Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 5 Biodiversity
The ancient Indian scriptures explain the geographical form of India as
उत्तरंयत्समुद्रस्य हिमाद्रेश्चैव दक्षिणम्।
वर्ष तद्भारतं नाम भारती यत्र सन्ततिः॥
Means land between north of Indian ocean and south of Himalaya is called India or Bharat Varsha. Environment and climate of India in north Jammu and Kashmir to south Kanyakumari is diversified. Due to climatic diversities people living in different parts of India have differences in -dress, culture, food habits. Climate effects the flora, fauna of a region.
Biodiversities: Species of plant and trees, animals and micro organism found in a special region is called biodiversity of that region. Due to different geographical conditions and environment species of plants, trees and animals also differs from region to region. In whole world approx 250000 plants species §ire found out, of them approx 45000 are found only in India. These differences are more in Indian species compared to other nation of the world. Therefore India is also called a land of diversities.
- Some plants and animals about which we have read in books or they are preserved in museums but are not found in natural and artificially reserved regions.
- Those are not found in natural habitat but are found in artificially reserved areas.
- If they are not conserved they will become extinct.
- Those which are found in special areas.
Above mentioned four types of plants and animals are classsified into different categories by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as follows:
- Extinct – Those species of plants, trees, birds and animals which have become extinct from entire earth like: Animals, Dodo bird, Wild pigeon, Woolly mamoth, Tasmanian Tiger.
Plants: Saint Halena, Jaitoon, Woods , Cykedus , Kokiya , Koki. - Extinct in natural habitat- They are found only in artificial habitats like Hawai crow, Vyoming frog, Black soft coated tortoise.
Plants: Kalimantan Mango (Kasturi) - Endangered – These are the species which are in danger of extinction. The survival of such species is difficult, if the negative factor that have led to a decline in their population continue to operate animal species – Asiatic Lion, Dolphin of Ganga River, Black Deer, Single Horn Rhinoceros, Desert Lizard, Godawazn, Son Chirraiya, Giddh, Bijju.
Plant species: Paneer bandh, Rohida, Indrok, Gugul, Fog or Rhogda. „ - Special zone species: Those which are found in special region, for example; sal, wild mango are special found in Panchmadhi reserved biosphere Indian giant squirrel and flying squirrel are special animal species, the other species are – snow leopard (Himalayan range), Dolphin of Ganga river.
Plant species: Indrok pempa khedula so Rhog (Rajasthan) Red Sandal (south- west ghats)
Degradation:
- Decline of biodiversity: Through media and special days like environmental day, earth day there is information that biodiversity is decreasing regularly. Continuous decline in biodiversity is called bio- diversity decline. Existence of plants and animals life depend upon mutual interaction and independence for living being. Existence of biodiversity is very essential.
Factors responsible for the degradation of biodiversity are: - Deforestation: Destruction of forest due to natural causes and man made cause is called deforestation.
- Causes of deforestation: Cutting of forest for wood blindly and uncontrolled to make furniture, decorative pieces, paper, fuel, ships etc. Overgrazing is the main cause of deforestation. Fast growing population and urbanization roads and railway tracks, dams, construction industries etc are responsible for deforestation.
- Hunting of animals and birds:
To get teeth, meat, skin, horns, bones, animals are hunted. - Harmful effects of deforestation
Soil erosion and fertility of the soil: Roots of plants bind the soil, cutting of trees loosen the soil. It could be easily erode by fast wind and water, humus and nutrients present in the top layer of the. Soil eroded with soil and decreases the soil fertility which put an adverse impact on vegetation. - Destruction of natural habitat of birds and animals.
Dis-balance in the environment among gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide. Plants balances the 02 and CO2 by the process of photosynthesis. Global temperature is increasing due to increase in CO2 in the environment, it is called global warming.Plants absorbs water from earth through roots. This water is released in the atmosphere through transpiration. Amount of water vapor is decreasing in the atmosphere due to cutting of forests. Its continuously decrease the rain fall Deforestation in hilly areas causes rock sliding such as tragedy of Uttarakhand. Soil, water and air pollution also put adverse impact on animal and plant life.Environment is changing rapidly due to natural and man made activities. Hence those species which cannot adjust in changing environment are become endangered and extinct.Natural calamities like earthquake, floods, drought, cyclones etc., in many regions are responsible for extinction of many plant and animal species.
Conservation of Biodiversity:
Methods of biodiversity:
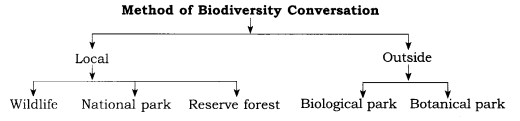
Sanctuaries:
Many National and International organization are indulged in conservation of forest and forest life. Our central and state governments, have made many rules, laws and policies for their conservation, we should follow these rules, laws policies and make aware others also for doing the same. Wildlife sanctuaries, National park, Zoo, Botanical parks etc., are secured places for plants and animals.
Wildlife Sanctuaries and National Parks:
To give conservation to important species of birds, animals and plants in their natural habitat. In many countries of the world, Wildlife sanctuaries and national parks are established. In our country more than 510 Wildlife sanctuaries and 102 national parks are there. In these forests cutting of trees and hunting of animals is prohibited, some of the Wildlife sanctuaries and national parks are as follows – Bandhavgarh (M.P) Tiger, Bandipur, Karnataka (Tiger), Gir Gujarat (Asiatic lion).
Causes of Decline
In Assam (Indian Rhino), in M.P Kanha (Tiger), in Kerela periya (Asiatic Elephant), in Jammu and Kashmir, Dachigam (Kashmir stag), In Bharatpur Keoladeo park (Bird Siberian Crane), Ranthambore tiger sanctuary Rajasthan, Bagh Sunder Van, Tiger Project Bagh. In Rajasthan 30 animals sanctuaries, National park and hunting field are reserved.
- Biological park and Zoo: Park is that place where birds and animals are kept to provide knowledge about wild animals and their show. They are providing services for breeding centres of extinct animals. Their main objectives is to make people aware for environmental conservation and love towards wild animals.
- Botanical Gardens: They are specially established to provide conservation naturally extinct and endangered species. In whole world 1600 botanical parks are there. These botanical parks serve as seed banks. In our country Aacharya Jagdish Chand Bose, Indian National Park Sibpur, Hawra are in West bengal. It is spread in 269 acres of land.
- Habitat of Migratory birds: Many foreign birds come to India due to adverse conditions (severe cold) of weather in winter after covering long distance for breeding. They are called migratory birds like – Kuranja (Siberian crane).
- Their important habitat in Rajasthan are as follows
- Khichan near Phalodi Jodhpur.
- Keoladeo National Park Ghana, Bharatpur.
- Near Guda Bishnoiyan Kakani Pond (Jodhpur).
- Talchapar Churu.
- Deedwana Nagaur.
Biodiversity Hotspot:
Those geographical regions which are important and in biodiversity rich as well as habitat for special species are destroying due to selfish activities of man are called biodiversity hotpots. According to (Norman Mayrus 1988) along these biodiversity hotpots species of endangered extinct naturally, plants and animals of special regions are also included.
In whole world 34 biodiversity hotpots are there. Among them two are located at Western Ghats and Eastern Himalayan region in Indian. Due to rapid deforestation species found in these hotpots are in danger. Hence it is essential to protect them. Plants and trees are only living beings on our earth which transforms that light energy obtained from sunlight in chemical energy in the form of our food products. Perhaps due to this reason it is said in our ancient scriptures that,
यादव भूमंडल धााते सशैलवन काननम्।
तावत् तिष्ठति मेदिन्याम् सन्ततिः पुत्र पैत्रिकी॥
Means till our land is prospered with trees, mountains and forests it would look after the children of man. Hence we should commit to put efforts regularly to save our biodiversity.
Recycle of paper: We should wisely use paper. By recycling of paper we cannot only save deforestation but can save water and energy utilized to produce paper.
- Red data book : It is the book in which records of endangered species is kept. Seperate data books are maintained for plants, animals and other species.
- Bio diversities of Cows in Rajasthan : Kankrej – fast in running and capable of carrying load, found in Barmer, Pali, Sanchore and Naigad region of district Jalore.
- Malvi : famous for carrying load, found in Malvi region of Jhalawar.
- Its of two types:
- Small malvi
- Big malvi
- Small malvi is found in Kota, Bundi and Udaipur.
- Big malvi is found in Jhalawar.
- Rathi : Gives greater amount of milk. They are hybrid variety of Sahiwal, Red sindi, and Haryana breeds. It is the best breeds of cow in India.
- Nagauri : Active and famous for ploughing, found in Solahak region of Nagaur other breeds are Tharparkar and Gir.