Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 9 Social Science Notes Chapter 18 Business and Commercial Activities
Classification of Human Activities
- Non-Economic Activities.
- Economic Activities.
- Non-Economic Activities: No direct benefit to the doer of these activities as going to school, cooking food, praying to God, playing etc. They are inspired by the spirit of love, affection, social and religious duties, physical needs
- Economic Activities as farmers’ work in the field, teaching by teacher in the school, selling of goods by the shopkeeper. They aim at economic gain by the production and distribution of goods and services.They can be divided into three classes:
- Profession: Any activity rendered by a specialist in return of fees or charges e.g. services of a doctor, a chartered accountant, a teacher etc.
- Service/Employment: A sort of contract between the employer and the employee. The employees works on certain conditions and get wages from his employer.
- Business: Any activity done with the basic aim to earn profit, of course also with an aim to promote social good so as to earn more profit. In fact business includes-legal human economic activities, regular production and distribution of goods and services, social satisfaction so as to raise living standard of the society.
Characteristics of Business:
- Human Economic Activities: Activities of only human beings and not of animals or non-economic man as a saint.
- Production of Goods and Services: To provide goods to consumers production is done in the industrial units. Such goods are purchased by the traders and sold to consumers in the market.
- Transaction of goods and services: Goods may be consumer’s clothes, jeweler etc. or industrial as machinery and services as banking, transportation etc. Distribution, production and exchange should be done continually.
- Continuity in Business: Trade of goods and services is done daily in the market. If it is done now and then it is not called business.
- Objective to earn profit: It is the main motive of business, without it business can not be run continuously.
- Uncertainity of Profit: Business is a risk. Though a businessman invests capital for profit but it is not sure how much profit or loss he would earn.
- Legality: Only legal activity is considered as business, illegal (activities) like gambling, stealing, black marketing are not considered as business.
- Presence of Risk: Possibility of loss in business is called risk.
- Means of Social change: By changing goods according to demand status of the people for their upliftment.
- Creation of utilities: Through business activities utility of goods created.
Objective of Business:
- As per traditional concept: To earn profit.
- According to Urwik: To serve the society.
- According to William G. Scott: Satisfaction of human needs. To Sum up:
- Profit objective
- Service objective
- Human objective.
Profit objective:
-
- It is the source of income for a trade as well as income to expand.
- It is the symbol of perfect business style.
- It increases the fame of business unit.
- To expand business activities.
- Service objectives involves to provide goods as per customers’ needs, better quality at fair price, after sale services, to avoid undesirable practices and illusive advertisements and to innovate new techniques to satisfy customers.
- Human objectives related with human behavior, adequate working conditions, labor welfare, redressal of grievances, opportunities of promotion for employees, security of invested capital, cooperative towards suppliers, national interest and priorities, maximum employment opportunities.
- Scope of Business: Covering production related activities i.e. Industry and distribution related activities are included in commerce.
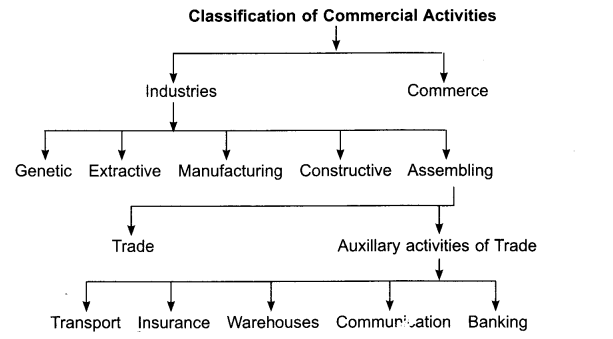
In this way commercial activities can be classified into two parts:
- Industries- Production Activities.
- Sale, purchase and distribution related activities are called commerce.
- Industry: Those business activities in which goods are produced by using physical or natural resources to meet the needs of the people. Thus industries create the ‘form utility.
Industries on the basis of work:
- Genetic Industries, as agriculture, gardening, animal husbandry etc.
- Extractive Industries, as mining, fishing, shooting etc.
- Manufacturing Industries, as sugar, cement, textile, Iron, Jute etc.
- Constructive Industries, as building roads, bridges, canals, dams etc.
- Assembling Industries related with computers, cars, watches etc.
- Commerce: Activities related with distribution of goods to consumers at proper place, time, manner, quantity and price.
Main Characteristics of Commerce:
- A link between producer and consumer.
- Easy exchange of goods.
- Time, Place and Authority utilities.
- Trade and Auxiliary activities are the part of business.
Classification of Commerce Related Activities:
- Trade
- Auxiliary activities of Trade.
Trade: Its Characteristics
- Sale and purchase of goods.
- Mutual interest of buyer and seller.
- Direct sale.
- Authority utility.
- A part of commerce.
Auxiliary Activities : serve place utility and time utility and assist the trade activities, e.g. transportation, ware-housing, Insurance, banking etc.
Differences between Trade, Commerce and Industry
Meaning:
- Trade: Purchase and sale of goods and services for profit.
- Commerce: Auxiliary activities.
- Industry: Production of goods and services.
Objective:
- Trade: Exchange of goods and services.
- Commerce: To facilitate exchange of goods and services.
- Industry: Production of goods and services.
Scope:
- Trade: Only purchase and sale.
- Commerce: Trade and auxiliary activities.
- Industry: All types of production related activities.
Creation of utility.
- Trade: Authority utility.
- Commerce: Time, place and authority utilities.
- Industry: Form utility.
Interdependence:
- Trade: Basis is industry.
- Commerce: Basis is trade.
- Industry: Basis is commerce.
- Besides wholesalers, retailers, agents and other mediators, there are agencies like insurance, bank, transportation, communications etc. which are involved in the commercial activities.
Bank:
- Meaning: An institution which transacts in money and credit and accepts deposits. Banking company does the banking business.
- Banking means accepting deposits for lending or investment to be returned on demand or withdrawn by cheque, draft, order etc.
Functions of the Bank
- Primary Functions:
- Accepting of Deposits
- Advancing of Loans
Accepting the Deposits: It means the public savings are deposited in the bank.
- Benefits:
- Security of savings,
- Earning from interest,
- Useful for National development.
Types of Bank Accounts for Savings
- Fixed Deposit Account: Money is deposited by the customer for a fixed time. The customer can take loan against it or can withdraw it as and when required, under the pre-determined terms and conditions.
- Saving Bank Account: Mainly for middle and lower class to encourage savings and earn interest on them.
- Current Account: Mainly for the business institutions, no interest is paid, can be withdrawn many times in a day. Overdraft facility is allowed.
- Recurring Deposit Account: A fixed amount at a fixed interval of 1 to 10 years to be deposited at the rate of interest higher than that in the saving account.
- Miscellaneous Account as Home saving account, Every Day saving scheme, monthly interest income, deposit scheme, minor saving scheme, etc.
Advancing of Loans
Loans are advanced to the businessmen, industrialists and others by charging rate of interest higher than paid to the depositors.
Loan Facilities in the Bank
- Cash Credit: Amount of loan is sanctioned by the bank and the loan withdraws as required, within limit and pays interest.
- Overdraft: The account holder can withdraw more than his deposits for a short time or in emergency.
- Loan and Advance: Special loans to the applicant against security and pre-determined conditions, to be deposited in the applicants’ loan account, rate of interest as per the purpose of loan, duration, security and business of the applicant.
- Discounting of Trade Bills: The traders are paid before maturity of the bills after discounting by the bank.
Agency Functions of the Bank
- Collection of cheques and Bill of Exchange, hundis, Promissory notes etc.
- Payment of Bill of Exchange, Cheques etc.
- Making Payment on behalf of Customer.
- Receiving Payments.
- Transfer of Money.
- Purchase and sale of Securities.
- Trustee and Performer. ‘
- Facility of passport, foreign exchange etc.
General Utility Functions
- Information about Financial Position.
- Bank issues travelling cheques.
- As a Financial Advisor.
- Arrangement of Public loans.
- Collection and publication of economic Information. Other Auxiliary Functions.
- Availability of Lockers.
- Handwriting the securities.
- Management of clearing houses.
- Provision for Foreign Exchange.
- Credit creations.
Types of Banks:
- Central Bank to regulate and control credit, all banking activities etc. Reserve Bank of India is the Central bank of India.
- Commercial banks both in public and private sectors. State Bank of India and its associates in public sector. Functions: deposits, loan, transfer of money etc.
- Cooperative banks mainly for agricultural credit at three levels:
- State Co-operative Bank (State level)
- Central Co-operative Bank (District level)
- Primary Agricultural Co-operative Society (Village level)
- Industrial Development Bank for loan to industrialists for long term on easy instalments:
- Central level Industrial Finance Corporation of India- 1948.
- Industrial credit and Investment corporation of India -1955 Industrial Development Bank of India- 1964.
- Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India-1985.
- State Finance Corporation at state level.
- Regional Rural Banks: 196 with 14000 branches in 516 districts for village level credit needs.
- Export-Import Bank since January, 1982 to facilitate export and import business.
- Investment Bank such as LIC, UTI, Mutual Funds etc.
- Saving Bank.
- International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (1944) or World Bank and its two associates:
- International Development Association.
- International Financial Corporation.
- Indigenous Bankers as Mahajans, Sahukars, Sarraf etc.
Main Documents of Banks:
Cheque: A bill of exchange drawn on a specific bank and not expressed to be payable otherwise on demand
Essential features of a cheque:
- A written order.
- No-condition.
- Payment to bearer or the specified person.
- Customers’ signature necessary.
- Printed in prescribed form
- Customer to bank.
- A fixed amount written therein.
- Payment on demand.
- Account No. and date on the Cheque
Parties of a Cheque:
- Drawer
- Receiver who is paid the amount
- Drawee or Debtor
Bank-Draft
Indian Negotiable Instrument Act, 1981, Section 85 (A)- “Bank draft is an order drawn by a branch of a bank in the name of other branch of the same bank in which order is given to make the payment of amount written therein on demand to an ordered person”.
Parties of Bank Draft:
- Issuing bank
- Purchaser
- Receiver
- Paying Bank
Features of Bank Draft:
- An easy and economic way of sending money.
- Bank charges the amount of draft and commission from the customer.
Pay Order (Banker’s Cheque):
For local payment to the customer by the bank after charging the amount and commission from the buyer.
Insurance
- Meaning of Insurance
- A contract between the insurer and the Insured: The former compensates the later for the loss as per pre-determined condition or pays certain amount in exchange of fixed return.
- Insurance: A social way of transferring the risk to others.
- Insurer: One who promises to compensate for the risk.
- Insured: One whose risk is covered by the insurer.
- Subject Matter of Insurance: Life or property.
- Sum Assured: The maximum amount for which one is insured.
- Premium: Amount to be paid by the Insured to the Insurer.
Utility of Insurance
Utility for Individual and Family:
- Economic security
- Increase in working efficiency
- Encouragement to economic self-dependence
- Development of saving habit
- Rebate in taxes
- Investment
- Awareness about health
- Planning for future needs
Utility for Business and Economic Point of View:
- Security against risks
- Increase in economic welfare
- Encouragement to Research and Innovations
- Helpful in development of Infrastructure
- Basis of credit
- Encouragement to foreign trade
Utility from Social Point of view:
- Stability in family life
- Increase in opportunities of employment
- Encouragement to education
- Role in Extension of Infrastructural facilities
- Division of risks
- Solution of social problems
- Encouragement to vigilance
National Utility:
- Increase in national savings
- Contribution in development of money market
- Increase in national income
- Contribution in foreign exchange reserve
- Control on inflation
Types of Insurance
- Life Insurance:
- The Insurer promises to pay a fixed amount after a definite period of time to the Insured or in case of death of the Insured to his heirs.
- Its Characteristics:
- A contract between the Insurer and the Insured
- Premium to be paid by the Insured
- In case of non-payment of premium the contract is nullified
- All types of risks of human lives
- The investment factor
- A contract of good faith
- Insurable interest of Insured in insured life
- Fire insurance:
- Insurer promises to the Insured, of protection against losses caused by fire of the Insured articles in exchange of fixed premium during a definite time period.
- Main Characteristics of Fire-Insurance:
- A co-operative measure
- Compensation for actual loss
- Policy generally, not more than a year
- Compensation only in case of loss by fire .
- Contract based on good faith, indemnity, insurable interest, etc.
- Marine Insurance:
- The insurer takes the responsibility for protection of losses against the marine risks in exchange of a definite return.
- Characteristics of marine Insurance:
- A co-operative measure.
- For specific voyage or for specific period.
- Responsibility only after the incident occurs.
- Based on utmost good faith, warranty, indemnity and insurable interest.
- Social Insurance:
- Some amenities are provided to the insured from a common fund in order to make up for his living standard in case of unemployment, disease or casual accidents.
- Features of Social Insurance:
- Funds from contributions by workers, employers, government etc.
- Cover of disease, unemployment, old age, disability etc.
- Insurance by government for weaker sections in exchange of nominal contribution.
- Miscellaneous Insurance:
- As vehicle insurance, Individual accident insurance, theft insurance, robbery insurance, crop insurance, live-stock insurance, crime insurance etc.
Transportation
- Transportation: Carrying of goods from one place to another, helps to create place utility.
- Classification of Transportation
- Land, rail and road transport.
- Air Transportation-Aeroplanes.
- Water Transportation-Shipping and Inland Water Transport.
- Land Transportation
- Rail Transport:
- Increase in demand in the industrial and agricultural field e.g. 5550.74 lac tonnes in 2003¬2004 from 930 tonnes goods in 1950-51.
- Efforts for improvement
- Increase in capacity of railways.
- More use of wagons with roller bearings.
- Uniguage system.
- 500 HP engines.
- Electrification of railway lines.
- Road-Transport
- About 65% goods transport by roads in India. Efforts in this direction:
- Road thickness
- Road broadening
- Connecting villages to cities
- Changing two lane National highways to four lanes.
- Swarnim Chaturbhuj Pariyojna to connect metropolitan cities.
- Corridor Pariyojna to connect north to south, east to west.
- Air Transport
- Air-A medium of transport.
- No surface obstruction.
- Highly developed, most challenging and most revolutionizing.
- Maximum use in travelling.
- Free space policy of 1990, hence increase in goods transport.
- Air cargos by many export houses.
- Increase in tendency to transport by air.
- Air taxi-services.
- Timely receipt of cargos of exporters and facility to choose the freight rates.
- Water Transport
- References to water transport in India are mentioned in Kautilaya’s Arthashastra. Magasthenese wrote about 58 navigable rivers in India.
- Two parts of Indian Water Transport
- Bhartiya Jahaj Rani: Sindhia steam Navigation Company was started in 1919. Bhartiya Jahaj Rani shares only 1% share in the world. Public sector Bhartiya Jahaj Rani Company- has loading capacity of 35 lac tonnes. For foreign trade foreign ships are used.
- Inland Water Transport: Rivers in the past important means but importance declined due to «. construction of railways. Central Water Transport Corporation has extended canal transport and river transport. The Brahmaputra is best for transport, also through boats in the Ganges, the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna etc. Obstacles such as floods, during rainy season, lack of water during summer and sand in the river.
Communication
- Means of Communication:
- Postal services
- Means of speedy communications.
- Postal Services provided by the post office
For Sending Message: - Post Card: Cheapest mode available for short message.
- Printed Post Card: Business organizations get them printed but must be affixed with stamp.
- Inland Letter for detailed message.
- Envelope: It is for detailed message to be written on separate sheets. Also facility of speed post is available. Self printed letters can be used by individuals and business organization, facility of registered letters also for legal, important and commercial documents.
- For Sending Articles:
- Costly but light weight articles up to 20 kg by parcel – registered or unregistered. For valuable articles also facility of Insurance at extra charges.
- Book post facility to send magazines, books, sample packet, book patterns at concessional rate.
- For sending money through postal order, money order and insured letters.
- Means of Speedy Communication:
- Speed Post helps in the fast delivery of letters.
- Telephone: Facility to talk, sitting at home, charges as per duration of talk.
- Telex: Printed message is sent, useful mainly for newspapers, business organisations etc.
- Fax: Transmission of written, printed or pictured message, within a few seconds.
- Internet: It is a network of computers of the world, interconnected to each other. One can send or receive a message, see or talk to the internet connected place.
- E- Mail: Facility to send message from one computer to any other computer anywhere in the world. This is called electronic mail.
- E- Commerce, i.e. trading through Internet.
- Video-Conferencing, i.e. communication facility between two or more persons at distant places.
Computer Information Technology
- To-day in every field whether transport, communication, hospital, railways, offices, shops everywhere you will find even selling and purchasing is done online through E-Commerce.
- C.D. ROM: In this informations could be read only. Many pages can be stored in it. No changes can be done in it. C.D can be copied, print, even more than one C.D can be read together.
- Multi Media: Means informations can be sent by different methods. Some are, television, satellite, tape-recorder, V.C.D, C.D and Disk.
- Multimedia is in fact combinedly use of reading material, pictures, Video, Audio, Animation. Simulation or personal contact or inter activity. By this user can contact with each other and can create some thing new.
Service field: It can be divided in three parts:
- Commercial Services: Banking, insurance, transport, communication and technology.
- Social services: These activities are done willingly to achieve some social objectives. Such as upliftment of weaker section of the society, programmes of cleanliness and health. Hygiene in slum areas. Normally these activities are done with social organizations willingly as social service i.e. without taking any value of such activities in the terms of money. Some times a charge is levied to cover the cost. Example N.G.O and Governmental agencies- Provide services related to health, education and cleanliness.
- Individual Services: Present time is an era of tough competition or in other word one who is capable can survive. These are those services which can be felt by different consumers or customers in different ways. There is lack of uniformity in them. Beside it depends upon linking and need of customers. Example-Tourism, Restaurants and entertainment services etc.
Timeline
- 1944 : World Bank
- 1948 : Industrial Finance Corporation of India.
- 1955 : Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India.
- 1964 : Industrial Development Bank of India.
- 1985 : Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India
Important terms
Genetic industry : Those industries that involve with producing breeding of certain species of plants or animals with the object of coming profits from this sale.
Extractive industry : Those industries that involve the extraction of raw materials from the earth to be used by consumers.
Insurance : It is an arrangement by which an organization undertakes to provide a guarantee of compensation for specified loss, damage, illness, etc. in return for payment of a specified premium.
Assembling industries : Those industries in which parts are added as the semi-finished assembly moves from one place to another