electric unit which is read by electric meter.
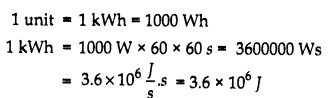
This means that when a bulb of 1 KW is used for 1 hour, it will consume 1 unit of electricity
RBSE Class 10 Science Notes