Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 14 Refraction of Light
- Light travels through a transparent medium in a straight line.
- When it strikes with an opaque object while travelling through a transparent medium in a straight line like (air), then it cannot go ahead and a shadow of object appears behind the, object.
Refraction of Light:
Fix a white paper sheet on a drawing board with the help of drawing pins. On paper keep a rectangular glass slab in centre. Draw sketch of a slab with pencil name this figure as PQRS. Remove slab and draw a normal at MON point O, MON also make an angle of incidence AO (30°) with the help of a protector and draw a line AB, on this line at point A and B, stick two pins vertically.
Now put again glass slab on the same sketch on opposite side. Look the images of pins and point A and B. Put a pin at point C in such a way that point C and images of point A and B should be in a straight line. Take one more pin and put in such a way that Point A,B,C and D look in a straight line, remove pins and slab. Where pins C and D were put. Encircle them and draw a line between them join it with O’. Draw normal O’N’ at point O’ on the surface SR.
Now, join O with O’ and extend A,B also we see that line in the direction of A, B blows into the air and light ray strikes the surface of the slab and enters it. On point O it bends towards normal, while enters from a rarer medium to denser medium, (i.e. air to glass). In the same manner when it travels from denser to the rarer medium (i.e. glass to air) on surface SR point O’ it goes away from the normal.
So we can say that:
- When light ray enters from rarer to the denser medium (air to glass) it bends towards normal.
- When light ray enters from denser to the rarer medium (i.e. glass to air) it goes away from the normal.
Refraction of light: When a light ray enters from one medium to another medium, then it deviates from its path. This phenomenon is called refraction of light.
Why Refraction takes place?:
The speed of light in dense medium (glass) is less than rarer medium (air). Hence it is clear that when light enters in the denser medium from rarer medium it’s speed becomes slow on the other hand when it enters from denser to the rarer medium, it’s speed increases. Hence refraction takes place due to difference in speed of travelling from one medium to another.
Coefficient of Refraction (Refraction Index): It is the proportion of speed of light in two mediums. It is constant and dimensionless quantity.
Refraction coefficient \((\mu)=\frac{\text { Speed of light in first medium }}{\text { Speed of light in second medium }}\)
\(\mu=\frac{V_{1}}{V_{2}}\)
Phenomenon based on Refraction:
- Raised bottom of water filled container: Put a coin in water filled bucket by keeping your eye on one side of water, try to lift. Repeat the activity. Now take a steel or plastic container and put a coin at its bottom. By seeing coin kept at bottom of the container, move back slowly till the coin becomes unseen. Now ask your friend to pour water in the container slcwly. Take precaution that coin do not move from its place. Coin is still seen. It happens due to refraction of light. When light rays travel from coin passes from water (denser medium) towards air (rarer medium) they move away from normal to the surface of water, and when reached to our eye, then coin looks raised from its place. In the same manner bottom of water filled container, pond and well, seems raised.
- Stars twinkle: Due to different densities of layer of air, their refractive index is different. Due to travelling different layers of light coming from stars deviates from its path. Hence stars seem twinkling.
- Pencil kept in water looks bended: Take a glass of water, fill it with water and keep a pencil inside it in such a way that its partially submerge in water, it looks bended at the upper surface of water. This also happens due to refraction. Light rays coming out of the submerged part of the pencil when comes out of the water and enters into the eyes of the observer. They move away from no/mal and hence pencil looks bend.
- Visibility of sun before sun rising and after sunset: In morning, light rays coming from the sun get refracted from different layers of the atmosphere and reach to our eye. Hence they look to us coming from the horizon, and the sun looks raised, because of this sun looks rising two minutes before actual sunrise. In the same manner after sunset the sun still visible to us even two minutes after the actual sunset. In this way the length of the day increases four minutes.
Lens:
A lens is a transparent medium surrounded by two curved surfaces.
Types of Lens:
Mainly lenses are of two types:
1. Convex lens
2. Concave lens.
- Convex Lens – A lens which is thick in middle portion and thin at the edges, is called convex lens. This lens converts all the beams of parallel light rays into single point, hence it is called a converging lens. The beams of light rays coming parallel to the axis refract from a convex lens and the point where they all are collect is called focal point of the lens. We should not see the sun through a convex lens neither sun rays should collect on any part of the body. It may cause skin burn and also damage eyes.
- Concave lens – A lens which is thick at the edges and thin in middle portion is called a concave lens. This lens diverge the light beam coming parallel to the Principal axis. Hence it is called diverging lens. Light rays passing through lens deviate from their path, hence we can say that lens refract the light rays.
Definitions related to lens:
Principal Axis: The line that passes through both the surfaces of lens through curvature is called Main axis or Prime axis or Principal axis (C1 and C2).
Optical Centre: Inside the lens the point through which the line that passes without deviation is called Optical centre of the lens (O).
Focal Point: The point where beam of parallel rays to the Principal axis collects after refraction from a convex lens is called focal point (F) of convex lens. The point from which parallel rays of light to the Principal axis after refraction from a concave lens, diverge is called focal point of concave lens.
Focal Length: Distance between focal point and optical centre of lens is called focal length (f).
Image formation by Convex lens: Take a convex lens and paper that allow sun rays to pass through the convex lens in such a way that it concentrate at one point on a paper sheet, wait till paper starts burning, the point at which convex lens focus the sun rays is called Focus of the lens. When the distance between image and lens is measured, it is found that this point is a very small image of the Sun, as this image can be formed on the screen, it is a real image which is always inverted. Hence we could say that when an object is situated at infinity then convex lens forms its real, inverted and diminished image at focal point.
Activity: Draw a line on table with chalk and form a point at its center. Keep a convex lens at this point in such a way that light of the lens should fall on this point. On its left hand, draw a point F’ at equal to the distance of focal distance from F’. On same distance put another point 2F’ in the same way on right hand side of the lens make point F and 2F. Now keep a burning candle away from 2F’. Stick a white paper on about 15 cm × 10 cm cardboard sheet. It would act as a screen. Keep it on the right hand side of the lens and move back and forth till we receive a bright image of candle flame. The image is small and inverted. As it could be taken on screen, hence it is real and would form between F and 2F.
In case of an object is kept between lens and F, we will not receive image on the screen to know the position of image. Take out lens from stand and keep near the words written on any book page. In this condition object (words) will be in between F and Optical center (0), we will get erect and large image.
Formation of Images by a Convex lens:
| S.No. | Position of object | Position of Image | Size of Image | Nature of Image |
| 1. | At Infinity | at F | Very Small, inverted | real |
| 2. | At small distance from F | Between F’ and 2F | Small and Inverted | real |
| 3. | At 2F | At 2F | Equal and inverted | real |
| 4. | Between F’ and 2F’ | Away from 2F | Large and inverted | real |
| 5. | At F’ | At infinity | Very large, inverted | real |
| 6. | between lens and F’ | Between Infinity and lens | Large and erect | Virtual |
Formation of image with concave lens:
From concave lens image is not formed on screen. It always form erect, virtual and diminished image.
Uses of Lens and Optical Instruments:
- In correction of defects of vision: In eradication of sight problems. In spectacles both types of lenses are used. Those who can not see things at distance clearly, they suffer from defect of near sightedness. Such people use concave lenses. Those who can not see things near by, they suffer from defect of far sightedness. They use convex lens.
- Simple microscope: Clock repairers use a convex lens to see the very small parts of clock. This single convex lens is called simple microscope. In this microscope the low focal length lens is used. By this small things can be magnified.
- Compound microscope: In this microscope two convex lenses are fitted in a metal tube. Lens is located on the side where object is kept, is called objective lens while lens which is kept near eye is called eye piece.
- Telescope: It is used to see things at very far distance. It also contains two convex lenses. They are also called objective lens and eye piece.
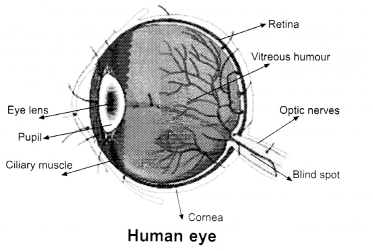
Human Eye:
In our eyes there is convex lens located which is formed by flexible muscles. Due to this lens, image of object formed at retina, and we can see things. Our eyes are round in shape* the outermost conversing of eye is white in front of it, transparent part cornea is situated, behind cornea dark coloured structure made of muscles is located, it is called iris. There is a small hole in iris called Pupil. Its size is controlled by the iris. In the case of more light the aperture of Pupil reduces and in low light it increases.
At the back of the pupil is eye lens which is located at its place with the help of muscles. The part between cornea and lens is filled with transparent fluid which called eye fluid or Aqueous humour. Through lens inverted image is formed on retina. Retina is a light absorber transparent membrane which has many light sensitive nerves, these are connected to brain. When these nerves send the message of the formation of image on retina to the brain, then brain converts inverted image into erect image and we see the object. The transparent fluid fill between lens and retina is called vitreous humour or fluid.
Dispersion of Light:
In rainy days when sun is at our back, we might have seen arc shaped seven colour bands in clouds. The group of these seven colour band is called rainbow.
Activity: Take a prism in sun and keep its one surface in front of the sun. Move it slight and allow light travelling through prism to fall on a wall under shadow. Now observe light fallen on the wall. We will see a group of seven colour bands on the wall. It is called spectrum of light. Sunlight is formed of seven colours but combinedly seen white. The different colours have different speed in denser medium. As speed of red colour is more so it less deviates while travelling through a prism. On the other hand speed of violet colour is less so it deviates more while travelling through prism. Hence when white beam of light enters the prism, it splits into its original colours red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet colour. This is called dispersion of light. In rain drops due to refraction white light split into colours or deviation of colours take place, due to which rainbow is seen.