Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 18 Carbon and Fuel
Presence of Carbon:
Out of 118 known elements in which 92 elements occurred naturally. Carbon is an important natural element which is present in all living beings and eatables. Its symbol is C. The word carbon is formed from Latin word Carbo means coal. Hence while writing with a pencil on paper the black mark, Kajal used for eyes, when wood is incompletely burn black residue is left in all these black substance, is called carbon. In non-living things it is also present in combined form or free form. Naturally occurring substances like sugar, glucose, tea, milk, coal, petrol, diesel, natural gas, kerosene, urea, diamond, graphite etc. have carbon in them.
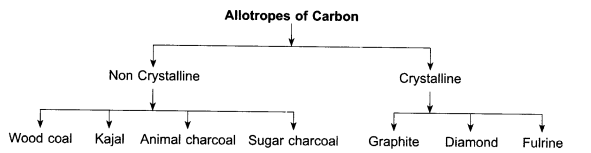
Allotropes of Carbon:
Coal, lamp black, graphite, diamond are the allotropes of carbon. They are example of free form of carbon. When an element is found in two or more than two forms, they have different physical properties but similar chemical properties, are called allotropes and this property is known as allotropies.
Crystalline allotropes of carbon: Those allotropes of carbon which have a definite geometrical structure. They are called crystalline carbon allotropes. Example; graphite, diamond and fullerenes.
Non-crystalline allotropes of carbon: Those allotropes of carbon in which carbon atoms do not have a definite geometrical structure. They are called non crystalline allotropes of carbon.
Example- wooden coal, kajal etc.
Difference between Graphite and Diamond:
| S.No. | Properties | Graphite | Diamond |
| (I) | Hard/Soft | It is a hazy/opaque substance on touch. It is smooth and slippery. | Transparent, hard easily cracks. |
| (II) | Structure | In graphite carbon atom on same surface joins three carbon and form a hexagonal structure.
Such surface are bonded with weak bonds hence they can slide on each other. So, they are soft. |
In diamond it joins with other nearest four carbons and forms a hard three dimensional structure. |
| (III) | Electricity
Conduction |
It is good conductor of electricity. | It is bad conductor of electricity but good conductor of heat. |
| (Iv) | Use | It is used in electric arc and diy cells. | It is used in jewellery, cutting, grinding, hole passing etc. |
Carbon Important/Essential Component of Fuel:
Fuels are those substances which produce heat on burning. In most of the fuels carbon is present in the form of compound or element. In daily life we use LPG, wood, bio gas to cook food. In present era the main source of energy is fuel. Its consumption is increasing day by day. In all fuels like petrol, diesel, kerosene, wood and coal, carbon is an essential element.
Sources of Fuel:
- Biomass: The substances present in the body of animals and plants is called biomass, like- wood, agricultural wastes and dung etc.
- Wells of crude oil: We get different fuels (petroleum) products from fractional distillation of crude oil. ‘
- Coal mines: Hard coal is obtained from mines.
Fuel Is Found In Three Forms Of Matter:- Solid fuel – Wood coal, Hard coal, Dung cakes, Agricultural wastes are all solid fuel.
- Liquid fuel – Kerosene, diesel, petrol, gasoline, alcohol etc are liquid fuel.
- Gaseous fuel: Gobar gas, water gas (H2 + CO) Producer gas (N2 + CO), Natural gas, Liquid petroleum gas (LPG) etc. are gaseous fuel.
- Coal (solid fuel): Millions of years ago there were dense forests on low layer of earth in flood area. Due to floods a natural calamity, these forests burried deep down the earth. They converted and compressed due to heavy deposition of soil on them. As the depth increased, temperature increased. Due to high pressure and temperature inside the earth they get converted into coal.
The conversion of dead plants by a slow process into coal is called carbonation. In coal carbon is the dominant element as it is formed due to remains of plants. Hence it is also a fossil fuel.
On the basis of carbon content present in coal it is divided in to four types:
- Peat (60% carbon)
- Lignite (67% carbon)
- Bituminous (80% Carbon)
- Anthracite (90-98% carbon)
Petroleum (liquid fuel): Petroleum is used in all vehicles. It is formed from organisms and vegetation of sea. Dead plants and animals in oceans burried crores of years ago due to geographical disturbance. Their bodies burried under soils at the bottom of the sea. Due to absence of air high temperature and pressure dead organism converted into petroleum gnd natural gas. World first oil well was drilled at Pennsylvania, America in 1859. After 8 yrs of this discovery in 1867 Digboi in Assam was discovered. In Rajasthan Mangla, Bhagyam, Aishwarya, Guda, Rajeshwari, Saraswati and Kameshwari wells are discovered in Barmer.
The word ‘Petroleum’ is originated from Latin word ‘Petra’ means ‘rock’ and ‘oleum’ means ‘oil’. As it is found inside the earth in rocks, it is called mineral oil. It is also called liquid gold. In present era it is more valuable than gold for any country in the world. It is very important in agriculture industries, transport, communication, etc.
Refining of Petrol: It is refined by fractional distillation method. Petroleum is a greasy, thick, brown liquid. It is a mixture of many hydrocarbons. The petroleum taken out directly from wells can’t be used. The boiling point of all elements of petroleum is different like- petroleum gas, petrol, nephtha, diesel, kerosene etc. Crude oil is filled in the bottom of a convex cylindrical container and slowly heated. Then first of all petroleum gas, then petrol, nephtha, kerosene, diesel etc moves upward in the column, which are condense at different level and collected separately. This process is called fractional distillation.
- Petroleum gas : In fractional distillation, petroleum gas is separated first at 250°C-300°C. It is mainly useful as fuel in kitchen as cooking gas and automobiles. It is a mixture of ethane, propane, butane, and isobutene. This mixture can be easily liquefied at high pressure, which is called liquefied Petroleum (LPG) gas. While filling cylinders some amount of mercaptan (thiol) is mixed, so any leakage of gas can be identified with its smell. It causes very less air pollution. It can be burn quickly and does not produce ash.
- Petrol: It is separated at 30°C-120°C. It is used as fuel in automobiles and dry cleaning.
- Nephtha: It is separated at 120°C-180°C. Beside fuel it is used in chemical reactions.
- Kerosene: It is separated at 180°C-260°C It is used in kitchen in stoves, jets, chimney, lamps etc.
- Diesel: It is separates at 260°C-340°C. It is used as fuel in heavy motor vehicles like truck, tractors and in electric generators etc.
- Lubricant: Separates at 350°C.
- Paraffin wax: It is used in candles, shoe polish, wax paper etc.
- Petroleum coal tar: It separates at 600°C. It is the last residue of fractional distillation. It is used to construct roads.
Compressed Natural Gas (CNG): It is obtained from petroleum mining. It contains mainly methane gas. It is used as fuel in automobiles. It is compressed and then filled in cylinders. Hence it is called compressed natural gas. Petroleum is non reversible energy resource as it is formed due to process of millions of years. It’s deposits are limited which can be continue for few years. It causes high air pollution. Hence they should be used wisely. If we use them excessively then it is possible that in near future their deposits will finish.
Combustion/Burning:
When any substance burns in the presence of oxygen then this activity is called burning or combustion. When a candle is let. it gives light and energy, if we put any thing like glass invertedly on candle it blows off. This shows oxygen is essential for burning glass cuts the supply of air and candle blows off.
- Ignition temperature: The temperature at which a substance burns is called its ignition temperature.
- Complete burning: When sufficient amount of oxygen is supplied to a burning substance, then it bums with blue flame, it is called complete burning.
- Example: Burning of LPG (Liquid Petroleum Gas)
- Incomplete burning: When any burning substance do not get sufficient amount of oxygen supply, then it burns with yellow flame. It is called incomplete burning.
- Example: Burning of wood that causes air pollution.
- Combustion: A chemical reaction in which substance combines with oxygen and produces heat and light. This reaction/process is called combustion/burning.
What is essential for burning a substance?:
Three things are essential for burning any substance
- air (oxygen)
- Optimum temperature
- Fuel
Energy Conservation:
- A long process and time is needed to form oxide oil or natural fuels.
- Their deposits are limited only for next 100 years.
- They cause air pollution.
- They help in global warming.
Hence it is essential that these should be used only when essential, It would result in environmental conservation, less danger of global warming, fuels would be available for long period.
How can we save petrol and diesel:
In India Petroleum Conservation and Research Committee (PCRA) advice’s.
- Drive vehicle at uniform and medium speed as possible.
- Put off engine at red light.
- Keep air pressure of tires maintained, keep maintenance of vehicle regularly.